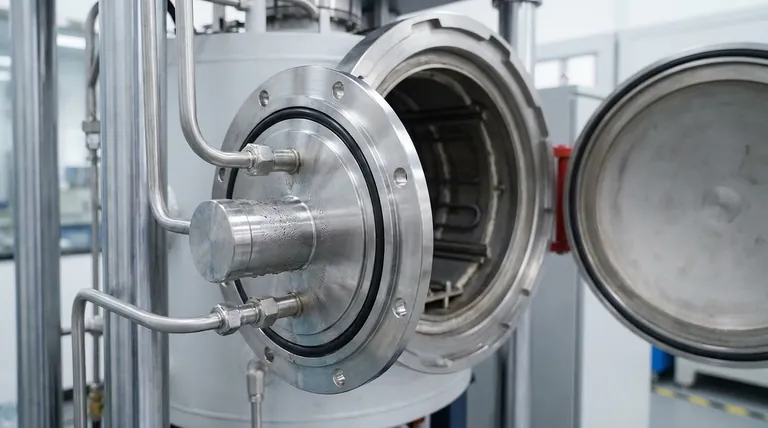
In short, active connection parts in a vacuum furnace are sealed using O-shaped rubber rings. To protect these rings from the furnace's extreme heat and maintain the integrity of the seal, the connections are actively cooled with water.
The core challenge of sealing a vacuum furnace is protecting the seal from the very heat the furnace is designed to create. The standard solution combines a simple, effective component—the rubber O-ring—with a vital support system in the form of water cooling, which keeps the seal within its safe operating temperature.
The Mechanics of an Active Vacuum Seal
To understand how a vacuum furnace maintains its integrity, we must look at the two key components responsible for sealing parts that need to move or be accessed.
The Role of the O-Shaped Rubber Ring
An O-ring is a simple, donut-shaped gasket, typically made of an elastomer like rubber. When placed in a groove between two connecting parts, it is compressed.
This compression deforms the O-ring, causing it to fill the microscopic imperfections on the metal surfaces. This creates an airtight (or vacuum-tight) barrier, preventing atmosphere from leaking into the furnace chamber.
O-rings are ideal for active connections because their flexibility can accommodate slight movements or repeated opening and closing without losing the seal.
The Necessity of Water Cooling
Vacuum furnaces operate at extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C (1832°F). Elastomer O-rings, however, degrade rapidly at temperatures far below this.
Without protection, the heat would cause the rubber to become brittle, crack, or melt, leading to a catastrophic seal failure and loss of vacuum.
To prevent this, the metal flanges that house the O-ring have internal channels through which cool water is constantly circulated. This water cooling system acts as a heat sink, drawing thermal energy away from the connection and keeping the O-ring at a low, stable temperature.
Why "Active" Connections Are Different
Not all seals in a furnace are the same. The distinction between active and static connections dictates the sealing strategy.
Defining an Active Connection
An active connection refers to any part of the furnace that is designed to be opened, closed, or moved during operation or between cycles. Common examples include:
- The main chamber door
- Ports for inserting or moving sensor probes
- Rotating feedthroughs for internal manipulators
These contrast with static connections, such as welded seams on the furnace body, which are permanent and not designed for access.
The Challenge of Dynamic Sealing
Movement creates a significant challenge for maintaining a perfect seal. An active connection requires a seal that is both robust and forgiving.
The combination of a flexible O-ring and a rigid, water-cooled flange provides the perfect solution. The O-ring maintains the seal during slight shifts, while the cooled flange provides a stable, temperature-controlled foundation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Points
While effective, this sealing method is dependent on the proper function of all its parts. Understanding its limitations is key to reliable operation.
Temperature Sensitivity of the Seal
The entire system's integrity hinges on the elastomer O-ring. This makes the water cooling circuit a critical component. Any interruption in water flow—from a pump failure, blockage, or leak—will quickly lead to the O-ring overheating and the vacuum seal failing.
Material Wear and Contamination
O-rings are consumable components. With each compression cycle, they experience wear and can eventually take a "compression set," where they no longer spring back to their original shape, weakening the seal.
Furthermore, the O-ring material itself can be a source of contamination in high-vacuum environments through a process called outgassing. Using a high-quality, vacuum-rated material like Viton™ is crucial for applications sensitive to impurities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Proper maintenance and awareness of these connections are critical for successful vacuum furnace operation. Your focus will determine your maintenance priorities.
- If your primary focus is operational reliability: Regularly inspect O-rings for signs of wear, cracking, or flattening, and verify that the cooling water is flowing at the correct rate and temperature.
- If your primary focus is achieving high vacuum levels: Ensure all flange surfaces are impeccably clean before assembly, as even a small particle can create a leak path, and use only certified low-outgassing O-rings.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a vacuum leak: Active connections are the most common leak points. Start your diagnosis by checking the O-ring integrity and confirming the proper function of the cooling system around the suspected seal.
By understanding the interplay between the simple O-ring and its critical cooling system, you can ensure the reliability and performance of your vacuum furnace.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| O-Ring | Creates airtight seal via compression | Accommodates movement and repeated use |
| Water Cooling | Cools metal flanges to protect O-ring | Prevents heat degradation and seal failure |
Need reliable vacuum furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?



















