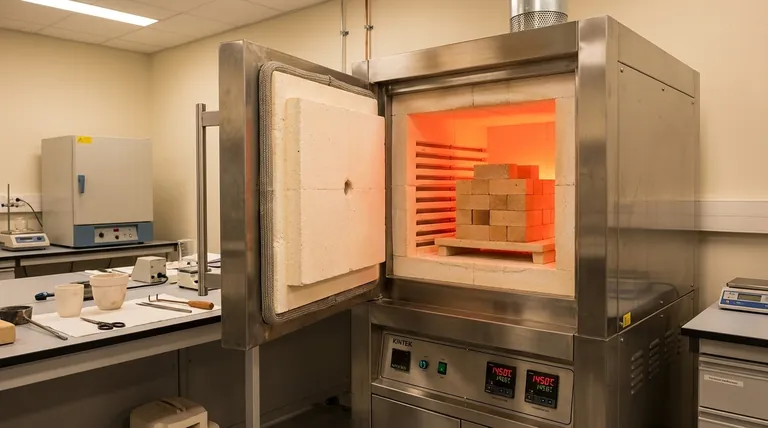
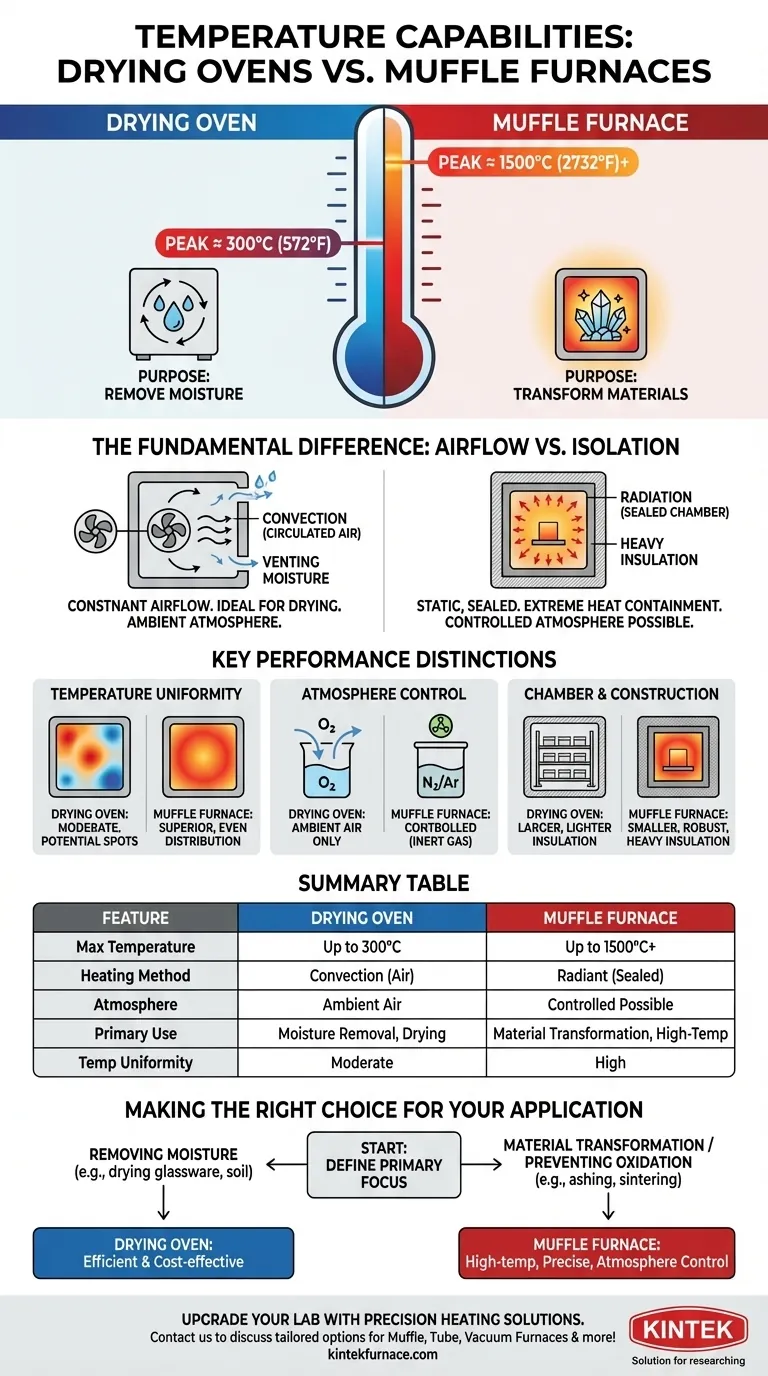
At a glance, a drying oven's temperature capabilities peak around 300°C (572°F), whereas a muffle furnace is designed for much higher temperatures, often reaching up to 1500°C (2732°F) or more. This significant difference is not arbitrary; it reflects their fundamentally distinct purposes, construction, and methods of heating. A drying oven is built to remove moisture, while a muffle furnace is built to transform materials.
The core distinction is simple: a drying oven uses circulated hot air to remove moisture at low temperatures, while a muffle furnace uses a sealed, insulated chamber to achieve extremely high, uniform temperatures for altering a material's chemical or physical properties.

The Fundamental Difference: Airflow vs. Isolation
The temperature gap between these two instruments is a direct result of their core operating principles. One is designed to move air, and the other is designed to contain heat.
How a Drying Oven Works
A drying oven functions through convection. It pulls in fresh, ambient air, passes it over heating elements, and circulates it throughout the chamber.
This moving hot air absorbs moisture from the materials inside and is then vented out. This constant airflow makes it ideal for drying but inherently limits its maximum temperature and creates an uncontrolled, air-based atmosphere.
How a Muffle Furnace Works
A muffle furnace, by contrast, is an isolated system. Its chamber is sealed and heavily insulated to minimize heat loss.
Heat is generated by electric elements that radiate energy evenly throughout the static, sealed chamber. This design is focused entirely on containing energy to reach and maintain very high temperatures with precision.
Key Distinctions in Performance and Design
Beyond temperature, the design differences create distinct performance characteristics you must consider for your application.
Temperature Uniformity
Drying ovens, with their reliance on circulated air, can suffer from hot and cold spots. The uniformity of the temperature is dependent on the efficiency of the fan and the placement of items.
Muffle furnaces provide superior temperature uniformity. The sealed chamber and radiant heating elements ensure that heat is distributed evenly, which is critical for processes where every part of a sample must be at the same temperature.
Atmosphere Control
A drying oven operates exclusively in ambient air. This is a critical limitation for any material that might oxidize or react with air at elevated temperatures.
A muffle furnace's sealed chamber allows for atmosphere control. By purging the air and introducing an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, you can heat materials without the risk of oxidation, a requirement for many advanced materials and metallurgical processes.
Chamber Size and Construction
Drying ovens often feature larger chambers with less insulation. They are built to accommodate bulk materials or a large number of samples for simple drying or gentle heating tasks.
Muffle furnaces have smaller, more controlled chambers. The focus is on precision and extreme heat containment, achieved through thick, heavy insulation and robust construction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these tools involves recognizing their inherent limitations and benefits.
The Purpose of Airflow
The constant air exchange in a drying oven is a feature, not a bug. It is the most effective way to carry moisture away from a sample. Attempting to dry a very moist sample in a sealed muffle furnace would simply trap the water vapor.
The Cost of High Temperatures
The robust insulation, high-power heating elements, and precise controllers required for a muffle furnace make it a more complex and expensive instrument. Its design is overkill for simple moisture removal.
The Limitation of an Open System
A drying oven is unsuitable for ashing, sintering, or heat-treating metals. Not only can it not reach the required temperatures, but the presence of oxygen would ruin the process for many materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture: A drying oven is the correct, efficient, and cost-effective tool for drying glassware, soil samples, or curing low-temperature coatings.
- If your primary focus is material transformation: A muffle furnace is necessary for processes like ashing organic matter, sintering ceramics, or heat-treating metals and alloys.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation at high heat: A muffle furnace with atmosphere control is your only option for processing sensitive materials.
Selecting the right equipment begins with a clear understanding of its fundamental purpose.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Drying Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 300°C (572°F) | Up to 1500°C (2732°F) or more |
| Heating Method | Convection with circulated air | Radiant heating in sealed chamber |
| Atmosphere | Ambient air, no control | Controlled atmosphere possible |
| Primary Use | Moisture removal, drying | Material transformation, high-temperature processes |
| Temperature Uniformity | Moderate, can have hot/cold spots | High, even distribution |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision heating solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with advanced high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs—whether for drying, ashing, sintering, or heat-treating. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















