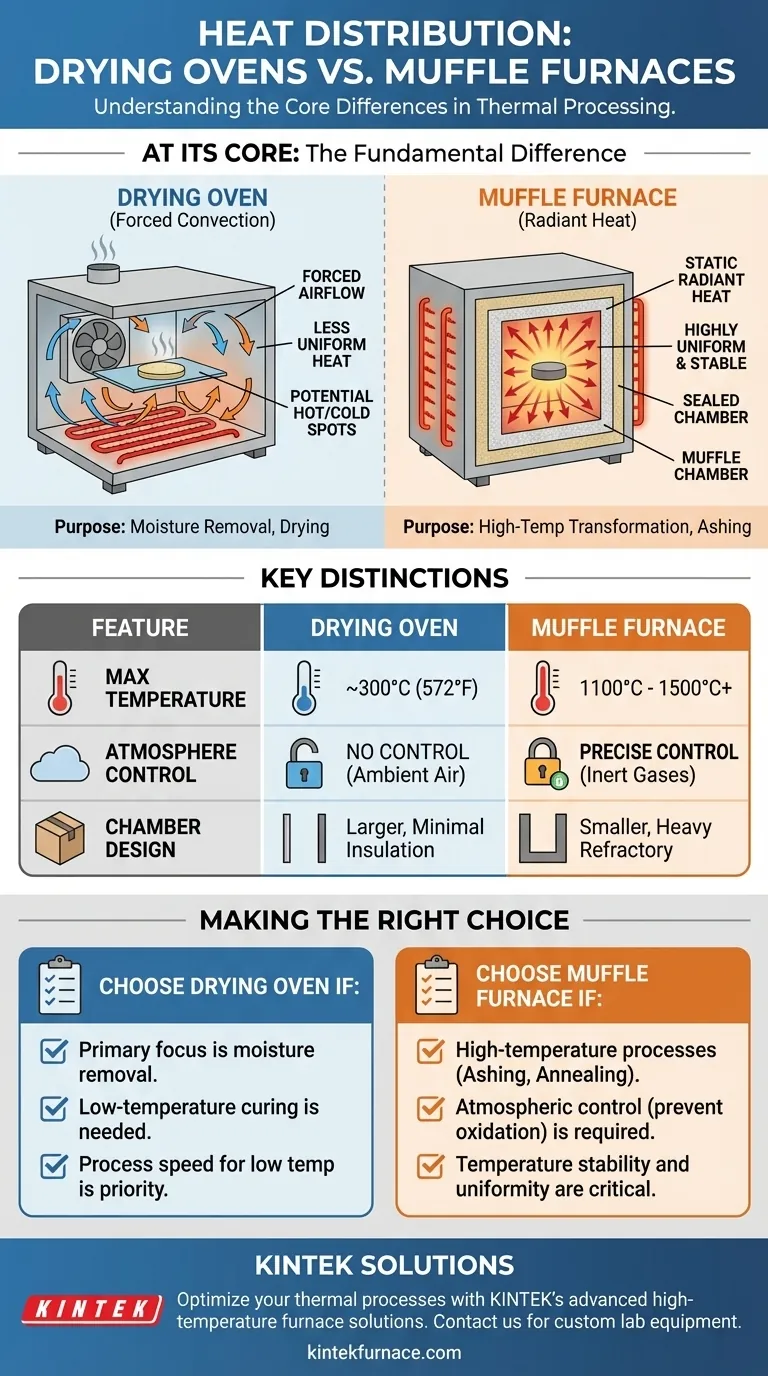
At its core, a muffle furnace provides significantly more uniform and stable heat distribution than a drying oven. This is a direct result of their fundamentally different heating mechanisms. A muffle furnace uses radiant heat within a sealed, heavily insulated chamber, while a drying oven relies on forced air convection, which inherently creates temperature variations.
The choice between a drying oven and a muffle furnace goes beyond simple temperature uniformity. It's a decision between a tool designed for low-temperature moisture removal (oven) and one designed for high-temperature, atmospherically stable material transformation (furnace).
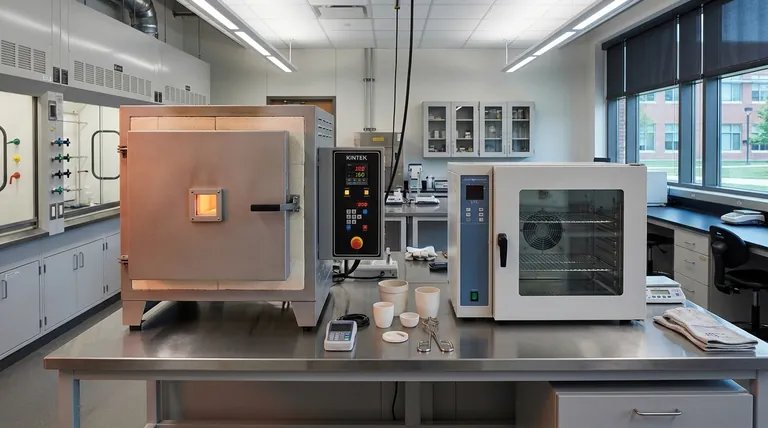

The Core Difference: Convection vs. Radiant Heat
The primary reason for the difference in heat distribution lies in how each device transfers thermal energy to the sample. One moves heated air; the other radiates heat from static surfaces.
How Drying Ovens Work (Forced Convection)
A drying oven's main purpose is to remove moisture. It achieves this by pulling in fresh air, passing it over heating elements, and circulating it throughout the chamber with a fan.
This constant movement of air actively carries heat to the sample's surface and, more importantly, carries evaporated moisture out through an exhaust vent.
While the goal is a uniform temperature, the nature of forced airflow can create hot and cold spots. Areas closer to the heating elements or directly in the fan's path will be hotter, while corners or areas with obstructed flow may be cooler.
How Muffle Furnaces Work (Radiant Heat)
A muffle furnace is designed for high-temperature stability. Its key feature is a "muffle"—a sealed inner chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements.
The electric elements heat the space around this chamber. The chamber walls then absorb this energy and radiate it evenly onto the sample inside.
Because the chamber is fully sealed during operation with no airflow, heat transfer is static and highly uniform. This design ensures that every surface of the sample receives a consistent amount of thermal energy.
Key Distinctions Beyond Heat Distribution
Understanding the purpose behind each design reveals other critical differences that will guide your choice.
Operating Temperature Range
This is often the most significant deciding factor.
- Drying Ovens typically operate at lower temperatures, usually maxing out around 300°C (572°F).
- Muffle Furnaces are built for high-heat applications and can easily reach 1100°C to 1500°C (2012°F to 2732°F) or higher.
Atmosphere Control
The sealed nature of a muffle furnace allows for precise control over the internal environment. You can introduce inert or reducing gases to prevent oxidation during heating.
Drying ovens, by design, constantly circulate ambient air and therefore offer no atmospheric control.
Chamber Design and Insulation
The high temperatures of a muffle furnace demand a smaller, highly controlled chamber made of refractory materials and surrounded by heavy insulation.
Drying ovens often have larger chambers with minimal insulation, as their goal is not extreme heat retention but efficient air exchange.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither device is inherently "better"; they are simply optimized for different tasks. Recognizing their limitations is key to using them correctly.
The Purpose-Driven Design
The potential for "uneven" heating in a drying oven is not a design flaw but a byproduct of its primary function. For drying bulk materials, the efficient removal of moisture via airflow is far more important than absolute temperature precision.
For processes like ashing, sintering, or heat-treating metals, the temperature stability and atmospheric control of a muffle furnace are non-negotiable.
Process Speed vs. Stability
A convection oven can often bring a sample to a low temperature more quickly due to the active circulation of hot air.
A muffle furnace heats more slowly and methodically, relying on radiation and thermal equilibrium to ensure stability and uniformity, which is critical for sensitive materials and analytical accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select your equipment based on the demands of your process, not just a single specification.
- If your primary focus is moisture removal, drying, or low-temperature curing: A drying oven's forced convection is the most efficient and appropriate tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processes like ashing, annealing, or materials science: A muffle furnace is required for its high-temperature capability, stability, and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or reaction with air: A muffle furnace is the only choice, as it allows for a controlled, inert atmosphere.
By understanding the fundamental heating mechanism—moving air versus static radiation—you can confidently select the right tool for your specific thermal processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Drying Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Forced convection with air circulation | Radiant heat in a sealed chamber |
| Heat Distribution | Less uniform, potential for hot/cold spots | Highly uniform and stable |
| Max Temperature | ~300°C (572°F) | 1100°C to 1500°C (2012°F to 2732°F) or higher |
| Atmosphere Control | No control, uses ambient air | Yes, allows inert or reducing gases |
| Primary Use | Moisture removal, low-temperature drying | High-temperature processes like ashing, annealing |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes with the right equipment? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















