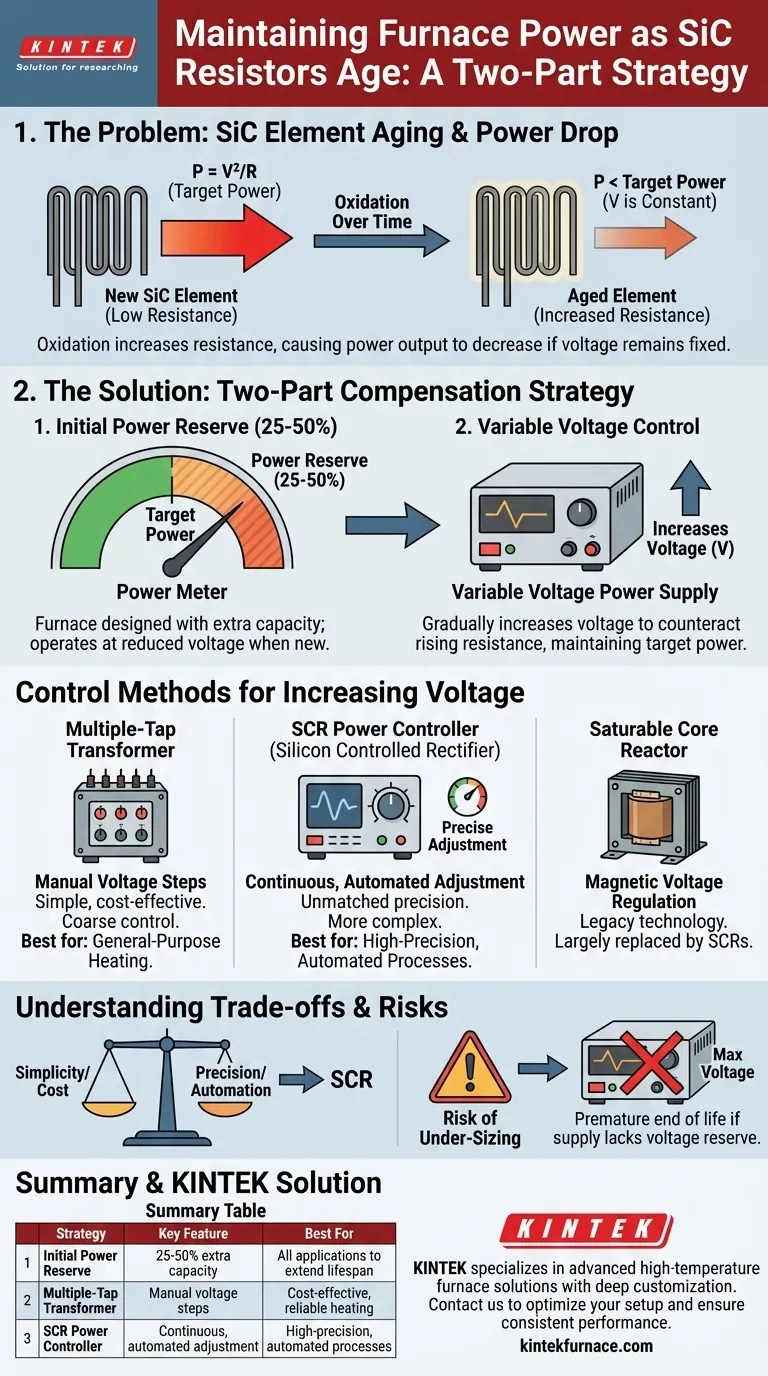
To maintain consistent furnace power as Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements age, a two-part strategy is employed. The furnace is first designed with significant power reserves, and then a variable voltage power supply is used to gradually increase the voltage over the element's lifespan. This compensates for the natural increase in electrical resistance that occurs with use.
The core challenge with SiC elements is that their resistance increases with use and age. To counteract the resulting power drop, you must have a power supply capable of increasing its output voltage over time, effectively forcing the required power through the higher-resistance material.

The Physics of SiC Element Aging
The Root Cause: Oxidation
Silicon Carbide heating elements operate at extremely high temperatures. At these temperatures, the material slowly reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere.
This process of oxidation forms a thin layer of silicon dioxide on the element's surface. While this layer is protective, it is less electrically conductive than the base SiC material.
The Impact on Power Output
As oxidation progresses over hundreds or thousands of hours, the element's overall electrical resistance increases.
According to Ohm's Law for power (P = V²/R), if the voltage (V) from the power supply remains constant while the resistance (R) goes up, the power output (P) must go down. This results in a cooler furnace and slower heat-up times.
The Two-Part Compensation Strategy
Phase 1: Initial Power Reserve
To ensure a long and useful service life, furnaces using SiC elements are intentionally designed with a power reserve of 25% to 50%.
This means that when the elements are new and have low resistance, the power supply is operated at a reduced voltage to deliver the correct target power. This "voltage reserve" provides the necessary headroom to increase the voltage as the elements age.
Phase 2: Variable Voltage Control
To counteract the rising resistance, the voltage applied to the elements must be increased over time. This is accomplished using a variable voltage power source.
Method 1: Multiple-Tap Transformers
A multiple-tap transformer is a straightforward and robust device with several output connections, or "taps," each providing a different, fixed voltage level.
As the elements age, an operator can manually switch the connection to a higher voltage tap to boost the power back to its target level.
Method 2: SCR Power Controllers
A Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) is a modern, solid-state device that allows for precise and continuous adjustment of the output voltage.
Unlike the stepped changes of a tap transformer, an SCR can make minute adjustments, often automatically, to hold the furnace power or temperature perfectly stable. This is the preferred method for high-performance applications.
Method 3: Saturable Core Reactors
This is an older technology that functions as a magnetic amplifier to regulate voltage. While effective, SCR controllers have largely replaced them in new designs due to their superior efficiency and control precision.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Multiple-Tap Transformers: Simplicity vs. Precision
A multiple-tap transformer is highly reliable and cost-effective. Its primary drawback is coarse control. The jump between taps can cause a noticeable change in power, which may not be acceptable for highly sensitive processes.
SCR Power Controllers: Precision vs. Complexity
SCRs offer unmatched precision and enable automation, allowing a control system to maintain a setpoint with no manual input. However, they are more complex, have a higher initial cost, and can introduce electrical noise (harmonics) if not specified correctly.
The Risk of Under-Sizing Your Supply
If a furnace power supply is not specified with enough voltage reserve, the elements will reach their "end of life" prematurely. This occurs when the power supply reaches its maximum voltage and can no longer deliver the required power to the high-resistance elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct control method depends entirely on your process requirements and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum precision and automation: An SCR power controller is the ideal choice for its continuous and automated voltage adjustment.
- If your primary focus is reliability and cost-effectiveness: A multiple-tap transformer provides a durable, simple, and proven solution for general-purpose heating.
- If you are operating an existing furnace with a fixed voltage supply: Your only options are to replace the SiC elements more frequently or to undertake a significant upgrade to a variable voltage power supply.
Ultimately, managing SiC element aging is not about fighting resistance, but about implementing a power system designed to adapt to it.
Summary Table:
| Strategy/Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Power Reserve | 25-50% extra capacity | All applications to extend lifespan |
| Multiple-Tap Transformer | Manual voltage steps | Cost-effective, reliable heating |
| SCR Power Controller | Continuous, automated adjustment | High-precision, automated processes |
| Saturable Core Reactor | Magnetic voltage regulation | Legacy systems (largely replaced) |
Struggling with furnace power drops from aging SiC elements? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring consistent performance and extended equipment life. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your furnace setup and keep your processes running smoothly!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















