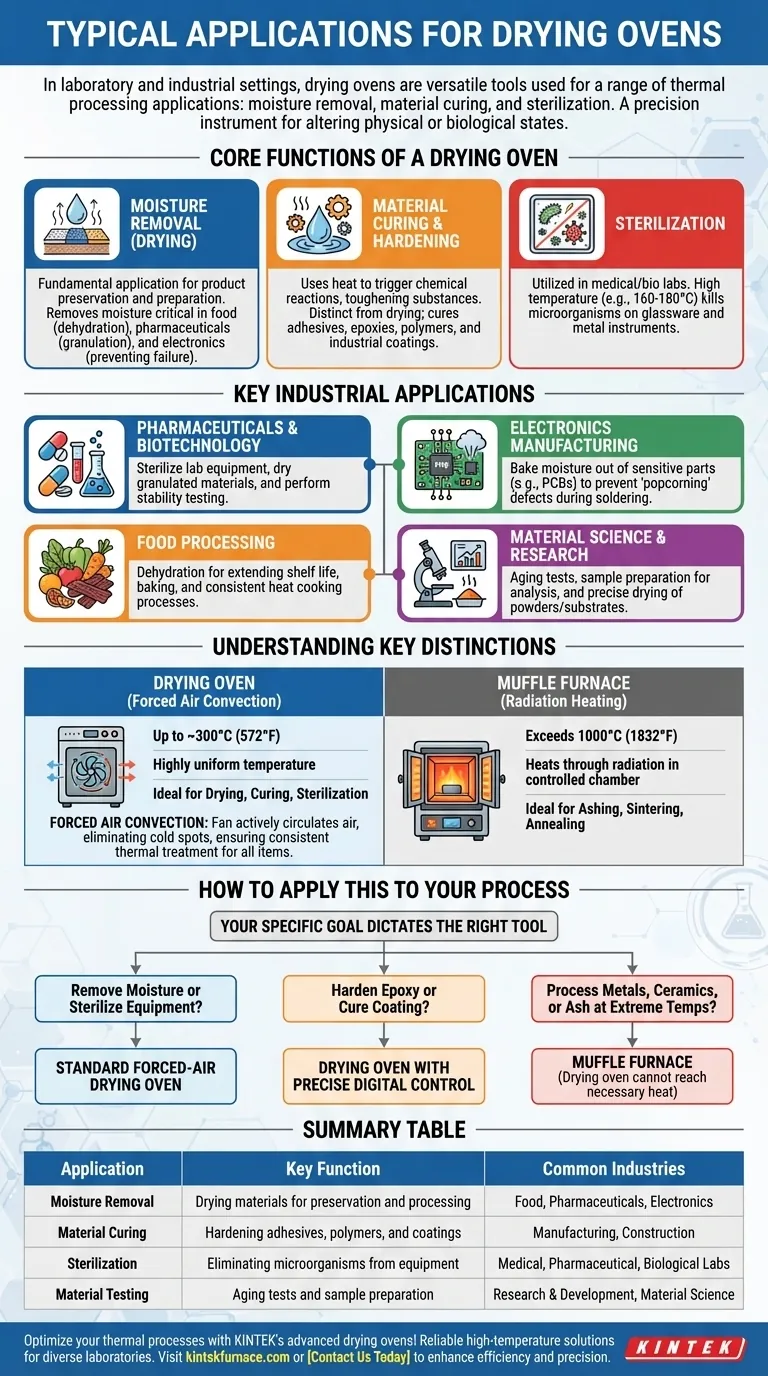
In laboratory and industrial settings, drying ovens are versatile tools used for a range of thermal processing applications. Their primary functions are to remove moisture from materials (drying), induce chemical changes to harden substances (curing), and eliminate microorganisms from equipment (sterilization).
A drying oven is not merely for making things "dry." It is a precision instrument that uses uniform, convection-based heat to reliably alter the physical or biological state of materials, from preparing pharmaceuticals to manufacturing electronics.

Core Functions of a Drying Oven
While often associated with simple moisture removal, the applications of a drying oven are driven by its ability to maintain precise and uniform temperatures over extended periods.
Moisture Removal (Drying)
The most fundamental application is drying. Removing moisture is critical for product preservation, quality control, and preparing materials for subsequent processing steps.
This is essential in food production for dehydration, in pharmaceuticals for preparing granulated compounds, and in electronics to prevent component failure.
Material Curing and Hardening
Curing is a process where heat is used to trigger a chemical reaction, causing a material to toughen or harden. This is distinct from simple drying, which only removes water.
Drying ovens provide the stable, consistent thermal environment needed to cure adhesives, epoxies, polymers, and various industrial coatings.
Sterilization
In medical, pharmaceutical, and biological labs, drying ovens are used for heat sterilization. By holding items like glassware and metal instruments at a high temperature (e.g., 160-180°C), they effectively kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
Key Industrial Applications
The controlled heating environment of a drying oven makes it indispensable across several high-tech and regulated industries.
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
Ovens are used to sterilize lab equipment and glassware. They are also used to dry granulated materials before they are compressed into tablets and to perform stability testing on final products.
Electronics Manufacturing
Moisture is a significant threat to electronic components. Drying ovens are used to bake moisture out of sensitive parts like circuit boards (PCBs) to prevent defects like "popcorning," where trapped moisture turns to steam and damages the component during soldering.
Food Processing
Commercial food production relies on drying ovens for dehydration, which extends the shelf life of products like fruits, vegetables, and jerky. They are also used for baking and other cooking processes that require consistent heat.
Material Science and Research
In research and development, ovens are used to test how materials react to prolonged heat exposure (aging tests), prepare samples for analysis, and dry powders or substrates to precise specifications.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
Not all heating equipment is interchangeable. Choosing the correct device depends entirely on the required temperature and process.
Drying Oven vs. Muffle Furnace
A drying oven typically uses forced air convection to circulate hot air, ensuring highly uniform temperature throughout the chamber, usually up to around 300°C (572°F). It is ideal for drying, curing, and sterilizing.
A muffle furnace, by contrast, is designed for very high-temperature applications like ashing, sintering, or annealing, often exceeding 1000°C (1832°F). It heats samples through radiation in a controlled chamber, isolating them from direct contact with the heating elements.
The Importance of Forced Air Convection
The "forced air" or "mechanical convection" feature mentioned for drying ovens is critical. A fan actively circulates air, eliminating temperature gradients and "cold spots" inside the chamber. This ensures that every item, regardless of its position, receives the exact same thermal treatment, leading to consistent and repeatable results.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your specific goal dictates the right thermal processing tool.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture or sterilizing equipment: A standard forced-air drying oven is the correct and most efficient tool.
- If your primary focus is hardening an epoxy or curing a coating: A drying oven with precise digital temperature control is required to manage the chemical reaction properly.
- If your primary focus is processing metals, ceramics, or ashing a sample at extreme temperatures: You must use a muffle furnace, as a drying oven cannot reach the necessary heat levels.
Understanding these core applications ensures you select the right tool for precise and repeatable thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Removal | Drying materials for preservation and processing | Food, Pharmaceuticals, Electronics |
| Material Curing | Hardening adhesives, polymers, and coatings | Manufacturing, Construction |
| Sterilization | Eliminating microorganisms from equipment | Medical, Pharmaceutical, Biological Labs |
| Material Testing | Aging tests and sample preparation | Research and Development, Material Science |
Optimize your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced drying ovens! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and precision in your drying, curing, or sterilization applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of ashing furnaces? Achieve Precise Ash Analysis for Material Quality
- What role does a high-temperature laboratory oven play in catalyst activation? Boost Surface Area and Performance
- What role do high-precision laboratory ovens play in assessing the energy potential of MSW? Enhancing Biomass Accuracy
- Why is dual heat treatment required for SnO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Oxidation for Superior Performance
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature furnace in eggshell powder pretreatment? Optimize AA6061 Composites



















