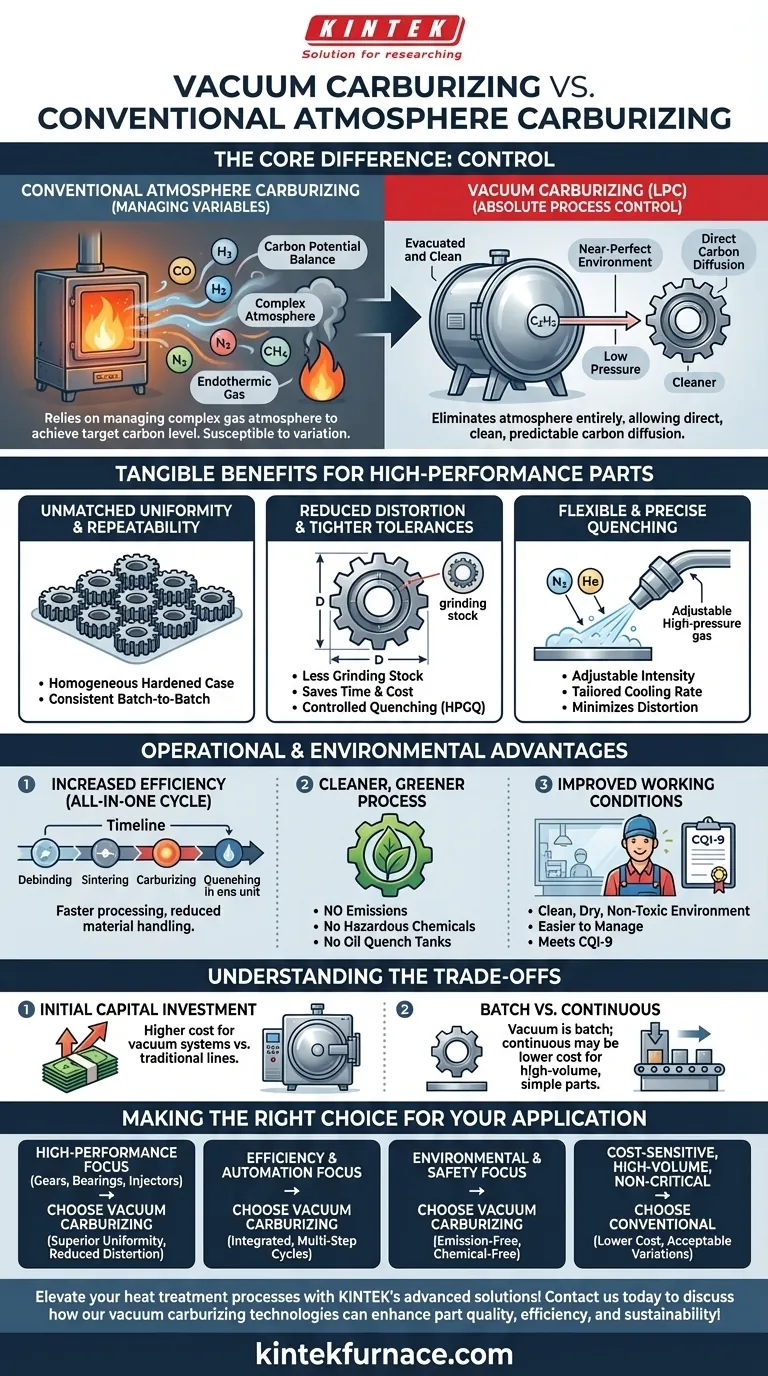
In the realm of case hardening, vacuum carburizing represents a significant technological leap over conventional atmosphere-based methods. Its primary advantages are superior uniformity, exceptional repeatability, and precise process control, which directly translate into higher-quality components with less distortion and tighter dimensional tolerances.
The core difference is one of control. Conventional methods focus on managing a complex gas atmosphere to achieve a target carbon level, while vacuum carburizing eliminates the atmosphere entirely, allowing for the direct, clean, and highly predictable diffusion of carbon into the steel.

The Core Principle: Absolute Process Control
At its heart, the superiority of vacuum carburizing, also known as Low-Pressure Carburizing (LPC), stems from its ability to create a near-perfect environment for carbon diffusion.
How Vacuum Carburizing Works
The process involves heating parts in a vacuum, which removes all atmospheric contaminants. A pure hydrocarbon gas, typically acetylene, is then introduced at a very low pressure. This gas breaks down, allowing carbon to deposit on and diffuse into the steel surface. This is often done in a series of "boost" (gas injection) and "diffuse" (gas off) steps to precisely control the case depth.
Eliminating Atmospheric Variables
Conventional atmosphere carburizing relies on maintaining a delicate balance of gases (an endothermic atmosphere) to control "carbon potential." This is inherently complex and susceptible to variation.
Vacuum, by its nature, provides a fundamentally cleaner environment. Achieving an equivalent level of atmospheric purity with gas processing is complex and costly, whereas a vacuum furnace achieves it simply by evacuating the chamber.
Tangible Benefits for High-Performance Parts
This superior control is not merely academic; it yields measurable improvements in the final product, which is why it is the preferred method for critical components like high-quality gears and bearings.
Unmatched Uniformity and Repeatability
Vacuum carburizing provides an exceptionally homogeneous hardened case across the entire workload. The process is remarkably consistent from one batch to the next, ensuring reliable and predictable results.
Reduced Distortion and Tighter Tolerances
This uniformity, combined with controlled quenching options like High-Pressure Gas Quenching (HPGQ), significantly reduces part distortion. This allows engineers to design parts with less grinding stock, saving valuable time and cost in post-heat-treat finishing operations.
Flexible and Precise Quenching
With HPGQ, the intensity of the quench can be adjusted by controlling the gas (often nitrogen or helium) pressure and velocity. This allows the cooling rate to be tailored to the part's specific geometry and material, further minimizing distortion while achieving the desired hardness.
Operational and Environmental Advantages
Beyond part quality, vacuum carburizing offers significant benefits for the manufacturing operation itself.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Modern vacuum furnaces can perform a complete "all-in-one" cycle, integrating debinding, sintering, carburizing, and quenching in a single, uninterrupted process. This dramatically reduces cycle times and material handling.
A Cleaner, Greener Process
Vacuum carburizing is considered an environmentally friendly process. It produces no emissions and eliminates the need to handle or dispose of hazardous chemicals associated with endothermic gas generation or large oil quench tanks.
Improved Working Conditions
The result is a clean, dry, and non-toxic work environment. Parts exit the furnace clean and ready for subsequent steps, and the process is easier to manage, helping to meet stringent quality standards like CQI-9.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While technologically superior, vacuum carburizing is not the universal solution for every application. Objectivity requires acknowledging its trade-offs.
Initial Capital Investment
Vacuum furnace systems represent a significantly higher initial capital investment compared to traditional atmosphere furnace lines.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Vacuum carburizing is fundamentally a batch process. For extremely high-volume production of simple, non-critical parts, large-scale continuous atmosphere furnaces can sometimes offer a lower cost per part.
Application Specificity
For components where slight variations in case depth are acceptable and dimensional tolerance is not a primary driver, the lower cost and established infrastructure of conventional carburizing may be a more pragmatic choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct carburizing method requires aligning the process capabilities with your component's specific requirements and your company's strategic goals.
- If your primary focus is high-performance components (gears, bearings, injectors): Vacuum carburizing's superior uniformity and reduced distortion are critical for meeting tight tolerances and performance demands.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and automation: The ability to run integrated, multi-step cycles in a single vacuum furnace offers a clear advantage in reducing lead times and handling.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and worker safety: The emission-free, chemical-free nature of vacuum carburizing makes it the superior long-term choice.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, high-volume production of non-critical parts: Conventional atmosphere carburizing may remain the more economical option, provided its process variations are acceptable.
By understanding these fundamental differences, you can select the case hardening process that aligns precisely with your technical requirements and business objectives.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Uniformity | Ensures homogeneous hardened case across all parts, improving quality and consistency. |
| Reduced Distortion | Minimizes part warping, allowing tighter tolerances and less post-processing. |
| Precise Process Control | Uses vacuum and controlled gas injection for accurate carbon diffusion and repeatability. |
| Environmental Benefits | Emission-free and eliminates hazardous chemicals, enhancing safety and compliance. |
| Operational Efficiency | Enables all-in-one cycles for faster processing and reduced handling in batch operations. |
Elevate your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, as well as CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether for high-performance gears, bearings, or other critical components. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum carburizing technologies can enhance your part quality, efficiency, and sustainability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















