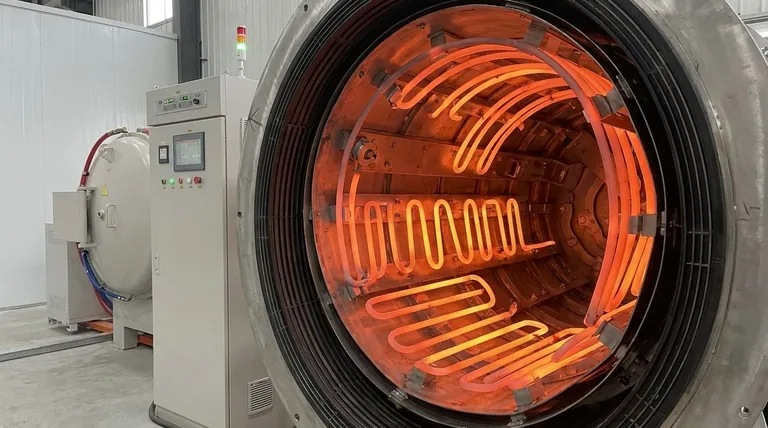
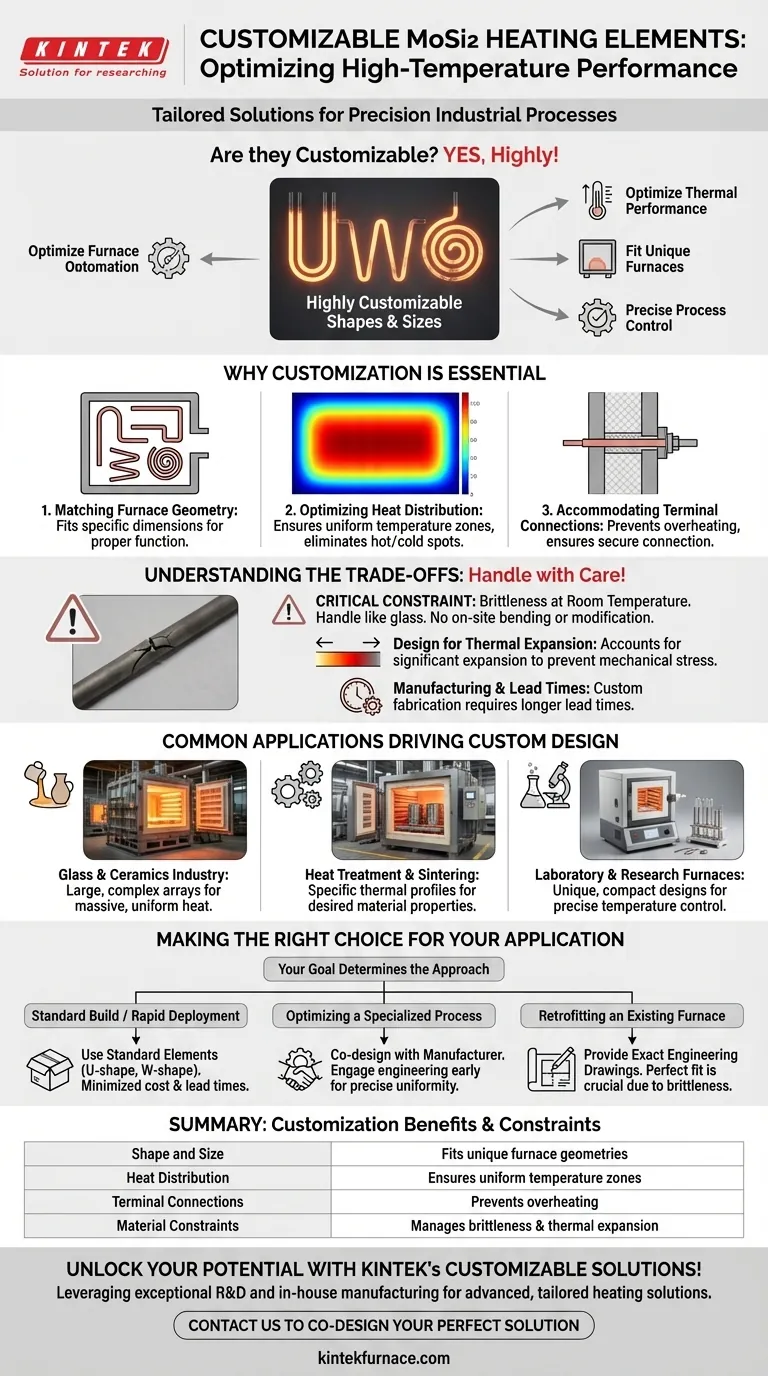
Yes, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements are highly customizable. Manufacturers can produce them in a wide variety of shapes and sizes to meet the precise requirements of specific high-temperature furnaces and industrial processes. This flexibility allows for optimized thermal performance in demanding applications.
While MoSi2 elements offer exceptional design flexibility for high-temperature applications, their inherent brittleness at room temperature is a critical design constraint that must be managed during specification, handling, and installation.

Why Customization is Essential
The need for custom MoSi2 elements stems from the unique demands of high-temperature industrial equipment. A one-size-fits-all approach is rarely sufficient for achieving optimal performance and efficiency.
Matching Furnace Geometry
Furnace chambers are not standardized. Custom elements, such as U-shaped, W-shaped, or multi-shank configurations, are fabricated to fit the specific dimensions and layout of a furnace, ensuring proper placement and function.
Optimizing Heat Distribution
Processes like ceramic sintering or semiconductor manufacturing demand extremely uniform temperature zones. Customizing the shape and size of the heating elements allows engineers to control heat distribution precisely, eliminating hot spots and cold spots within the furnace chamber.
Accommodating Terminal Connections
MoSi2 elements consist of a hot zone and colder terminal ends. These terminals must pass through the furnace insulation. Customization ensures the terminal length and diameter are correct for the furnace wall thickness, preventing overheating and ensuring a secure connection.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, the material properties of molybdenum disilicide introduce important constraints that you must factor into your design and handling procedures.
The Brittleness Factor
MoSi2 is a cermet (ceramic-metallic composite). At room temperature, it is extremely brittle and fragile, similar to glass. Elements cannot be bent or modified on-site; they are manufactured into their final shape and must be handled with extreme care to prevent fracture during transport and installation.
Design for Thermal Expansion
The material expands significantly as it heats to its operating temperature. A custom design must account for this thermal expansion. Without proper clearance, the element will be subjected to mechanical stress, leading to premature failure.
Manufacturing and Lead Times
Custom fabrication is not an instantaneous process. Creating specialized molds and manufacturing non-standard shapes requires longer lead times compared to purchasing stock elements. This must be factored into project timelines.
Common Applications Driving Custom Design
The need for custom shapes is driven by the specialized equipment used across various industries.
Glass and Ceramics Industry
Large melting tanks and complex kilns often require large, intricate element arrays to deliver massive amounts of uniform heat for melting, forming, and firing processes.
Heat Treatment and Sintering
Furnaces for metal heat treatment or powder metallurgy sintering rely on custom elements to create specific thermal profiles necessary to achieve desired material properties.
Laboratory and Research Furnaces
Specialized laboratory equipment and research furnaces often have unique, compact chamber designs. Custom-made elements are essential to fit these non-standard geometries and provide precise temperature control for experiments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine the best approach to specifying MoSi2 elements.
- If your primary focus is a standard furnace build or rapid deployment: Consider using standard, off-the-shelf U-shaped or W-shaped elements to minimize cost and lead times.
- If your primary focus is optimizing a specialized process: Engage with the manufacturer's engineering team early to co-design a custom element that ensures precise thermal uniformity and fits your unique chamber.
- If your primary focus is retrofitting an existing furnace: Provide exact engineering drawings of the required element. Due to the material's brittleness, a custom replacement must be a perfect fit, leaving no room for on-site adjustment.
By understanding both the design flexibility and the physical constraints of MoSi2, you can confidently specify a heating solution that precisely matches your high-temperature requirements.
Summary Table:
| Customization Aspect | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Shape and Size | Fits unique furnace geometries for precise placement |
| Heat Distribution | Ensures uniform temperature zones, eliminating hot/cold spots |
| Terminal Connections | Prevents overheating with correct length and diameter |
| Material Constraints | Manages brittleness and thermal expansion for durability |
Unlock the full potential of your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's customizable MoSi2 heating elements! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced solutions tailored for diverse laboratories and industries. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring optimal thermal performance, efficiency, and reliability. Don't settle for one-size-fits-all; contact us today to discuss how we can co-design the perfect heating solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control



















