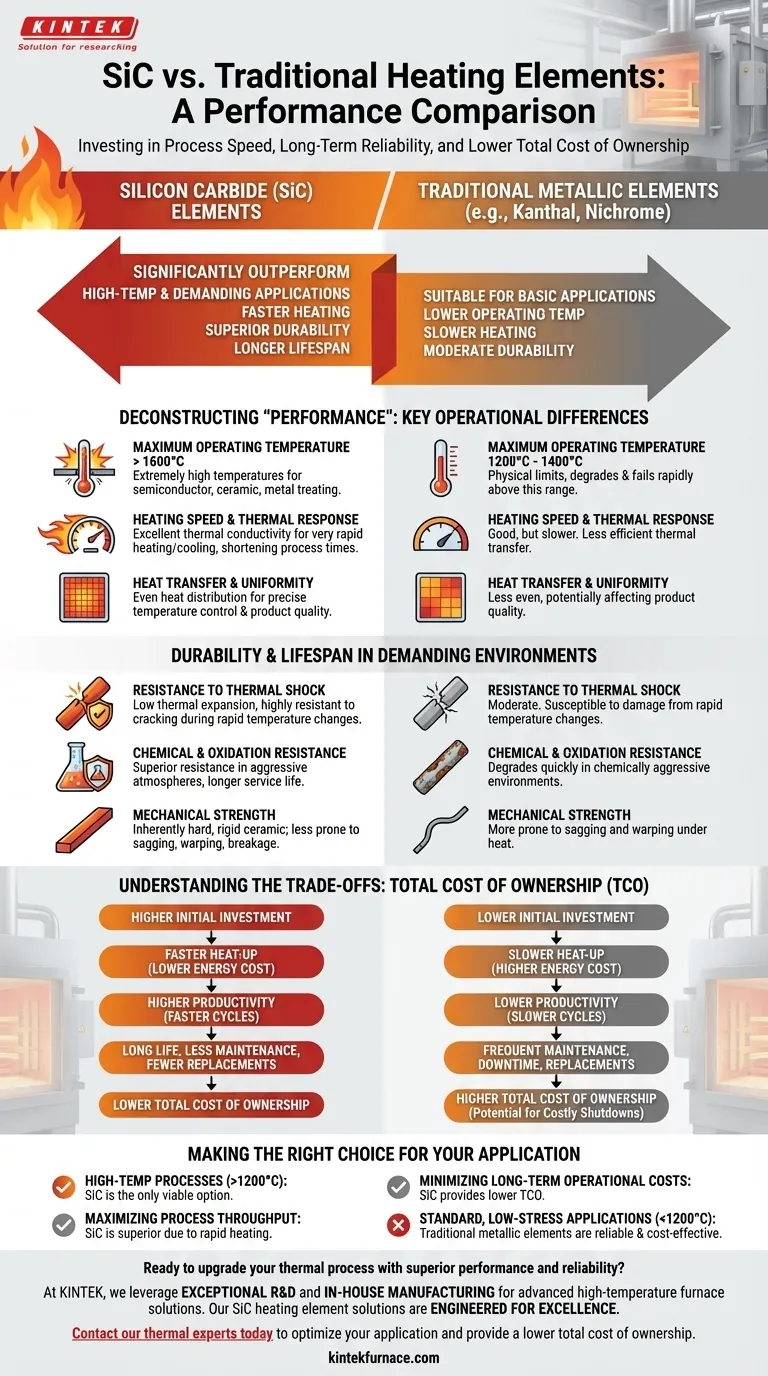
In short, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements significantly outperform traditional metallic resistance elements in nearly every performance metric, especially in high-temperature and demanding industrial applications. They offer a much higher operating temperature, faster heating rates, superior durability, and a longer operational lifespan.
While traditional heating elements are suitable for basic applications, SiC elements represent a fundamental upgrade in thermal technology. The decision is not merely about generating heat, but about investing in process speed, long-term reliability, and a lower total cost of ownership in challenging environments.

Deconstructing "Performance": Key Operational Differences
When comparing heating elements, "performance" is not a single attribute. It is a combination of temperature capability, speed, and efficiency, where SiC demonstrates clear advantages.
Maximum Operating Temperature
Traditional metallic heating elements, such as those made from Kanthal (FeCrAl) or Nichrome (NiCr), have physical limits, typically capping out around 1200°C to 1400°C. Above this, they degrade and fail rapidly.
Silicon carbide elements, by contrast, can operate at extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 1600°C. This makes them the default choice for applications like semiconductor manufacturing, ceramic firing, and metal heat treating.
Heating Speed and Thermal Response
SiC elements possess excellent thermal conductivity. This allows them to transfer heat energy with remarkable efficiency, resulting in very rapid heating and cooling cycles.
This rapid response shortens process times, increases furnace throughput, and minimizes wasted energy during heat-up. This efficiency directly contributes to lower operational costs and a more sustainable process.
Heat Transfer and Uniformity
The high conductivity of SiC also ensures even and uniform heat distribution across the element's surface and within the heating chamber. This uniformity is critical for processes where precise temperature control is necessary to guarantee product quality.
Durability and Lifespan in Demanding Environments
The true value of SiC is most apparent in its structural integrity and resistance to the harsh conditions found in industrial furnaces.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
A key advantage of SiC is its low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts very little when heated and cooled, drastically reducing internal stress.
This property makes it highly resistant to thermal shock, minimizing the risk of cracking or breakage during rapid temperature changes and significantly extending its usable life.
Chemical and Oxidation Resistance
High-temperature industrial processes often involve chemically aggressive atmospheres. SiC exhibits superior resistance to both oxidation and chemical corrosion compared to metallic elements, which degrade quickly in such environments.
This resistance ensures consistent performance and a much longer service life, reducing the frequency of costly maintenance and element replacement.
Mechanical Strength
Silicon carbide is an inherently hard and rigid ceramic material. This gives the heating elements outstanding mechanical strength and makes them far less prone to sagging, warping, or accidental breakage during installation and operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Total Cost of Ownership
No technical choice is without trade-offs. The primary consideration when choosing between SiC and traditional elements is the balance between upfront cost and long-term value.
The Initial Investment
Silicon Carbide heating elements carry a higher initial purchase price than their traditional metallic counterparts. This can make them seem like a more expensive option on paper.
The Impact on Operational Costs
However, the initial cost is only one part of the equation. The energy efficiency gained from SiC's faster heat-up times leads to lower electricity consumption over the element's lifespan.
Faster cycle times also mean higher productivity and throughput from a single piece of equipment, generating more value over the same period.
The Value of Reliability
The most significant factor is the total cost of ownership. SiC's long life and resistance to failure reduce expenses related to maintenance labor, production downtime, and frequent replacement parts. For many industrial users, the cost of a single unplanned shutdown far exceeds the initial cost difference of the elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of heating element should be directly informed by your operational priorities and process requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processes (>1200°C): SiC is your only viable option, as traditional metallic elements cannot withstand these conditions.
- If your primary focus is maximizing process throughput: SiC is the superior choice due to its rapid heating capabilities, which significantly reduce cycle times.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: SiC provides a lower total cost of ownership through superior energy efficiency, reliability, and lifespan, justifying its higher initial price.
- If your primary focus is a standard, low-stress application below 1200°C: Traditional metallic elements remain a perfectly reliable and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element is an investment in the performance and reliability of your entire thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Performance Metric | Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements | Traditional Metallic Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature | > 1600°C | 1200°C - 1400°C |
| Heating Rate / Thermal Response | Excellent (High Thermal Conductivity) | Good |
| Lifespan & Durability | Very High (Resistant to Thermal Shock & Corrosion) | Moderate |
| Ideal For | High-temp processes, demanding environments, rapid cycling | Standard, low-stress applications (<1200°C) |
Ready to upgrade your thermal process with superior performance and reliability?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Whether your priority is achieving temperatures beyond 1600°C, maximizing throughput with rapid heating, or minimizing long-term operational costs, our SiC heating element solutions are engineered for excellence.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss how we can optimize your application and provide a lower total cost of ownership.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















