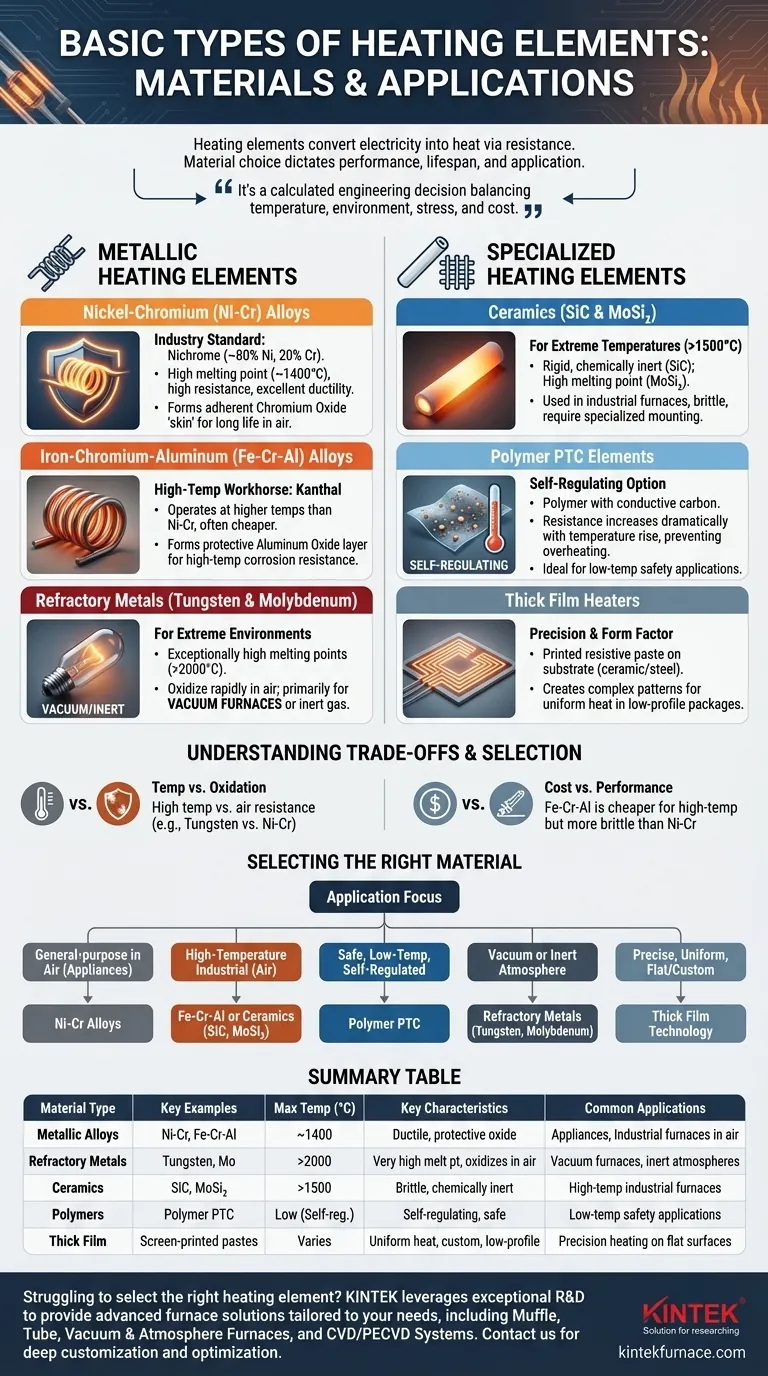
At their core, heating elements convert electricity into heat through resistance, but the material used to achieve this dictates their performance, lifespan, and application. The primary material families are metallic alloys, such as Nickel-Chromium and Iron-Chromium-Aluminum, and non-metallic materials like ceramics (Silicon Carbide) and specialized polymers. Each category is chosen for its unique balance of electrical resistivity, resistance to high-temperature oxidation, and mechanical properties.
The choice of a heating element material is not about finding the one with the highest resistance. It is a calculated engineering decision that balances the required operating temperature against the chemical environment, mechanical stress, and total cost of the system.
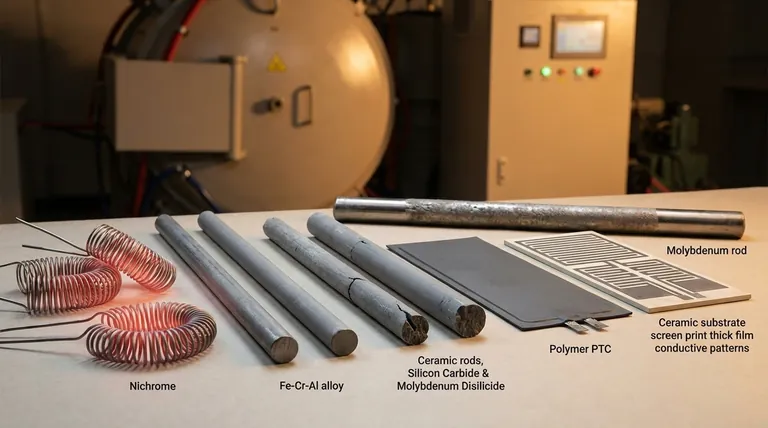
The Foundation: Metallic Heating Elements
Metallic alloys are the most common materials used for resistive heating elements. Their popularity stems from a predictable and stable combination of ductility, strength, and electrical properties.
Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr) Alloys: The Industry Standard
The most widely recognized metallic element is Nichrome, an alloy of approximately 80% nickel and 20% chromium.
Its prevalence is due to a superior combination of properties: a high melting point (~1400°C), high electrical resistance, and excellent ductility.
Crucially, when heated, it forms an adherent outer layer of chromium oxide. This protective "skin" prevents the material from oxidizing further, ensuring a long operational life in open-air environments.
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al) Alloys: The High-Temp Workhorse
Often sold under the trade name Kanthal, Fe-Cr-Al alloys serve as a primary alternative to Nichrome.
These alloys can often operate at even higher temperatures than Ni-Cr and are typically less expensive. Like Nichrome, they form a protective oxide layer (aluminum oxide) that provides excellent high-temperature corrosion resistance.
Refractory Metals (Tungsten & Molybdenum): For Vacuum Environments
Materials like Tungsten and Molybdenum have exceptionally high melting points, making them suitable for extreme-temperature applications.
However, they oxidize (essentially burn up) very rapidly in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures. For this reason, their use is almost exclusively limited to controlled environments, such as in vacuum furnaces or inert gas atmospheres.
Beyond Metals: Specialized Heating Elements
For applications where standard metallic alloys are unsuitable due to extreme temperatures, chemical environments, or the need for self-regulation, other materials are used.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) & Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂): For Extreme Temperatures
These are ceramic materials used in high-temperature industrial furnaces operating well above the limits of metallic alloys.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is rigid and chemically inert, while Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) is valued for its high melting point and resistance to corrosive environments. They are brittle and require specialized mounting and control systems.
Polymer PTC Elements: The Self-Regulating Option
Polymer PTC heaters are composites made of a polymer doped with conductive carbon particles. Their key feature is a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC).
As their temperature rises to a specific point, their electrical resistance increases dramatically, which significantly reduces current flow and heat output. This creates a self-regulating effect that prevents overheating, making them ideal for low-temperature applications where safety and precise temperature maintenance are critical.
Thick Film Heaters: For Precision and Form Factor
Thick film heaters are not a single material but a manufacturing technology. A resistive paste (containing metals and glass) is screen-printed onto a substrate, typically ceramic or stainless steel, and then fired at high temperatures.
This process allows for the creation of heaters with complex geometric patterns, providing highly uniform heat distribution in a low-profile package.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right material requires understanding the compromises inherent in their design and properties. These trade-offs are central to a successful and reliable heating application.
Operating Temperature vs. Oxidation Resistance
This is the most critical trade-off. Materials like Tungsten can get incredibly hot, but without protection from air, they are destroyed. Ni-Cr alloys, on the other hand, sacrifice some top-end temperature capability for the ability to operate reliably in air for thousands of hours.
Cost vs. Performance
Fe-Cr-Al alloys are often a more cost-effective choice than Ni-Cr for high-temperature applications. However, they can be more brittle after temperature cycling, which may be a disqualifying factor where vibration or mechanical stress is a concern.
Environment Is Everything
The operating atmosphere dictates material choice. Air requires a material that forms a stable oxide layer (Ni-Cr, Fe-Cr-Al). A vacuum demands a refractory metal (Tungsten, Molybdenum). A chemically corrosive environment may necessitate a robust ceramic like SiC.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by the primary goal of your application.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in air (appliances, dryers): Ni-Cr alloys offer the best balance of performance, durability, and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial furnaces in air: Fe-Cr-Al alloys (for cost-effectiveness) or ceramic elements like SiC and MoSi₂ (for extreme heat) are the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is safe, low-temperature, self-regulated heating: Polymer PTC elements provide built-in over-temperature protection.
- If your primary focus is heating in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: Refractory metals like Tungsten and Molybdenum are required.
- If your primary focus is precise, uniform heating on a flat or custom-shaped surface: Thick film heater technology is the ideal solution.
Understanding these core material properties empowers you to move beyond a simple component choice to a deliberate engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Max Operating Temp (°C) | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Ni-Cr (Nichrome), Fe-Cr-Al (Kanthal) | ~1400 | High ductility, forms protective oxide layer | Appliances, industrial furnaces in air |
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten, Molybdenum | >2000 | Very high melting point, oxidizes in air | Vacuum furnaces, inert atmospheres |
| Ceramics | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | >1500 | Brittle, chemically inert, extreme heat resistance | High-temperature industrial furnaces |
| Polymers | Polymer PTC | Low (self-regulating) | Self-regulating, prevents overheating | Low-temperature safety applications |
| Thick Film | Screen-printed pastes | Varies | Uniform heat, custom shapes, low-profile | Precision heating on flat surfaces |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your lab's unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you need precise temperature control, resistance to harsh environments, or self-regulating safety features, we can help optimize your heating applications. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your experimental outcomes and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















