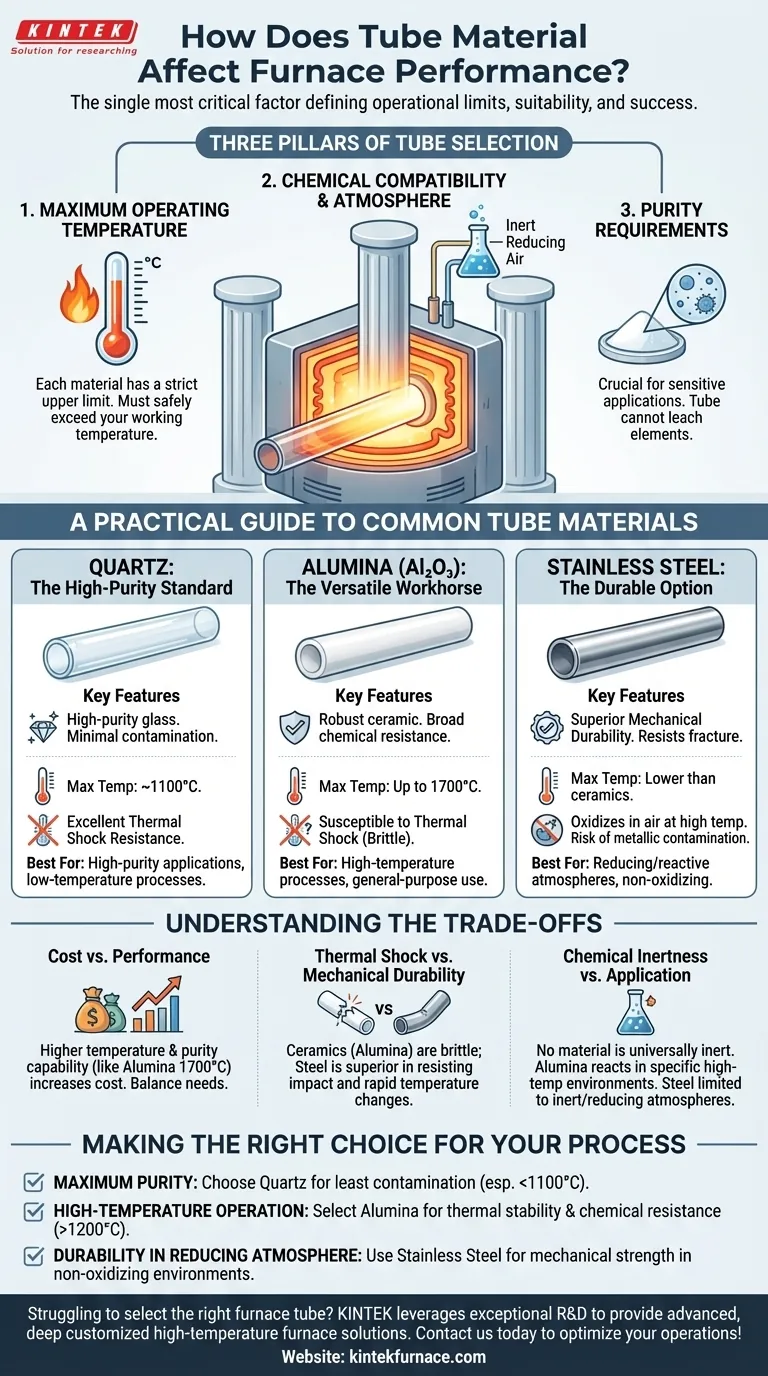
The material of your furnace tube is not a minor detail; it is the single most critical factor defining the furnace's operational limits and suitability for your specific application. The material dictates the maximum temperature, the types of chemical atmospheres you can use, and the level of purity you can achieve in your process.
The core challenge is not simply choosing a material, but matching the material's inherent properties—its temperature ceiling, chemical inertness, and durability—to the precise demands of your scientific or industrial process.

The Three Pillars of Tube Selection
To select the correct tube, you must evaluate your process against three fundamental criteria. The tube material you choose is a direct consequence of these requirements.
1. Maximum Operating Temperature
The most immediate constraint is temperature. Each material has a strict upper limit beyond which it will soften, melt, or fail.
Furnaces are often categorized by their temperature range (e.g., up to 1100°C, 1200-1300°C, 1400-1700°C). Your choice of tube must be rated to safely exceed your actual working temperature. Exceeding this limit risks catastrophic failure and damage to the heating elements.
2. Chemical Compatibility & Atmosphere
The inside of the furnace is a reactive environment. The tube must be chemically inert to both the sample you are heating and any process gases being used.
Gas composition and flow rate are critical variables. The tube material must not react with or be degraded by the atmosphere, whether it is an inert gas, a reducing gas, or simply air. An incompatible material can contaminate your sample or degrade, leading to vacuum leaks or system failure.
3. Purity Requirements
For sensitive applications like semiconductor manufacturing or trace material analysis, the tube itself cannot be a source of contamination.
The material must not leach elements into the sample at high temperatures. This is why certain materials, like high-purity quartz, are considered the standard for processes demanding the cleanest possible environment.
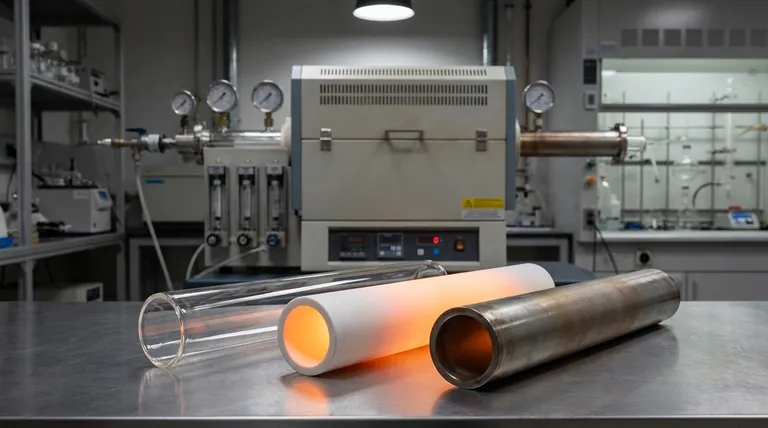
A Practical Guide to Common Tube Materials
While many specialized materials exist, most applications are served by three primary options, each with a distinct purpose.
Quartz: The High-Purity Standard
Quartz is a form of high-purity glass. It is the go-to choice for applications demanding minimal contamination.
It offers excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning it can handle relatively rapid temperature changes without cracking. However, its maximum working temperature is typically limited to around 1100°C.
Alumina: The Versatile Workhorse
Alumina (Al2O3) is a robust ceramic material ideal for a wide range of high-temperature applications, often up to 1700°C.
It offers excellent thermal stability and broad chemical resistance, making it suitable for many general-purpose heating processes. It is less pure than quartz but far more capable at extreme temperatures.
Stainless Steel: The Durable Option
For processes involving reducing or reactive atmospheres where ceramics might be unsuitable, stainless steel is a strong choice.
Its primary benefit is mechanical durability and resistance to fracture. However, it has a much lower maximum temperature limit than ceramics and can be a source of metallic contamination, making it unsuitable for high-purity work.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a tube material is an exercise in balancing competing factors. An ideal material for one metric is often compromised on another.
The Cost vs. Performance Balance
Higher performance comes at a price. High-purity alumina tubes capable of reaching 1700°C are significantly more expensive than standard quartz tubes. You must justify the material's capability against the actual needs of your process.
Thermal Shock vs. Mechanical Durability
Ceramic tubes like alumina are very strong under compression but are brittle and highly susceptible to thermal shock. Heating or cooling them too quickly will cause them to crack. Quartz is better, but steel is far superior in resisting both mechanical impact and thermal shock.
Chemical Inertness vs. Application
No single material is universally inert. While alumina is resistant to many chemicals, it may react in specific high-temperature environments. Stainless steel is durable but will oxidize rapidly in air at high temperatures, limiting its use to inert or reducing atmospheres.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct tube material ensures the safety, repeatability, and success of your work. Base your decision on the primary goal of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Choose a quartz tube, as it introduces the least contamination into your process, especially below 1100°C.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation (above 1200°C): Select a high-purity alumina tube for its excellent thermal stability and general chemical resistance.
- If your primary focus is durability in a reducing atmosphere: Use a stainless steel tube, which offers superior mechanical strength and is well-suited for non-oxidizing environments.
By aligning the tube material with your specific temperature, atmosphere, and purity needs, you ensure reliable, repeatable, and safe furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Up to 1100°C | High purity, excellent thermal shock resistance | High-purity applications, minimal contamination |
| Alumina | Up to 1700°C | Versatile, broad chemical resistance, thermal stability | High-temperature processes, general-purpose use |
| Stainless Steel | Lower than ceramics | Durable, resistant to mechanical impact and thermal shock | Reducing atmospheres, non-oxidizing environments |
Struggling to select the right furnace tube for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, enhancing performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your furnace operations and drive success in your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















