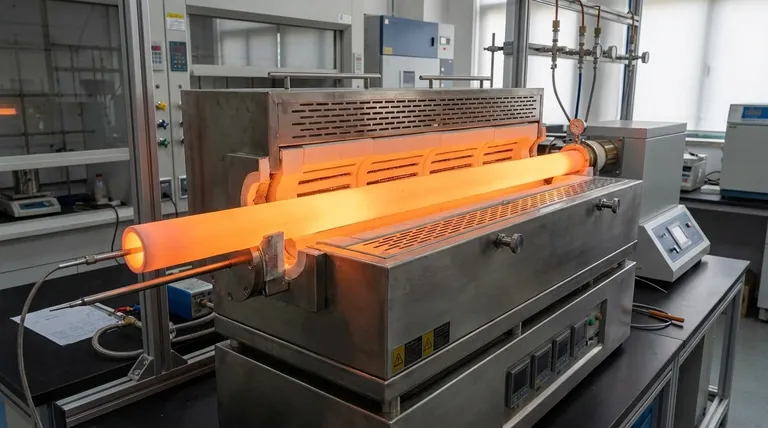
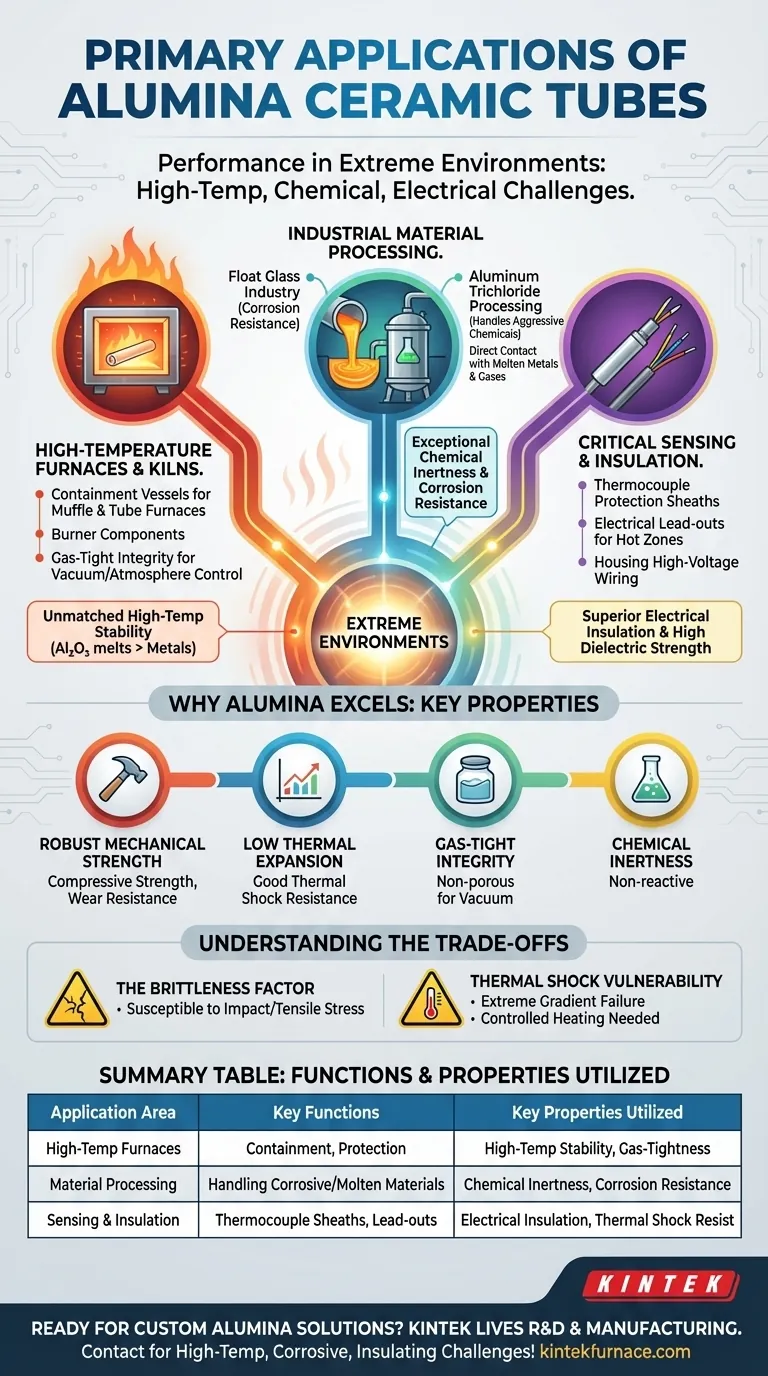
At their core, alumina ceramic tubes are primarily used in applications that demand exceptional performance in extreme environments. They serve as containment vessels in high-temperature furnaces, act as durable components in industrial chemical and material processing, and function as critical insulators for thermal and electrical management systems.
Alumina ceramic is not chosen for a single trait, but for its unique combination of high-temperature stability, chemical inertness, and electrical insulation. These properties make it the definitive material solution for industrial processes where metals and plastics would instantly fail.

The Foundation: Why Alumina Excels in Extreme Environments
To understand alumina's applications, you must first understand the properties that make it so indispensable. It is the convergence of these characteristics that qualifies it for such demanding roles.
Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) maintains its structural integrity and strength at extremely high temperatures, far beyond the melting point of most metals. This makes it a default choice for any application involving intense, sustained heat.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Alumina is an excellent electrical insulator, possessing high dielectric strength. It does not conduct electricity, even at elevated temperatures, which is critical for safely housing heating elements and high-voltage wiring.
Exceptional Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
The material is highly inert and does not react with most corrosive chemicals, molten metals, or aggressive gases. This allows it to directly contact substances that would rapidly degrade other materials.
Robust Mechanical and Thermal Properties
Alumina features very high compressive strength and significant resistance to wear and abrasion. It also has low thermal expansion and good thermal shock resistance, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes better than many other ceramics.
Gas-Tight Integrity
High-purity alumina tubes can be manufactured to be non-porous and gas-tight. This is crucial for maintaining a vacuum or a controlled protective atmosphere in furnaces, which is essential in fields like semiconductor manufacturing and advanced materials research.
Key Applications in Practice
The properties of alumina translate directly into its most common industrial and scientific applications.
High-Temperature Furnaces and Kilns
Alumina tubes form the heart of many electric furnaces, including vacuum, muffle, and laboratory analysis furnaces. They act as the central chamber, containing the sample and protecting it from the heating elements, or vice versa. They also serve as durable burner components in gas and oil-fired kilns.
Industrial Material Processing
In the float glass industry, alumina components resist corrosion from molten glass. In the aluminum trichloride industry and other chemical processing applications, the tubes handle highly corrosive chemicals at high temperatures, ensuring process purity and equipment longevity.
Critical Sensing and Insulation Components
Because they are stable and inert, alumina tubes are the standard material for thermocouple protection sheaths. The tube shields the sensitive temperature-measuring instrument from the harsh process environment without interfering with the reading. They are also used as lead-outs to insulate electrical cables passing through hot zones.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly capable, alumina ceramic is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these is key to successful implementation.
The Brittleness Factor
Alumina has immense compressive strength but is a brittle material. It is susceptible to fracture from sharp mechanical impacts or high tensile stress. Careful handling and installation are non-negotiable to prevent cracking.
Thermal Shock Vulnerability
Despite having good thermal shock resistance for a ceramic, extreme temperature gradients can still cause failure. A controlled rate of heating and cooling is often necessary to maximize the tube's service life, especially in very large or thick-walled components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting alumina is a decision driven by the severity of your operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is stable, high-temperature processing: Alumina is the standard for creating a contained and controlled environment within a furnace, protecting both the sample and the heating system.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation in a hot zone: Alumina's excellent dielectric properties make it the ideal choice for safely housing heating elements or routing wiring through extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is processing corrosive materials: Its chemical inertness makes alumina the superior option for handling aggressive chemicals, gases, or molten materials that would destroy metals.
Ultimately, alumina ceramic tubes are a specialized engineering solution for when heat, chemistry, and electricity create an environment too hostile for conventional materials to survive.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Functions | Key Properties Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Furnaces | Containment vessels, protection for samples/elements | High-temperature stability, gas-tight integrity |
| Industrial Material Processing | Handling corrosive chemicals, molten materials | Chemical inertness, corrosion resistance |
| Sensing and Insulation | Thermocouple sheaths, electrical lead-outs | Electrical insulation, thermal shock resistance |
Ready to enhance your lab's performance with custom alumina ceramic tube solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, delivering durability and efficiency in extreme conditions. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature, corrosive, or insulating challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions



















