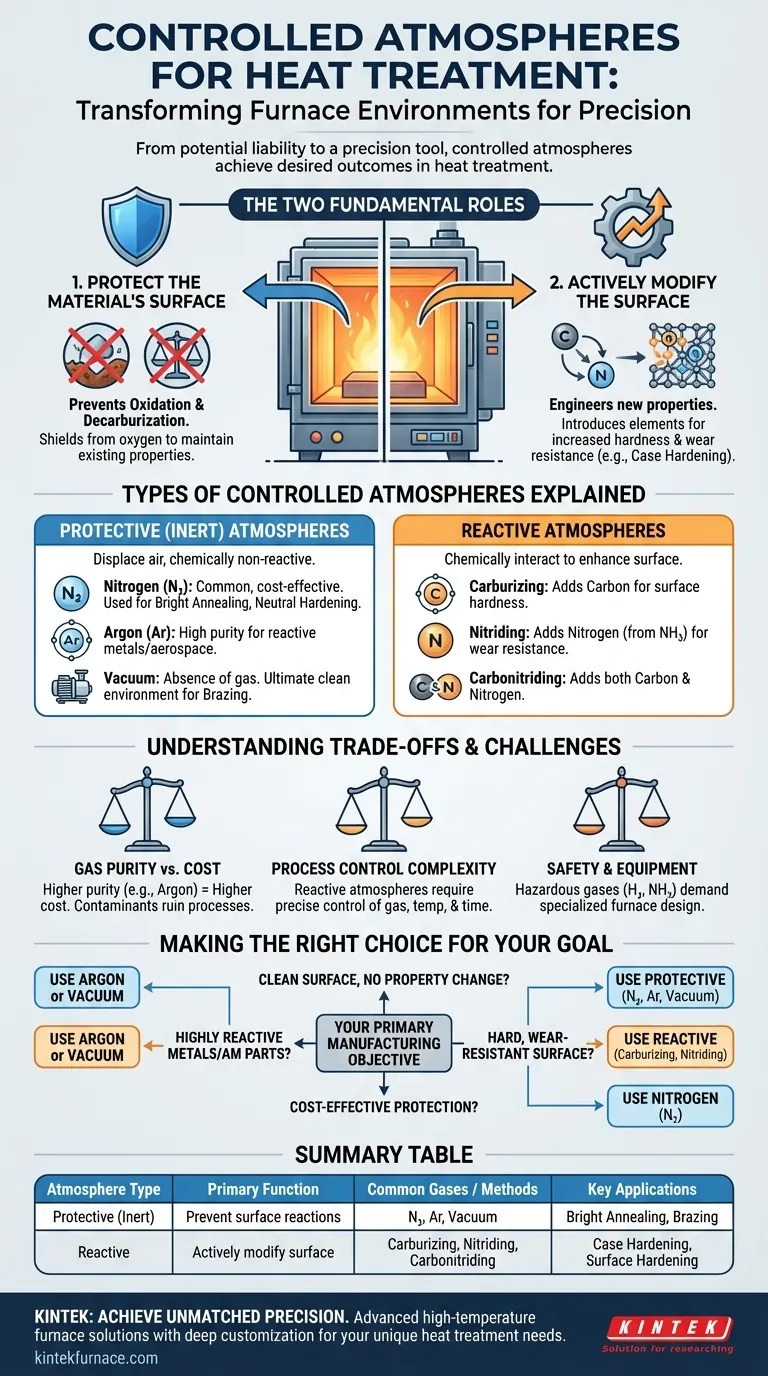
In heat treatment, a controlled atmosphere is a specific mixture of gases, or a vacuum, intentionally introduced into a furnace to achieve a desired outcome. These atmospheres are broadly categorized into two types: protective atmospheres, which prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, and reactive atmospheres, which are designed to actively change the surface chemistry of the metal part.
The central purpose of a controlled atmosphere is to transform the furnace environment from a potential liability into a precision tool. It allows you to either perfectly preserve a component's existing properties or deliberately engineer new ones onto its surface, such as increased hardness and wear resistance.
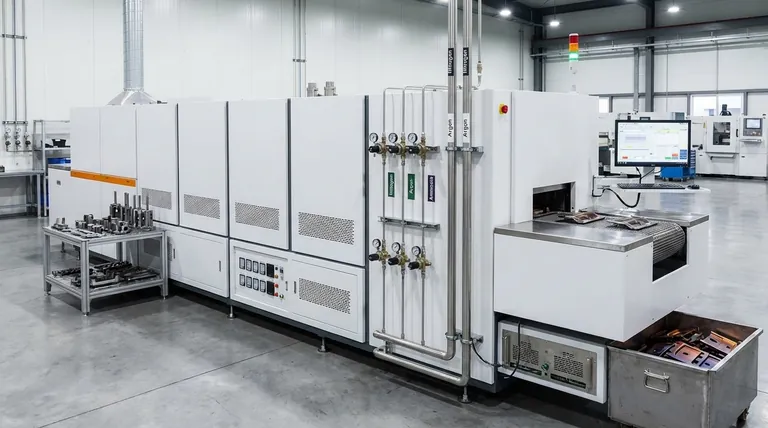

The Two Fundamental Roles of a Furnace Atmosphere
At the high temperatures required for heat treatment, metals become highly susceptible to chemical reactions with the surrounding air. A controlled atmosphere is the primary method for managing these reactions.
1. To Protect the Material's Surface
The most common goal is to shield the hot metal component from atmospheric elements, primarily oxygen.
This protection prevents harmful surface reactions like oxidation (scaling or rust) and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel, which makes it softer).
2. To Actively Modify the Material's Surface
The second role is to use the atmosphere as a reactive carrier that donates specific elements to the surface of the part.
This is a core principle of case hardening processes, where the atmosphere is precisely engineered to diffuse elements like carbon or nitrogen into the steel to create a hard, wear-resistant outer layer.
Types of Controlled Atmospheres Explained
The choice of atmosphere is dictated by the process and the desired final properties of the component.
Protective (Inert) Atmospheres
These atmospheres are chemically non-reactive with the metal being treated. Their sole purpose is to displace the ambient air, especially oxygen.
- Nitrogen (N₂): The most common protective gas due to its relative inertness with steel and lower cost. It is widely used for processes like bright annealing and neutral hardening, where the goal is a clean, scale-free surface.
- Argon (Ar): A more purely inert gas than nitrogen, but also more expensive. It is used for heat-treating highly reactive metals or for applications in the aerospace and medical fields where absolute purity is critical.
- Vacuum: The ultimate protective "atmosphere" is the absence of one. By removing nearly all gas molecules from the furnace chamber, a vacuum provides an exceptionally clean environment, preventing any gas-metal reactions. It is common for brazing and treating sensitive materials.
Reactive Atmospheres
These atmospheres are designed to chemically interact with the workpiece to enhance its surface properties.
- Carburizing Atmospheres: These are carbon-rich environments used to increase the surface hardness of low-carbon steels. The atmosphere donates carbon atoms, which diffuse into the steel's surface.
- Nitriding Atmospheres: These atmospheres, often derived from ammonia (NH₃), introduce nitrogen into the surface of the steel. This forms hard nitride compounds, creating exceptional wear resistance.
- Carbonitriding Atmospheres: As the name implies, these atmospheres introduce both carbon and nitrogen into the steel's surface, combining the benefits of both processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, implementing controlled atmospheres requires careful consideration of several factors.
Gas Purity and Cost
The effectiveness of an atmosphere hinges on its purity. Contaminants like moisture or oxygen can ruin a process, even in trace amounts. High-purity gases like argon are effective but carry a significant cost premium over industrial-grade nitrogen.
Process Control Complexity
Reactive atmospheres are powerful but unforgiving. Achieving the correct case depth and hardness in a carburizing process requires precise control over gas composition, temperature, and time. Poor control can lead to soot formation on the part or incorrect and inconsistent material properties.
Safety and Equipment
Many gases used in controlled atmospheres present safety hazards. Hydrogen is flammable, and dissociated ammonia used for nitriding is toxic. Furnaces must be designed to handle these gases safely and prevent leaks that could compromise both the process and personnel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of atmosphere must align directly with your manufacturing objective. A controlled atmosphere is not an afterthought; it is a critical process variable.
- If your primary focus is a clean surface with no change in properties: Use a protective atmosphere like nitrogen for most steels, or argon/vacuum for more sensitive materials and critical applications like brazing.
- If your primary focus is creating a hard, wear-resistant surface on steel: You must use a reactive atmosphere, such as a carburizing or nitriding gas mixture.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective protection for general heat treatment: Nitrogen is almost always the most economical and practical choice for preventing oxidation on common steels.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals (e.g., titanium) or additively manufactured parts: A high-purity argon atmosphere or a high-quality vacuum is non-negotiable to prevent contamination.
By correctly selecting and controlling the furnace atmosphere, you elevate the heat treatment process from simple heating and cooling to a sophisticated material engineering discipline.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Primary Function | Common Gases / Methods | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protective (Inert) | Prevent surface reactions (oxidation, decarburization) | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar), Vacuum | Bright Annealing, Neutral Hardening, Brazing |
| Reactive | Actively modify surface chemistry | Carburizing, Nitriding (e.g., Ammonia), Carbonitriding | Case Hardening, Surface Hardening |
Achieve Unmatched Precision in Your Heat Treatment Processes
Selecting and controlling the right furnace atmosphere is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we understand that every material and application is unique. Our advanced high-temperature furnace solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces—are engineered for exceptional control and reliability.
Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities, we provide diverse laboratories with the tools they need to master material transformation. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your furnace system is tailored to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements, whether you need a protective nitrogen environment or a complex reactive atmosphere for surface engineering.
Ready to transform your heat treatment outcomes? Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can bring precision and reliability to your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity



















