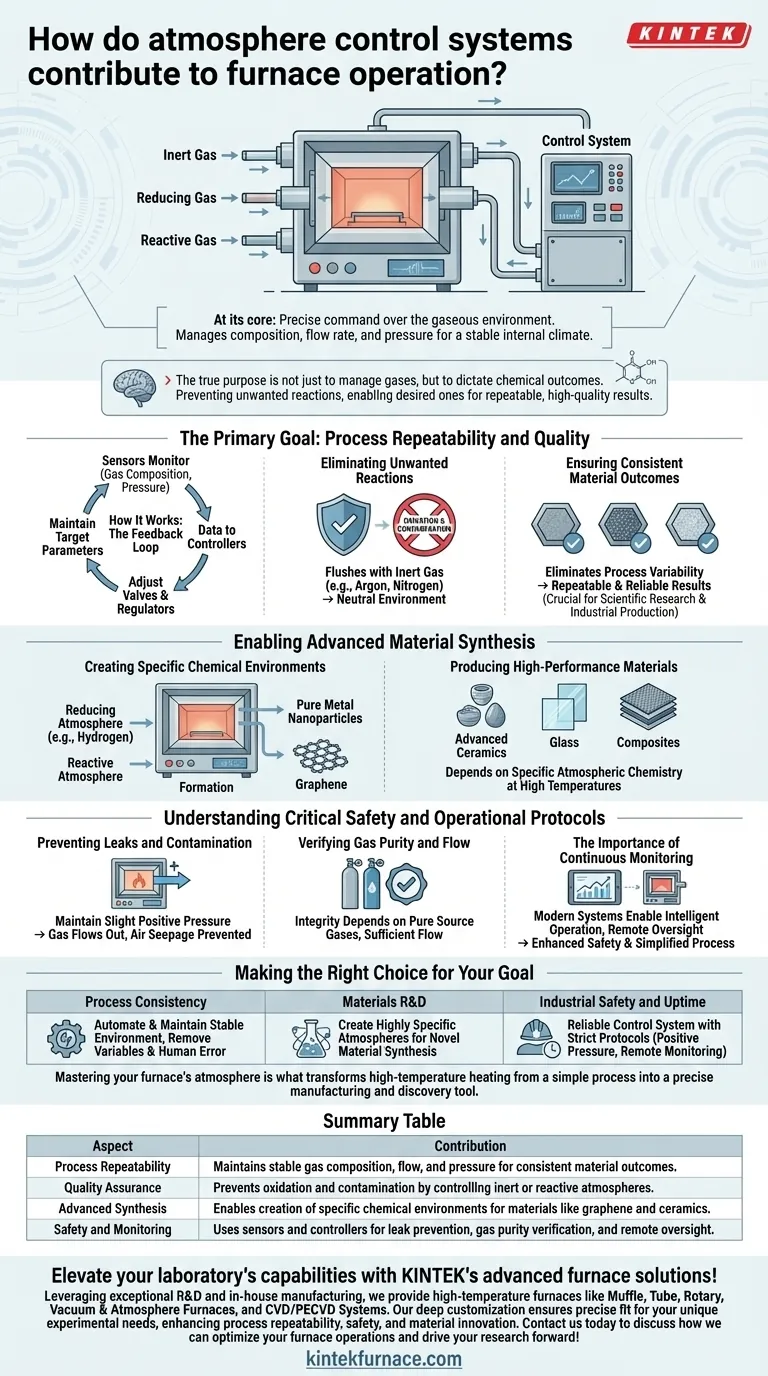
At its core, an atmosphere control system gives you precise command over the gaseous environment inside a furnace. It uses a network of sensors and controllers to meticulously manage the composition, flow rate, and pressure of the gases, creating a highly specific and stable internal climate for material processing.
The true purpose of atmosphere control is not just to manage gases, but to dictate chemical outcomes. By preventing unwanted reactions and enabling desired ones, these systems are the foundation for achieving repeatable, high-quality results and synthesizing advanced materials.
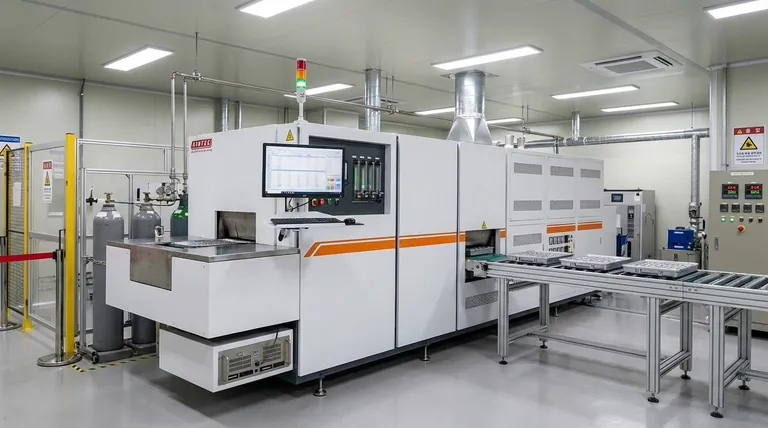

The Primary Goal: Process Repeatability and Quality
A furnace's primary job is to apply heat, but the atmosphere in which that heat is applied is often just as critical. Uncontrolled environments introduce variables that can ruin a process.
How It Works: The Feedback Loop
Atmosphere control systems operate on a continuous feedback loop. Sensors constantly monitor the conditions inside the furnace, such as gas composition and pressure.
This data is fed to controllers, which automatically adjust valves and regulators to manage the flow of different gases, ensuring the environment remains precisely within its target parameters.
Eliminating Unwanted Reactions
Many materials are highly reactive with oxygen and moisture in the ambient air, especially at high temperatures. This can lead to unwanted oxidation and contamination, compromising the material's properties.
An atmosphere control system can flush the furnace with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, creating a neutral environment that prevents these destructive reactions from occurring.
Ensuring Consistent Material Outcomes
By creating a stable and precisely defined environment, these systems eliminate a major source of process variability. This ensures that every batch of material is treated under the exact same conditions, leading to repeatable and reliable results that are crucial for both scientific research and industrial production.
Enabling Advanced Material Synthesis
Beyond simply preventing unwanted reactions, atmosphere control is a powerful tool for inducing specific chemical transformations to create new materials.
Creating Specific Chemical Environments
You can use a control system to introduce a reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen) or a reactive atmosphere to achieve specific goals.
For example, heating metal oxides in an inert atmosphere can produce pure metal nanoparticles. Similarly, heating carbon-containing materials in a reducing atmosphere is a method for producing advanced materials like graphene.
Producing High-Performance Materials
This level of control is fundamental to preparing many high-performance materials. The synthesis of specialized ceramics, glass, and composites often depends on maintaining a specific atmospheric chemistry during the high-temperature phases of production.
Understanding Critical Safety and Operational Protocols
Working with controlled gas atmospheres introduces operational complexities and safety risks that must be managed. The control system is only one part of a larger safety protocol.
Preventing Leaks and Contamination
A properly sealed furnace is non-negotiable. The system should maintain a slight positive pressure inside the chamber, ensuring that if any minor leak exists, gas flows out rather than allowing contaminated outside air to seep in.
Verifying Gas Purity and Flow
The integrity of your process depends on the purity of the source gases. Always verify the quality of your gas supply and ensure flow rates are sufficient and stable throughout the operation.
The Importance of Continuous Monitoring
Modern control systems enable intelligent operation, including remote monitoring. This not only simplifies the process for operators but also enhances safety by allowing constant oversight of temperature and atmosphere without direct exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The value of an atmosphere control system is directly tied to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: The system's ability to automate and maintain a stable, repeatable environment is its greatest benefit, removing variables and human error.
- If your primary focus is materials research and development: The key is the system's power to create highly specific inert, reducing, or reactive atmospheres to synthesize novel materials with unique properties.
- If your primary focus is industrial safety and uptime: The value lies in integrating a reliable control system with strict safety protocols like positive pressure, leak prevention, and remote monitoring.
Mastering your furnace's atmosphere is what transforms high-temperature heating from a simple process into a precise manufacturing and discovery tool.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Process Repeatability | Maintains stable gas composition, flow, and pressure for consistent material outcomes. |
| Quality Assurance | Prevents oxidation and contamination by controlling inert or reactive atmospheres. |
| Advanced Synthesis | Enables creation of specific chemical environments for materials like graphene and ceramics. |
| Safety and Monitoring | Uses sensors and controllers for leak prevention, gas purity verification, and remote oversight. |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing process repeatability, safety, and material innovation. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your furnace operations and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















