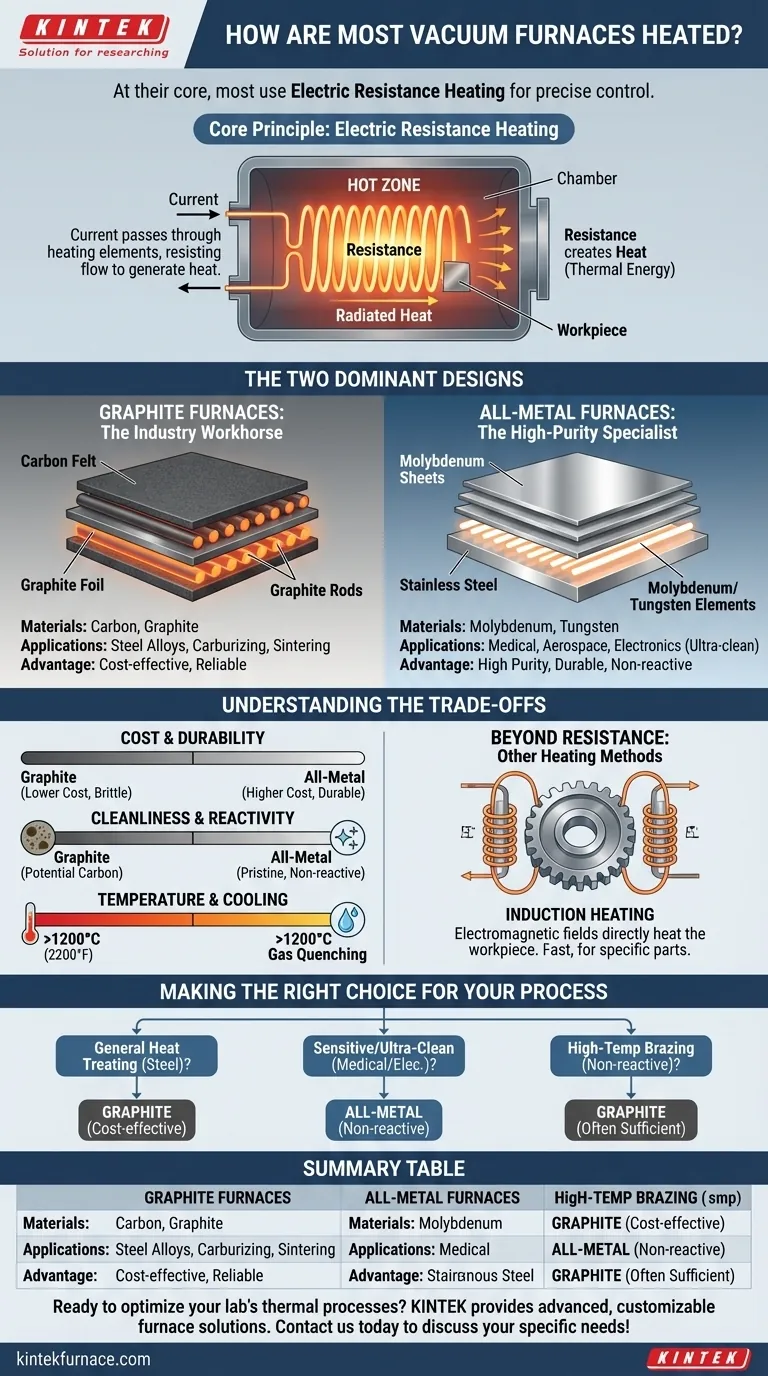
At their core, most vacuum furnaces are heated using electric resistance. This process involves passing a high electrical current through specialized heating elements, which resist the flow of electricity and convert that electrical energy into heat within the furnace's insulated chamber. The specific material used for these elements—typically graphite, ceramic, or a refractory metal—is the defining factor in the furnace's performance and application.
The choice of heating technology in a vacuum furnace is not arbitrary; it is a critical engineering decision. The selection between a graphite-based or an all-metal hot zone directly dictates the furnace's suitability for a given industrial process, balancing cleanliness, temperature capability, and cost.
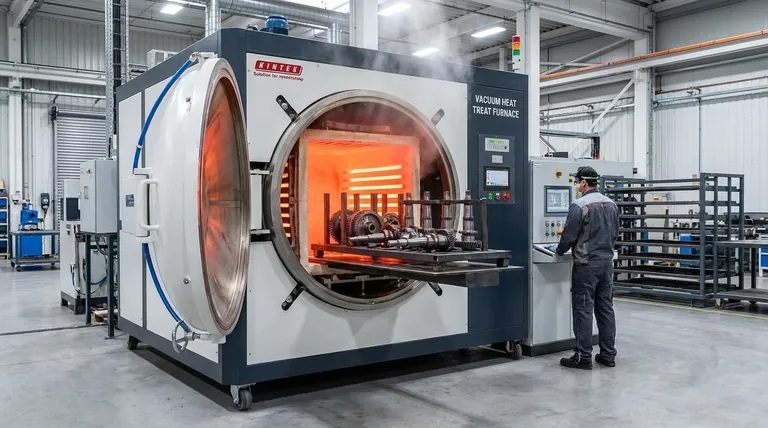

The Core Principle: Electric Resistance Heating
The vast majority of vacuum furnaces operate on the simple, reliable principle of resistance heating. This method provides excellent temperature uniformity and control, which is critical for sensitive thermal processes.
How It Works
Electric resistance heating functions much like the glowing element in a toaster. A controlled electric current is sent through heating elements made of materials with high electrical resistance. This resistance causes the elements to heat up significantly, radiating thermal energy throughout the furnace chamber.
The "Hot Zone" Concept
These heating elements are arranged within a highly insulated chamber known as the hot zone. The hot zone's purpose is to contain the heat, protect the outer furnace vessel, and ensure the energy is focused on the workpiece. The construction of this zone is the primary differentiator between furnace types.
The Two Dominant Designs: Graphite vs. All-Metal
While the principle is the same, the materials used to build the hot zone create two distinct categories of furnaces, each with specific strengths.
Graphite Furnaces: The Industry Workhorse
Graphite-based hot zones are the most common configuration. They are constructed with layers of carbon felt and graphite foil for insulation, with robust graphite bars or rods serving as the heating elements.
This design is highly effective and relatively inexpensive, making it the standard for a wide range of applications like the heat treatment of steel alloys, vacuum carburizing (case hardening), and sintering processes.
All-Metal Furnaces: The High-Purity Specialist
All-metal hot zones are designed for applications demanding exceptional cleanliness. The insulation consists of layered sheets of molybdenum and stainless steel, and the heating elements are also made from refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten.
This construction avoids the carbon particles that can be shed by graphite, making it essential for ultra-clean processing of materials for the medical, aerospace, and electronics industries where contamination is not an option.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a graphite and an all-metal design involves a clear set of engineering trade-offs. Your process requirements will determine which is the appropriate choice.
Cost and Durability
Graphite is significantly more cost-effective to manufacture and replace, making it the default economic choice. However, it can be brittle and susceptible to damage. All-metal hot zones are more expensive but offer greater durability and a longer operational lifespan if used correctly.
Cleanliness and Reactivity
This is the most critical distinction. Graphite furnaces are not suitable for processes where carbon contamination is a concern. All-metal furnaces provide a pristine, non-reactive environment, which is mandatory for processing reactive materials like titanium or high-purity medical implants.
Temperature and Cooling
Both designs can reach very high temperatures, often well above 1200°C (2200°F). After the heating cycle, a process called gas quenching is used for rapid cooling. An inert gas like Argon is circulated through the hot zone and a heat exchanger to bring the parts down to a safe handling temperature.
Beyond Resistance: Other Heating Methods
While less common, other specialized heating methods exist for specific use cases.
Induction Heating
Induction heating uses electromagnetic fields to directly generate heat within the metal workpiece itself, rather than heating the entire chamber. This can be extremely fast and efficient but is typically limited to specific part geometries and materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The optimal heating system is dictated entirely by the demands of your application. Understanding your primary goal is the first step toward selecting the right furnace technology.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating of steel alloys: A graphite furnace provides the most cost-effective and reliable performance for standard industrial applications.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive medical or electronic components: An all-metal furnace is the only choice to guarantee the necessary ultra-clean, non-reactive environment.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature brazing or sintering non-reactive materials: A graphite furnace is often sufficient and more economical, provided minor carbon transfer is acceptable.
Ultimately, understanding the function and trade-offs of the furnace's hot zone empowers you to match the right technology to your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Key Materials | Common Applications | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Resistance (Graphite) | Graphite elements, carbon felt insulation | Heat treatment of steel alloys, vacuum carburizing, sintering | Cost-effective, reliable, good for general use |
| Electric Resistance (All-Metal) | Molybdenum/tungsten elements, metal insulation | Medical, aerospace, electronics (ultra-clean processes) | High purity, durable, non-reactive environment |
| Induction Heating | Electromagnetic fields (direct workpiece heating) | Specific geometries, fast heating | Rapid, efficient for certain materials |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processes? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need cost-effective graphite furnaces for general heat treating or ultra-clean all-metal systems for sensitive applications, we deliver tailored solutions to enhance efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















