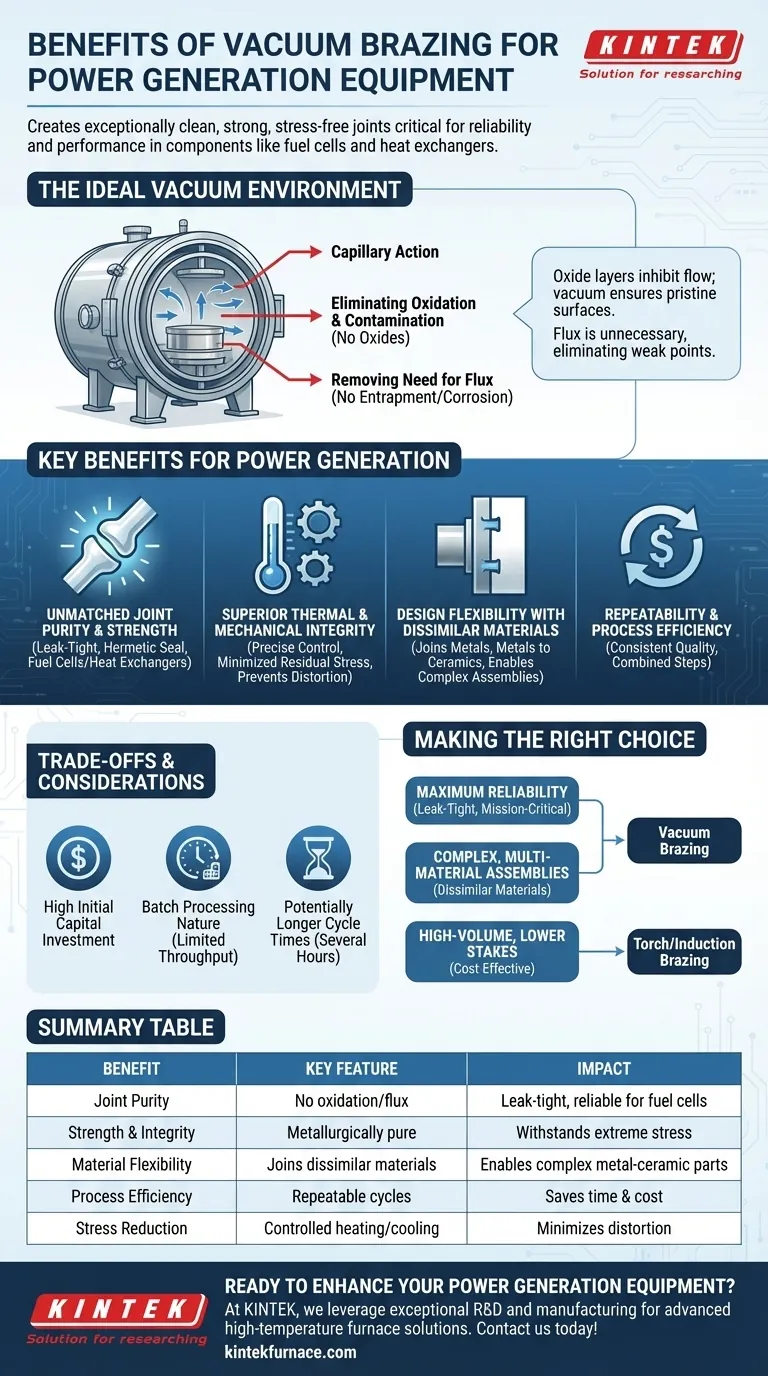
At its core, vacuum brazing is chosen for power generation equipment because it creates exceptionally clean, strong, and stress-free joints that are critical for reliability and performance. This process happens inside a vacuum, which prevents the formation of oxides and eliminates the need for corrosive fluxes, resulting in metallurgically pure bonds that are essential for components like fuel cells and heat exchangers.
The fundamental challenge in manufacturing power generation components is ensuring absolute reliability under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. Vacuum brazing solves this by creating a perfectly controlled environment that produces joints with superior integrity, free from the contamination and internal stresses that cause failures in other joining methods.

Why a Vacuum is the Ideal Environment
To understand the benefits of vacuum brazing, you must first understand the role of the vacuum itself. The process involves heating a filler metal between two components inside a vacuum furnace until it melts and flows into the joint via capillary action.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
By removing air from the furnace, you eliminate oxygen and other atmospheric gases. This prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces during heating.
Oxide layers act as barriers that inhibit the flow of filler metal and create weak, unreliable bonds. A vacuum ensures the surfaces remain pristine, leading to a strong, clean joint.
Removing the Need for Flux
In traditional brazing, a chemical flux is required to dissolve oxides and clean the metal surfaces. However, flux can become trapped within the joint, creating a point of weakness or a source for future corrosion.
Vacuum brazing makes flux entirely unnecessary. This eliminates the risk of flux entrapment and the need for intensive post-brazing cleaning processes, saving both time and cost.
The Key Benefits for Power Generation Components
For power generation equipment, where failure is not an option, these process advantages translate into tangible performance benefits.
Unmatched Joint Purity and Strength
The contamination-free environment produces bright, shiny joints that are metallurgically pure. This results in maximum bond strength and hermetically sealed, leak-tight connections.
For applications like fuel cells or high-pressure heat exchangers, this level of joint integrity is non-negotiable for both safety and efficiency.
Superior Thermal and Mechanical Integrity
Vacuum furnaces allow for precise control over heating and cooling rates. This slow, uniform thermal cycling minimizes residual stress within the component.
Reduced internal stress prevents distortion, cracking, and premature failure, especially in parts that undergo constant thermal expansion and contraction during operation. This preserves the intended metallurgy and strength of the parent materials.
Design Flexibility with Dissimilar Materials
Vacuum brazing excels at joining dissimilar materials, such as different metals or even metals to ceramics.
This capability is critical for complex assemblies like solid oxide fuel cells, which often combine metallic and ceramic components to manage heat and electrical conductivity.
Repeatability and Process Efficiency
Once a brazing cycle is programmed, it can be repeated with exceptionally high fidelity. This ensures consistent quality across high-volume production runs.
Furthermore, processes like heat treating and age hardening can often be performed in the same furnace cycle as the brazing itself, significantly streamlining the manufacturing workflow.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum brazing is not the universal solution for all joining needs. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
High Initial Capital Investment
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital expense compared to other joining equipment like torch or induction systems. The cost must be justified by the need for high-quality, repeatable results.
Batch Processing Nature
Vacuum brazing is inherently a batch process. Components are loaded, the furnace is sealed, a vacuum is pulled, and the thermal cycle is run. This can limit throughput compared to continuous processes.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
While combining steps is efficient, the required slow heating and cooling rates mean that a single furnace cycle can take several hours. This must be factored into production planning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right joining process depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for performance, cost, and scale.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and leak-tight performance: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice for mission-critical components where failure could be catastrophic.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, multi-material assemblies: The ability of vacuum brazing to join dissimilar materials like metals and ceramics is a key enabler.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simpler components with lower stakes: Other methods like torch or induction brazing may offer a more cost-effective solution if absolute metallurgical purity is not required.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum brazing is an investment in process control to guarantee the highest level of component integrity.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Feature | Impact on Power Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Purity | No oxidation or flux | Leak-tight, reliable connections for fuel cells |
| Strength and Integrity | Metallurgically pure bonds | Withstands extreme thermal and mechanical stress |
| Material Flexibility | Joins dissimilar materials | Enables complex assemblies like metal-ceramic parts |
| Process Efficiency | Repeatable cycles with combined steps | Saves time and cost in manufacturing |
| Stress Reduction | Controlled heating and cooling | Minimizes distortion and failure risks |
Ready to enhance your power generation equipment with reliable vacuum brazing?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs, delivering clean, strong joints for components like fuel cells and heat exchangers.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your equipment's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments



















