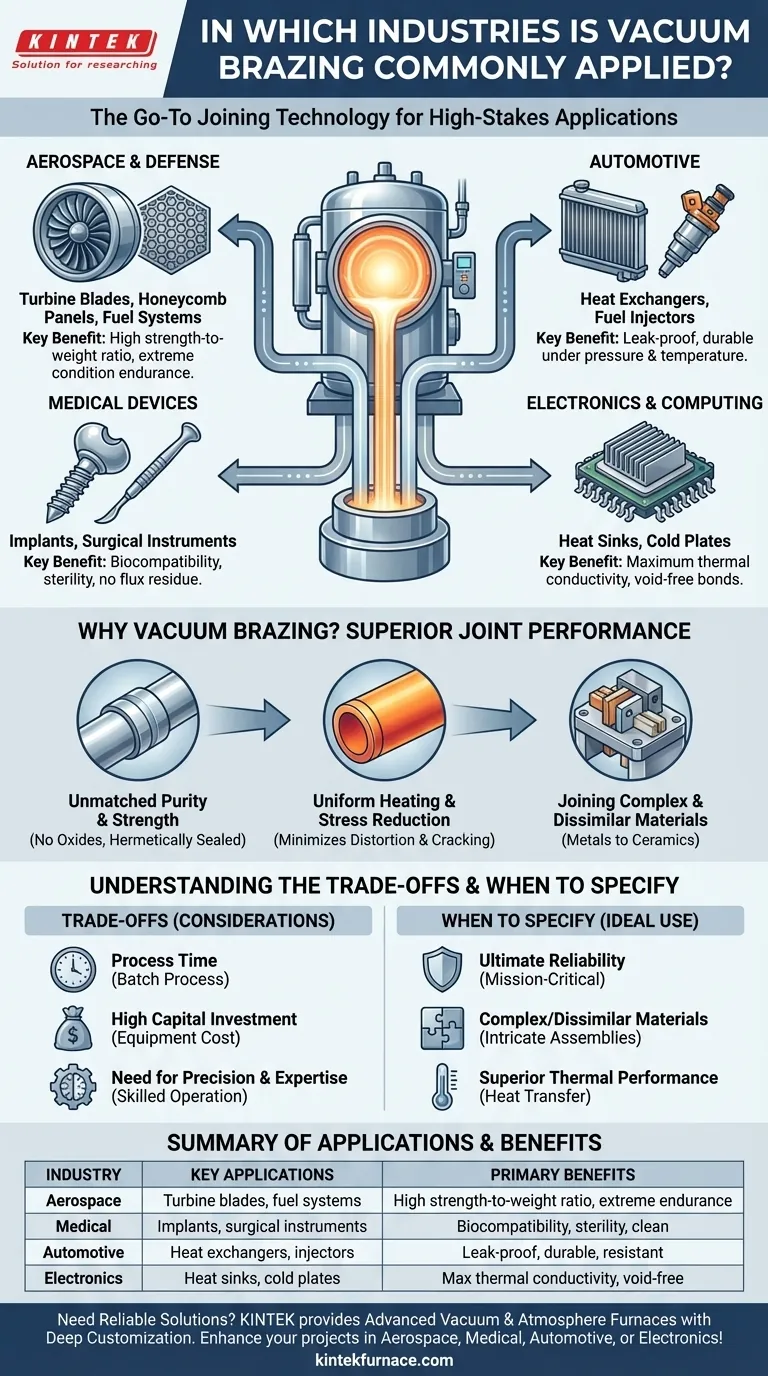
At its core, vacuum brazing is the go-to joining technology for industries where failure is not an option. It is most commonly applied in the aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics sectors. These industries rely on the process to create exceptionally strong, clean, and complex assemblies that are impossible to produce with conventional welding or soldering.
The decision to use vacuum brazing is driven by a need for ultimate reliability. By performing the joining process in a vacuum, it eliminates oxides and contaminants, resulting in a joint that is often as strong as the parent materials themselves.

Why Vacuum Brazing is Chosen for Critical Applications
Vacuum brazing is not just another way to join metal; it is a highly controlled metallurgical process. Its selection is a deliberate engineering choice based on several unique advantages over other methods.
Unmatched Joint Purity and Strength
The process takes place inside a vacuum furnace, which removes the oxygen and other atmospheric gases that cause contamination and weaken joints. This prevents the formation of oxides, eliminating the need for corrosive chemical fluxes. The result is an exceptionally clean, strong, and hermetically sealed bond.
Uniform Heating and Stress Reduction
Unlike welding, which applies intense heat to a localized spot, vacuum brazing heats the entire assembly uniformly. This gradual heating and cooling cycle minimizes internal stresses in the components, drastically reducing the risk of distortion or cracking, which is critical for parts with tight dimensional tolerances.
Joining Complex and Dissimilar Materials
Vacuum brazing excels at creating complex, multi-part assemblies in a single step. Furthermore, it is one of the few methods that can reliably join dissimilar materials, such as copper to stainless steel, titanium to nickel alloys, or even metals to ceramics.
A Look at Key Industry Applications
The specific problems solved by vacuum brazing become clearer when looking at its use cases within each major industry.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, the strength-to-weight ratio is paramount. Vacuum brazing is used to manufacture lightweight yet robust components like turbine blades, honeycomb panels, and critical fuel system assemblies. The process ensures these parts can withstand extreme temperatures and vibration without failing.
Medical Devices
For medical implants and surgical instruments, biocompatibility and sterility are non-negotiable. Because vacuum brazing uses no flux, there is no risk of corrosive residue being left on the final part. This creates the pristine, pore-free joints required for devices placed inside the human body.
Automotive
The automotive industry uses vacuum brazing to produce complex, leak-proof components like heat exchangers, radiators, and fuel injectors. The ability to join thin aluminum sections into intricate assemblies allows for the creation of efficient and durable parts that can handle constant pressure and temperature fluctuations.
Electronics and Computing
In high-power electronics, managing heat is the primary challenge. Vacuum brazing is used to manufacture heat sinks and cold plates for cooling processors and power modules. The process creates a perfect, void-free bond between the base plate and fins, ensuring maximum thermal conductivity and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum brazing is not the right solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Process Time and Batch Limitations
Vacuum brazing is a batch process. Loading, pumping down the vacuum, running the heating cycle, and cooling can take several hours. It is not as fast as automated welding and is less suited for very high-volume, low-complexity parts.
High Capital Investment
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital expense. The cost of the equipment and the required infrastructure means this process is typically performed by specialized firms or large-scale manufacturers.
Need for Precision and Expertise
Success in vacuum brazing depends on precise control over temperature, vacuum levels, and material preparation. It requires skilled operators and a deep understanding of metallurgy to design a successful brazing cycle, especially for complex assemblies.
When to Specify Vacuum Brazing for Your Project
Choosing the right joining method depends entirely on the requirements of your component. Use these guidelines to determine if vacuum brazing is the correct path.
- If your primary focus is ultimate reliability and joint integrity: Specify vacuum brazing for any mission-critical component where failure could have catastrophic consequences.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or dissimilar materials: It is the superior choice for creating intricate assemblies or bonding materials like metals to ceramics.
- If your primary focus is superior thermal performance: For heat sinks, cold plates, or any component where maximizing heat transfer is essential, vacuum brazing is unparalleled.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-volume production of simple parts: Other methods like conventional welding or soldering will likely be more cost-effective.
Ultimately, vacuum brazing is the definitive choice when the performance and integrity of the joined assembly cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, honeycomb panels, fuel systems | High strength-to-weight ratio, withstands extreme conditions |
| Medical | Implants, surgical instruments | Biocompatibility, sterility, no corrosive residues |
| Automotive | Heat exchangers, radiators, fuel injectors | Leak-proof, durable under pressure and temperature changes |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, cold plates | Maximum thermal conductivity, void-free bonds |
Need reliable vacuum brazing solutions for your critical applications? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering unmatched joint purity, strength, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your projects in aerospace, medical, automotive, or electronics industries!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















