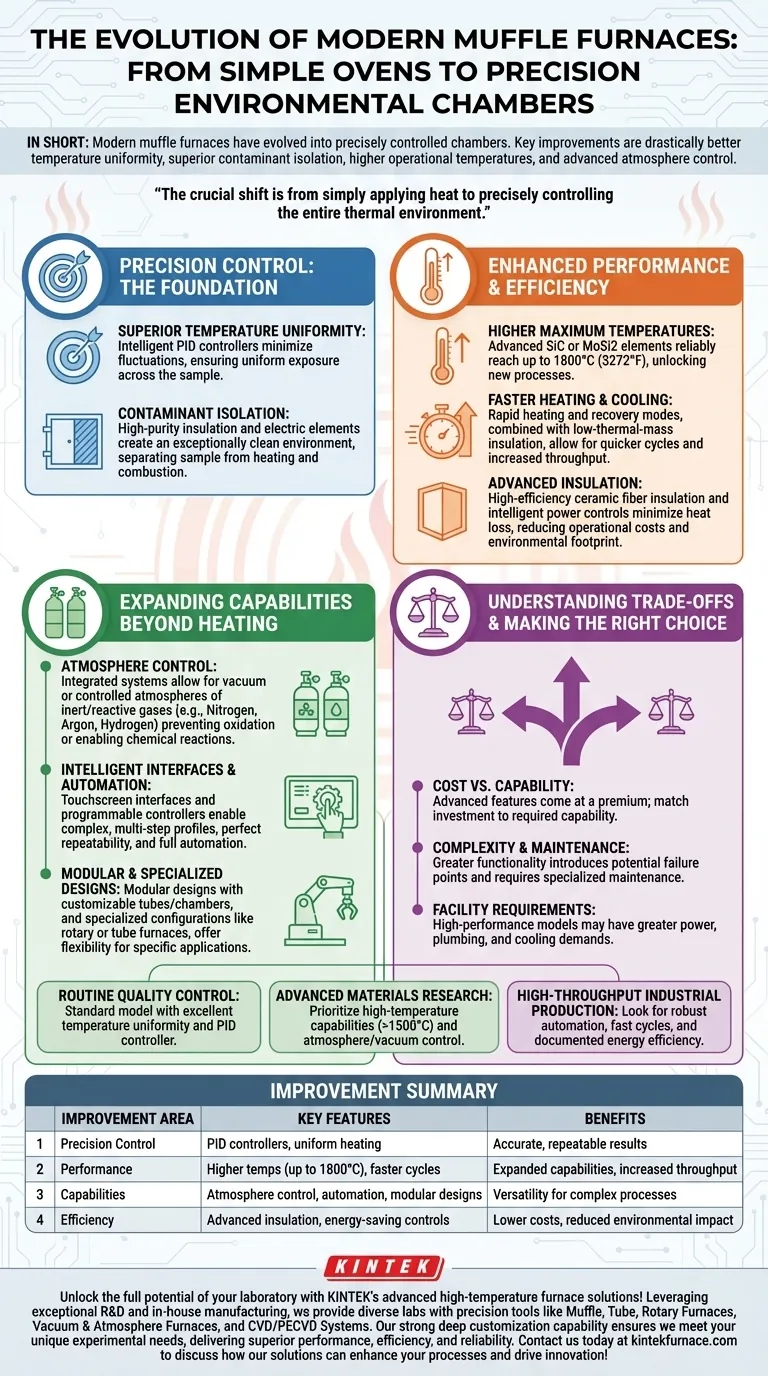
In short, modern muffle furnaces have evolved from simple high-temperature ovens into precisely controlled environmental chambers. The key improvements are drastically better temperature uniformity, superior isolation from contaminants, higher operational temperatures, and advanced features like atmosphere control, which together deliver more accurate, efficient, and repeatable results.
The crucial shift is from simply applying heat to precisely controlling the entire thermal environment. While older furnaces were effective for basic heating, modern versions provide the accuracy and versatility required for advanced materials science, sensitive analytics, and specialized industrial processes.
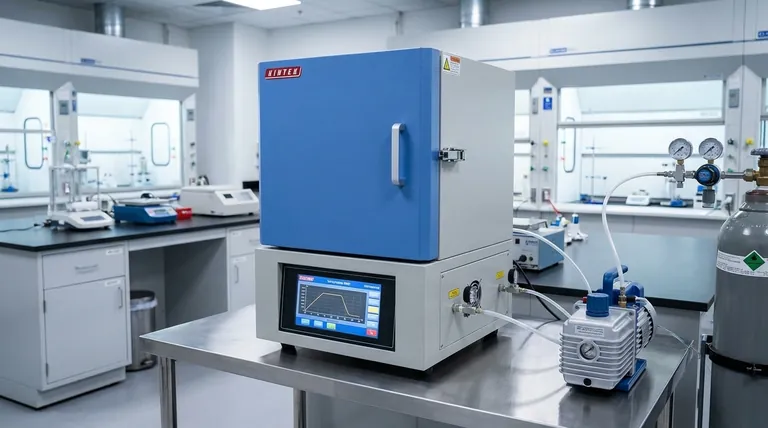

Precision Control: The Foundation of Modern Furnaces
The most significant advancements lie in the ability to dictate and maintain exact conditions within the furnace chamber. This precision is the bedrock of reliable and repeatable thermal processing.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
Modern furnaces use intelligent PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers to minimize temperature fluctuations. These systems constantly adjust power to the heating elements.
This ensures that the entire sample is exposed to a uniform temperature, eliminating hot or cold spots that could compromise the integrity of research or manufacturing processes.
Contaminant Isolation
The core design of a muffle furnace separates the sample from the heating elements and any potential combustion byproducts. Modern electric furnaces perfect this concept.
By using high-purity insulation and electrical heating elements, they create an exceptionally clean environment, which is critical for applications like ashing or processing sensitive alloys where contamination would invalidate the results.
Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
Beyond control, modern furnaces are faster, hotter, and more energy-efficient than their predecessors, expanding their operational capabilities while reducing costs.
Higher Maximum Temperatures
Advances in materials have pushed operational limits significantly. While older models were often limited, modern furnaces equipped with silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements can reliably reach temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F).
This capability unlocks processes for technical ceramics, powder metallurgy, and refractory metals that were previously impossible.
Faster Heating and Cooling
New designs feature rapid heating and recovery modes. Combined with more efficient, low-thermal-mass insulation, this allows for quicker cycles.
Faster processing increases throughput in industrial settings and saves significant time in research labs.
Advanced Insulation and Energy Savings
Modern furnaces utilize high-efficiency ceramic fiber insulation that minimizes heat loss. This, along with intelligent power controls that optimize energy usage, makes them far more energy-efficient.
The result is lower operational costs and a reduced environmental footprint, a key consideration for any modern laboratory or facility.
Expanding Capabilities Beyond Simple Heating
Modern muffle furnaces are no longer just for heating in air. They have become versatile tools capable of creating highly specific processing conditions.
Atmosphere Control
A game-changing advancement is the integration of atmosphere control systems. These allow processes to be run under a vacuum or in a controlled atmosphere of inert or reactive gases like nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen.
This is essential for preventing oxidation in brazing and sintering applications or for creating specific chemical reactions on a material's surface.
Intelligent Interfaces and Automation
Outdated analog dials have been replaced with touchscreen interfaces and programmable controllers.
Operators can now program complex, multi-step heating profiles with precise ramps and dwells, ensuring perfect process repeatability and enabling full automation.
Modular and Specialized Designs
The industry now offers modular designs with customizable furnace tubes and chambers. Specialized configurations, such as rotary or tube furnaces, are available for continuous processing or unique sample shapes.
This flexibility allows users to acquire a furnace tailored precisely to their specific application rather than adapting their process to a generic box furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While modern furnaces offer clear advantages, it's critical to understand the associated considerations to make an informed decision.
Cost vs. Capability
Advanced features come at a premium. A basic furnace for ashing is far less expensive than a high-temperature model with full atmosphere control. It is vital to match the investment to the required technical capability.
Complexity and Maintenance
Greater functionality can introduce complexity. A furnace with vacuum pumps and gas flow controllers has more potential failure points and requires more specialized maintenance than a simple air-atmosphere furnace.
Facility Requirements
High-performance models often have greater power demands. Furnaces with atmosphere or water-cooling systems also require specific plumbing and facility hookups that must be planned for.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate furnace requires a clear understanding of your primary goal. Use these points as a guide.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control or ashing: A standard model with excellent temperature uniformity and a reliable PID controller is your most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research: Prioritize models with high-temperature capabilities (above 1500°C) and atmosphere or vacuum control to ensure maximum experimental flexibility.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial production: Look for robust automation, fast heating/cooling cycles, and documented energy efficiency to maximize productivity and minimize operational costs.
Ultimately, choosing the right muffle furnace is about aligning its specific technological advantages with the precise demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Improvement Area | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Control | PID controllers, uniform heating | Accurate, repeatable results |
| Performance | Higher temperatures (up to 1800°C), faster cycles | Expanded capabilities, increased throughput |
| Capabilities | Atmosphere control, automation, modular designs | Versatility for complex processes |
| Efficiency | Advanced insulation, energy-saving controls | Lower costs, reduced environmental impact |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with precision tools like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering superior performance, efficiency, and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















