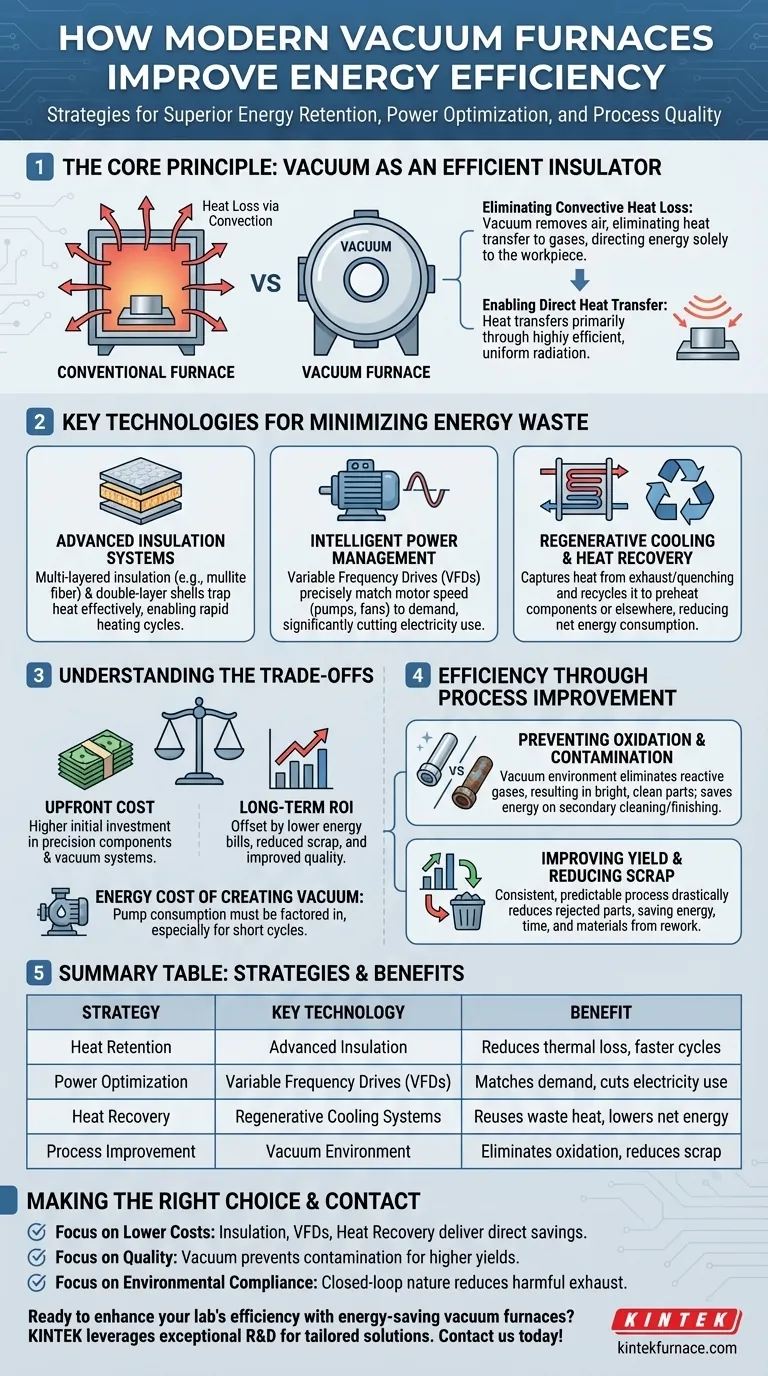
In essence, modern vacuum furnaces achieve superior energy efficiency through a combination of three core strategies. They leverage advanced insulation to retain heat, use intelligent power controls like Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) to optimize electricity use, and harness the inherent physical properties of a vacuum to eliminate heat loss from atmospheric gases.
The true efficiency of a vacuum furnace extends beyond just reducing power consumption. It stems from a holistic approach that minimizes thermal waste, optimizes power delivery, and critically, improves final product quality, which reduces energy-intensive rework and scrap.

The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum Is Inherently Efficient
A vacuum is not just an empty space; it is a powerful insulator. By removing air and other gases, a vacuum furnace fundamentally alters how heat behaves, creating an exceptionally efficient environment for thermal processing.
Eliminating Convective Heat Loss
In a conventional furnace, a significant amount of energy is wasted heating the surrounding air, which then carries that heat away through convection.
A vacuum nearly eliminates this mode of heat transfer. With no gas molecules to heat, energy is not lost to the atmosphere within the chamber, allowing it to be directed exclusively at the workpiece.
Enabling Direct Heat Transfer
With convection removed from the equation, heat is transferred primarily through radiation from the heating elements.
This direct, line-of-sight energy transfer is highly efficient and uniform, ensuring the part heats quickly and evenly without wasting energy on an intermediary medium like air.
Key Technologies for Minimizing Energy Waste
Modern furnaces are engineered systems where every component is designed to prevent energy from escaping. This efficiency is achieved through several key technological advancements.
Advanced Insulation Systems
To trap heat effectively, furnaces use multi-layered insulation. Materials like high-quality polycrystalline mullite fiber offer low thermal conductivity, enabling rapid heating cycles while conserving energy.
Designs often incorporate double-layer furnace shells with air cooling between them. This creates an additional insulating barrier, further reducing heat loss to the surrounding environment.
Intelligent Power Management
Auxiliary equipment like pumps and cooling fans can be major sources of energy consumption. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are used to precisely match the motor speed of these components to the exact demand of the process cycle.
Instead of running at full power continuously, VFDs ramp down during periods of lower demand, significantly cutting electricity usage without compromising performance.
Regenerative Cooling and Heat Recovery
The cooling cycle also presents an opportunity for energy savings. Regenerative cooling systems capture heat from the exhaust gases or quenching medium.
This recovered thermal energy can then be recycled to preheat components or used elsewhere in the facility, reducing the overall net energy consumption of the entire process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, a vacuum furnace is a complex piece of equipment. A clear-eyed view of the trade-offs is necessary to determine if it is the right solution for your operation.
The Upfront Cost vs. Long-Term ROI
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to their atmospheric counterparts. The precision components, robust chamber, and vacuum pumping systems contribute to a higher initial cost.
However, this cost is often offset over the long term by lower energy bills, reduced material scrap, and improved product quality, leading to a strong return on investment.
The Energy Cost of Creating the Vacuum
Achieving a vacuum is not a zero-energy process. A system of mechanical pumps (to create a base vacuum) and diffusion or molecular pumps (to achieve a high vacuum) consumes electricity.
The energy consumed by the pumps must be factored into the total energy equation. For processes requiring only short cycles, this initial energy expenditure can be a notable part of the overall consumption.
Beyond Kilowatts: Efficiency Through Process Improvement
The most significant, yet often overlooked, aspect of a vacuum furnace's efficiency is its ability to perfect the metallurgical process itself.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The vacuum environment is fundamentally protective. By removing oxygen and other reactive gases, it eliminates oxidation, decarburization, and contamination of the material surface during heating.
This results in bright, clean parts that do not require subsequent cleaning or surface finishing, saving both time and the energy associated with those secondary processes.
Improving Yield and Reducing Scrap
Because a vacuum provides a pristine and highly controllable environment, process outcomes are more consistent and predictable.
This drastic reduction in rejected or scrapped parts is a massive, indirect energy saving. Every part that must be scrapped or reworked represents a complete waste of the energy, time, and raw material used to create it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
To determine if a vacuum furnace is the correct investment, align its benefits with your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is lowering operational costs: The combination of superior insulation, VFDs on pumps, and regenerative heat recovery will deliver direct and measurable reductions in your monthly energy bills.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: The vacuum's ability to prevent oxidation and contamination is its greatest strength, leading to higher process yields and a superior final product.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: The closed-loop nature of a vacuum furnace prevents the release of harmful exhaust gases, helping you meet environmental standards and reducing downstream treatment costs.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace technology requires looking at the total cost of ownership, where energy savings and process improvements work together to deliver value.
Summary Table:
| Strategy | Key Technology | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Advanced Insulation (e.g., mullite fiber, double-layer shells) | Reduces thermal loss, enabling faster heating cycles |
| Power Optimization | Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) | Matches motor speed to demand, cutting electricity use |
| Heat Recovery | Regenerative Cooling Systems | Captures and reuses waste heat, lowering net energy consumption |
| Process Improvement | Vacuum Environment | Eliminates oxidation and contamination, reducing scrap and rework energy |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with energy-saving vacuum furnaces? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, helping you reduce energy costs and improve product quality. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can benefit your operation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















