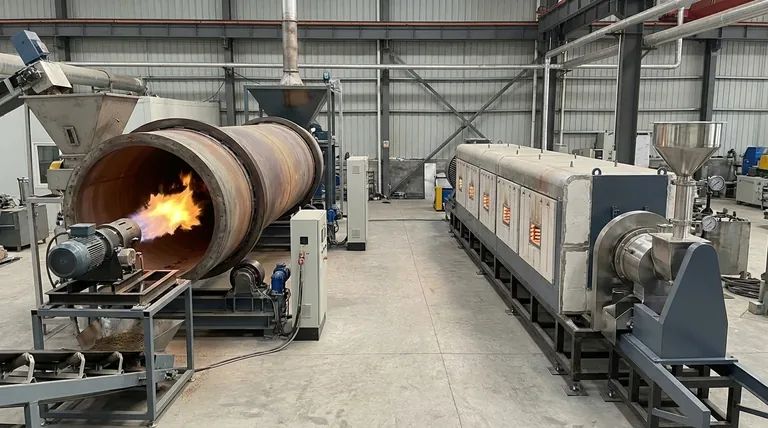
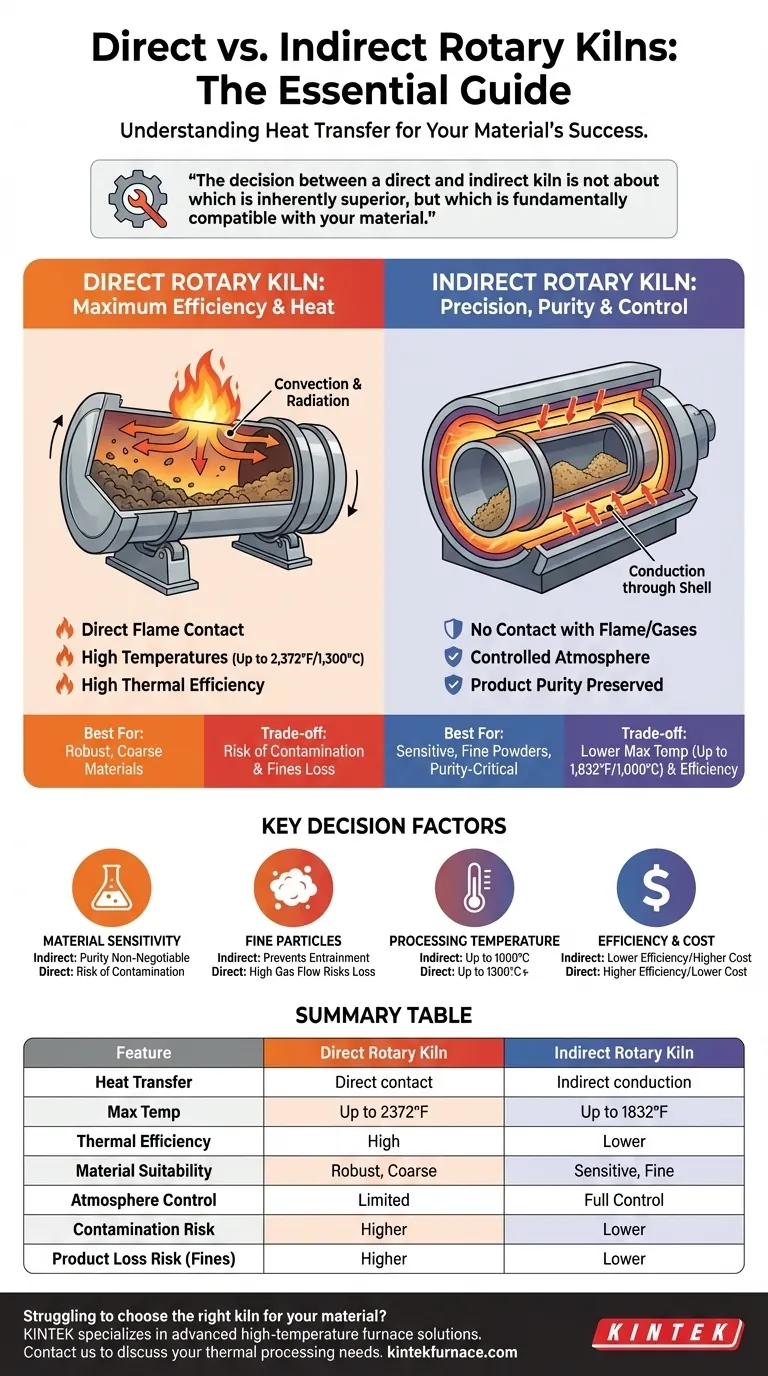
The primary difference between direct and indirect rotary kilns lies in the method of heat transfer. A direct kiln heats material through immediate contact with the flame and combustion gases inside the rotating drum. In contrast, an indirect kiln heats the exterior of the drum, transferring thermal energy through the shell wall to the material inside, which remains isolated from the heating source.
The decision between a direct and indirect kiln is not about which is inherently superior, but which is fundamentally compatible with your material. Direct kilns offer greater thermal efficiency and higher temperatures, while indirect kilns provide the process control and purity required for sensitive materials.

The Mechanics of Heat Transfer
The core distinction between these two kiln types dictates their ideal applications, efficiency, and operating parameters. Understanding the mechanism of each is the first step in making an informed choice.
Direct-Fired Kilns: Maximum Thermal Efficiency
In a direct-fired system, a burner injects a flame and hot combustion gases directly into the rotating drum. The material tumbles through this hot gas stream.
Heat is transferred through both convection (from the gas) and radiation (from the flame and hot refractory walls) directly to the material bed. This method is highly efficient because the heat source is in immediate contact with the product.
Because of this direct transfer, these kilns can achieve very high process temperatures, often reaching up to 2,372°F (1300°C), making them suitable for demanding thermal processes like calcination of petroleum coke or minerals.
Indirect-Fired Kilns: Precision and Purity
An indirect-fired kiln, sometimes called a calciner, keeps the material completely separate from the combustion gases.
The rotating drum is enclosed within a furnace or wrapped with an external heating element. Heat is applied to the outside of the kiln shell and transfers to the material via conduction through the metal wall.
This design is essential when direct contact with combustion by-products would contaminate the material or when a specific process atmosphere (e.g., inert, reducing, or oxygen-free) is required. However, the indirect heating path limits the maximum temperature, typically to around 1,832°F (1000°C).
Key Decision Factors for Your Process
Your material's physical and chemical properties will almost always dictate the correct kiln technology.
Material Sensitivity and Chemical Integrity
If your material is sensitive to or can be chemically altered by flue gases, an indirect kiln is non-negotiable. This ensures product purity by creating a controlled environment.
This is critical for applications like producing specialty chemicals, activating carbon, or processing food-grade products where contamination is unacceptable.
Handling of Fine Particles
Direct-fired kilns operate with a high velocity of process gas flowing through the drum. This gas flow can easily pick up and carry away fine particles, a phenomenon known as entrainment.
If you are processing fine powders or materials that degrade into fines, an indirect kiln is the superior choice. The lack of internal gas flow ensures your valuable product remains inside the drum.
Required Processing Temperature
For processes requiring temperatures above what an indirect kiln can provide, a direct-fired system is the only option. Sintering, certain types of calcination, and specific reduction reactions often demand the high heat that only direct firing can efficiently deliver.
Thermal Efficiency and Operating Cost
Due to the immediate contact between the heat source and the material, direct-fired kilns are more thermally efficient. Less heat is lost to the surrounding environment, resulting in lower fuel consumption for a given throughput.
Indirect kilns inherently lose some energy from the external furnace to the atmosphere, making them less efficient and potentially more expensive to operate from a fuel-cost perspective.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a kiln involves balancing process requirements against operational efficiency. Each type presents a fundamental compromise.
The Direct Kiln Dilemma: Efficiency vs. Risk
With a direct kiln, you gain high thermal efficiency, higher potential temperatures, and often a simpler design.
The trade-off is the risk of product contamination from combustion gases and the potential for significant product loss if you are processing fine materials. They are best suited for robust, coarse, or bulk materials where purity is not compromised by flue gas.
The Indirect Kiln Dilemma: Control vs. Cost
With an indirect kiln, you gain absolute control over the process atmosphere, ensuring product purity and preventing the loss of fines.
The trade-off is lower thermal efficiency, which translates to higher fuel costs. The design is also more complex, involving an external furnace or heating jacket, and is limited to lower maximum operating temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your process goals will point you directly to the correct technology.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and energy efficiency for a robust material: A direct-fired kiln is almost always the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is product purity, preventing contamination, or processing fine powders: An indirect-fired kiln is necessary to protect the material and prevent loss.
- If your primary focus is operating in a specific atmosphere (e.g., inert or reducing): An indirect-fired kiln is your only option, as it isolates the material from combustion gases.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental distinction between direct contact and controlled isolation is the key to selecting the right thermal processing technology for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct Rotary Kiln | Indirect Rotary Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer | Direct contact with flame and gases (convection/radiation) | Indirect through kiln shell (conduction) |
| Max Temperature | Up to 2,372°F (1,300°C) | Up to 1,832°F (1,000°C) |
| Thermal Efficiency | High | Lower |
| Material Suitability | Robust, coarse materials | Sensitive, fine powders, purity-critical |
| Atmosphere Control | Limited, exposed to combustion gases | Full control, isolated environment |
| Risk of Contamination | Higher | Lower |
| Product Loss Risk | Higher for fines | Lower |
Struggling to choose the right kiln for your material? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom rotary kilns tailored to your unique needs. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we ensure optimal performance for processes requiring precise temperature control, purity, or efficiency. Whether you're handling sensitive chemicals, fine powders, or high-temperature applications, our deep customization capabilities deliver reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- Why is an industrial-grade rotary reactor necessary in the oil sludge pyrolysis process? Maximize Yield & Efficiency
- What is the role of indirect-fired rotary kilns in energy production? Unlock Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Solutions
- What are the key components and parameters of a rotary kiln? Optimize Your High-Temperature Processing
- How does a rotary furnace compare to a fixed-bed furnace for powder? Optimize Uniformity in Large-Scale Production
- What is the significance of rotation in a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion



















