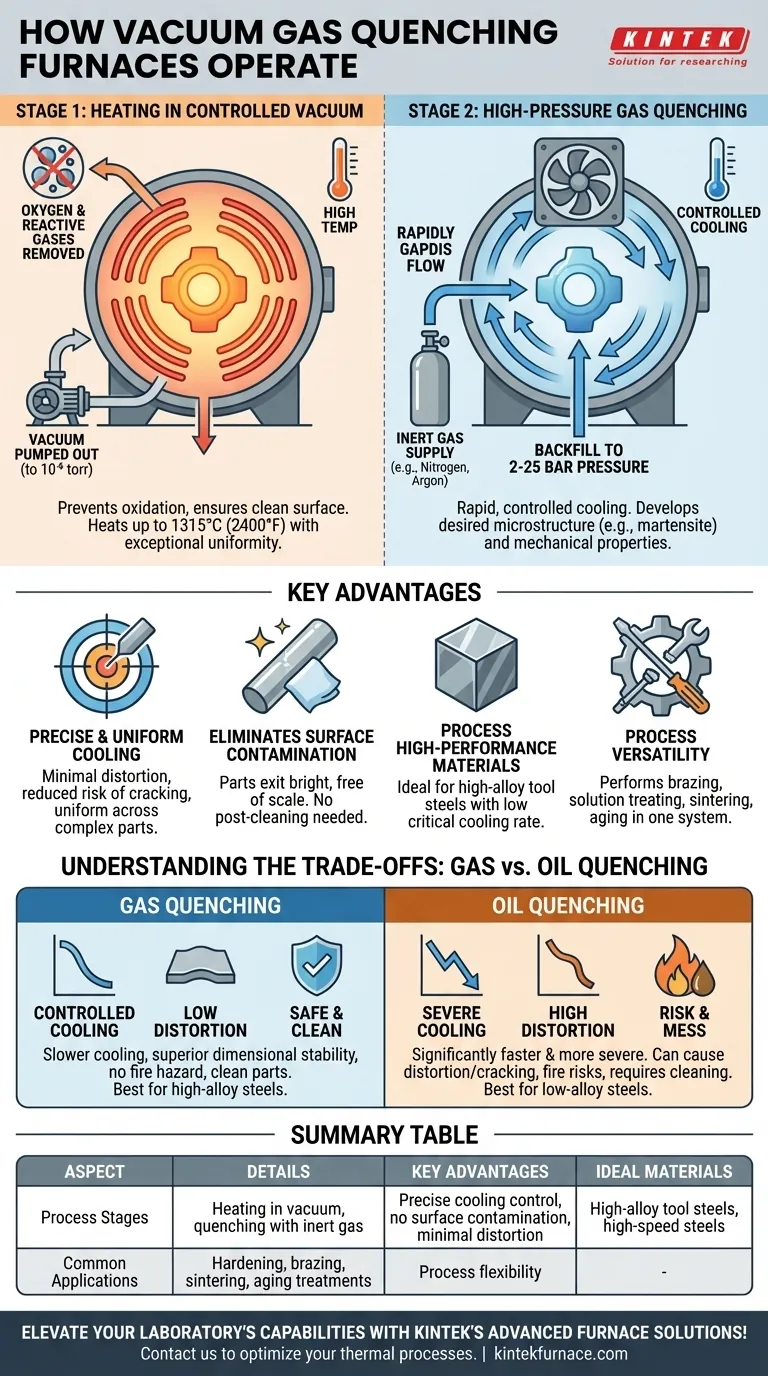
At its core, a vacuum gas quenching furnace is a highly controlled system for heat treating materials through a two-step process. First, the material is heated to a specific temperature within a high-vacuum chamber to prevent oxidation and contamination. Second, it is rapidly cooled (quenched) by introducing a high-pressure, inert gas, which allows for precise control over the final properties of the material.
The fundamental advantage of vacuum gas quenching is not just cooling speed, but unparalleled control. It provides a clean, predictable, and uniform environment to achieve specific metallurgical properties in high-performance alloys while minimizing the part distortion common with traditional liquid quenching.

The Two-Stage Process: Heating and Quenching
The operation is a sequence of precisely controlled events, each critical for the final outcome. The entire process takes place within a single, sealed chamber.
Stage 1: Heating in a Controlled Vacuum
The process begins by placing the workpiece inside the furnace and pumping out the air to create a deep vacuum, often in the 10⁻⁶ torr range.
This vacuum is critical because it eliminates oxygen and other reactive gases. This prevents oxidation, decarburization, and other surface reactions that would otherwise occur at high temperatures, ensuring the part emerges from the furnace clean and chemically unaltered.
Heating is accomplished using robust elements, typically made of curved graphite or molybdenum, inside an all-graphite or all-metal "hot zone." The furnace can reach temperatures up to 1315°C (2400°F) with exceptional uniformity.
Stage 2: High-Pressure Gas Quenching
Once the material has been held at the target temperature for the required time, the quenching phase begins.
The vacuum is broken by backfilling the chamber with an inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon, to pressures ranging from 2 to 25 bar. A powerful fan then circulates this high-pressure gas at high velocity throughout the chamber.
This rapid flow of gas effectively removes heat from the part, causing it to cool at a controlled rate. This cooling rate is what develops the desired final microstructure and mechanical properties, such as the formation of martensite in steels for maximum hardness.
Key Capabilities and Advantages
The design of a vacuum gas furnace provides distinct advantages over older methods like atmosphere furnaces or open-air quenching.
Precise and Uniform Cooling
The flow of quenching gas can be precisely directed and controlled. This ensures uniform cooling across the entire part, even with complex geometries, which significantly reduces the risk of thermal stress, distortion, and cracking.
Eliminating Surface Contamination
Because the entire process occurs in a clean, vacuum environment, parts exit the furnace bright and free of scale. This often eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming post-processing steps like sandblasting or chemical cleaning.
Processing High-Performance Materials
The method is ideal for high-alloy tool steels, such as high-speed steels and high-chromium steels. These materials possess a low "critical cooling rate," meaning they do not require the extreme severity of an oil quench to achieve full hardness, making controlled gas quenching a perfect fit.
Process Versatility
Modern vacuum furnaces are not limited to just hardening. They are highly functional systems capable of performing a wide variety of thermal processes, including high-temperature brazing, solution treating, sintering of powdered metals, and aging treatments.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Gas vs. Oil Quenching
While powerful, gas quenching is not a universal solution. The primary alternative is oil quenching, and the choice between them involves clear trade-offs.
Cooling Rate and Severity
Oil is a liquid and has a much higher heat transfer capability than any gas. Therefore, oil quenching is significantly faster and more severe than gas quenching. Some low-alloy steels require this severity to achieve maximum hardness.
Gas quenching, even at high pressures like 20 bar, provides a slower cooling rate. It is best suited for materials that are "air-hardening" or do not require a violent quench.
Part Distortion and Safety
The extreme thermal shock of plunging a hot part into cool oil creates significant internal stresses, often leading to part distortion or even cracking. Gas quenching is much gentler, resulting in superior dimensional stability.
Furthermore, oil quenching involves fire hazards, messy parts, and the need for post-process cleaning, all of which are eliminated with gas quenching.
System Cost and Complexity
Vacuum gas quenching furnaces are more complex pieces of equipment. The need to contain high gas pressures and maintain a deep vacuum makes them more expensive to build and maintain than simpler oil quench systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct quenching method depends entirely on the material being treated and the desired final outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness in low-alloy steels: Traditional oil quenching may be necessary due to its more severe cooling rate.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion and ensuring cleanliness on sensitive or high-alloy materials: Vacuum gas quenching is the superior choice for its unparalleled control and clean finish.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and automation in a modern facility: A vacuum gas furnace offers a versatile platform for hardening, brazing, and sintering in a single, automated system.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to select the precise thermal process that meets your material's needs and your organization's quality standards.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process Stages | Heating in vacuum, quenching with inert gas |
| Key Advantages | Precise cooling control, no surface contamination, minimal distortion |
| Ideal Materials | High-alloy tool steels, high-speed steels |
| Common Applications | Hardening, brazing, sintering, aging treatments |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering clean, controlled heat treatment for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















