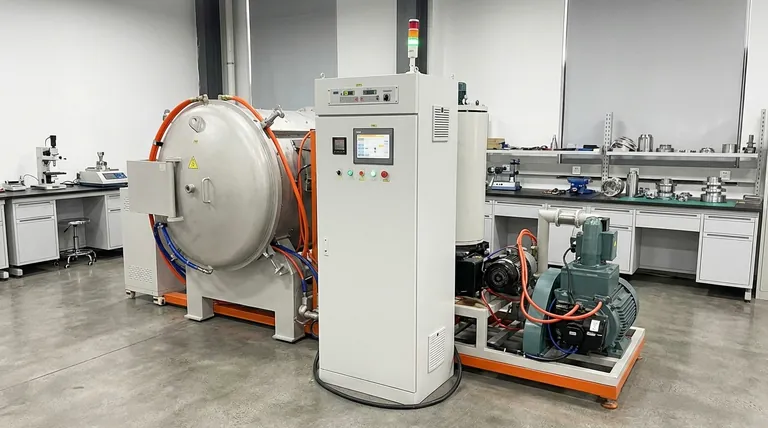
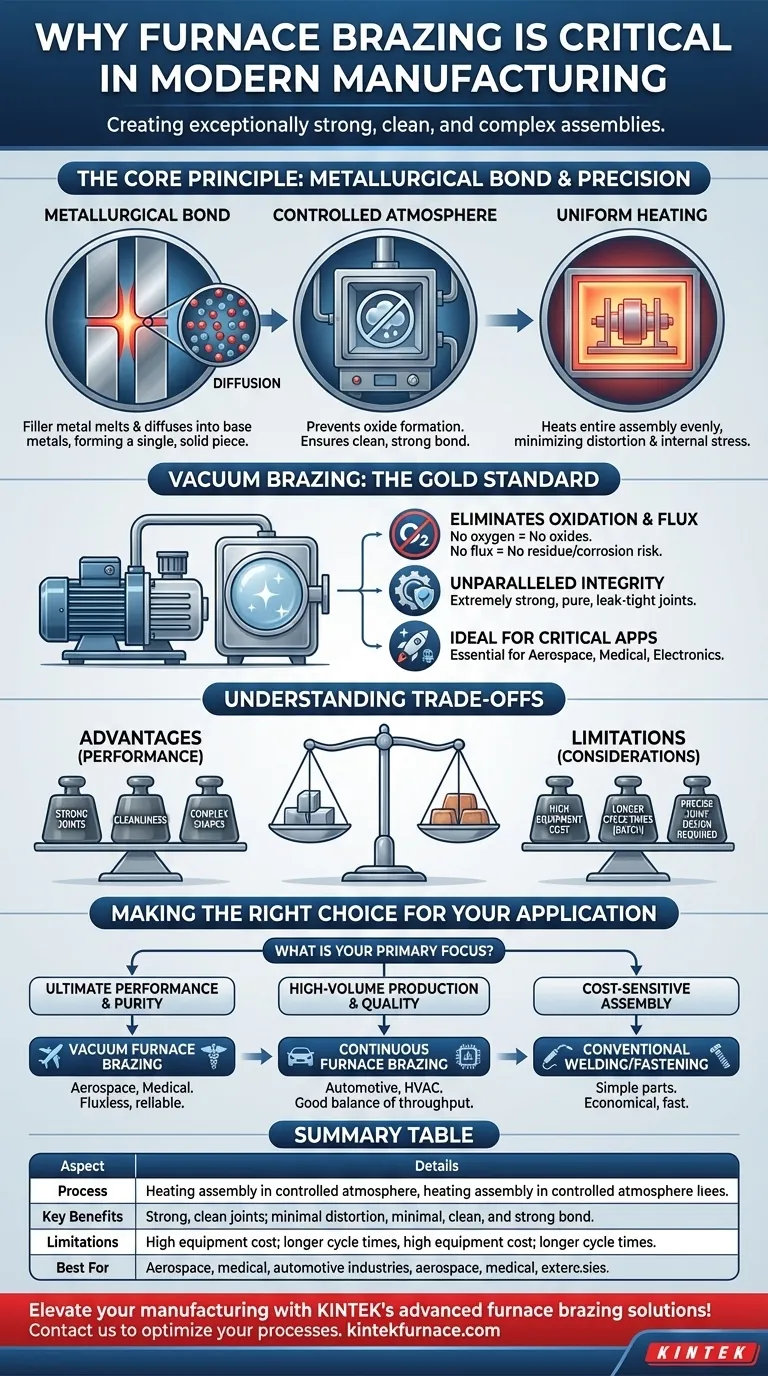
At its core, furnace brazing is considered a critical process because it enables the creation of exceptionally strong, clean, and complex assemblies that are often impossible to produce with other joining methods. By heating an entire assembly in a highly controlled atmosphere, it uses a filler metal to form a metallurgical bond between components, resulting in a single, integrated part with superior reliability and performance.
Furnace brazing solves a fundamental manufacturing challenge: how to join multiple, often intricate, metal parts without compromising their individual integrity. The process creates joints that are not merely stuck together but are metallurgically fused, delivering leak-tight, high-strength results essential for critical applications.

The Core Principle of Furnace Brazing
Furnace brazing is far more than simply melting metal between two parts. The process is governed by precise thermal and chemical principles that ensure a superior outcome.
The Metallurgical Bond: More Than Just Glue
The process relies on heating parts to a temperature where a filler metal, but not the base metals, melts. This molten filler is drawn into the tight gap between the components through capillary action.
As it cools, the filler metal doesn't just solidify; it diffuses into the base metals, creating a metallurgical bond. This new alloy at the joint interface ensures the final assembly behaves like a single, solid piece.
The Controlled Atmosphere: The Key to Purity
All furnace brazing occurs in a tightly controlled environment, typically a gaseous atmosphere or a near-perfect vacuum.
This atmosphere prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces during heating. Clean, oxide-free surfaces are essential for the filler metal to flow properly and form a strong bond.
Uniform Heating for Minimal Distortion
Unlike welding, which applies intense, localized heat, furnace brazing heats the entire assembly uniformly.
This gradual and even heating and cooling cycle minimizes the internal stresses that can cause distortion or cracking, making it ideal for delicate or dimensionally critical parts.
Why Vacuum Brazing Is the Gold Standard
While various atmospheres can be used, performing the process in a vacuum furnace offers distinct advantages that make it the premier choice for the most demanding applications.
Eliminating Oxidation and Flux
A vacuum environment removes reactive gases like oxygen. This physically prevents oxidation from occurring, achieving the highest possible level of cleanliness.
Because no oxides can form, there is no need for a chemical flux to clean the surfaces. This eliminates the risk of flux entrapment, which can cause corrosion and joint failure over time.
Unparalleled Joint Integrity and Cleanliness
The absence of flux means there is no residue to clean off after brazing. This is non-negotiable for components used in medical, aerospace, or electronic applications where any contamination could be catastrophic.
The result is an extremely strong, pure, and leak-tight joint with excellent mechanical and electrical properties, straight from the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, furnace brazing is not the universal solution for every joining task. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Furnaces, particularly high-vacuum systems, represent a significant capital investment. The cost and complexity of the equipment can be a barrier for smaller operations.
Longer Cycle Times
Furnace brazing is a batch process. The time required to load the furnace, pull a vacuum, run the heating and cooling cycle, and unload can be substantial compared to instantaneous processes like welding.
Requirement for Precise Joint Design
The success of brazing depends entirely on capillary action. This requires parts to be designed with a very specific, consistent gap between them—typically a few thousandths of an inch—which adds a layer of design and machining precision.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right joining process depends entirely on your project's specific priorities of performance, volume, and cost.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance and purity (Aerospace, Medical): Vacuum furnace brazing is the definitive choice for its clean, fluxless, and exceptionally reliable joints.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with strong joints (Automotive, HVAC): Continuous furnace brazing in a controlled gas atmosphere provides an excellent balance of throughput and quality.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive assembly of simple parts: Conventional welding or mechanical fastening will likely be a more economical and faster solution.
Ultimately, choosing furnace brazing is a decision to prioritize the absolute integrity of the final component over all other considerations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating assembly in controlled atmosphere with filler metal for metallurgical bond |
| Key Benefits | Strong, clean joints; minimal distortion; suitable for complex parts |
| Limitations | High equipment cost; longer cycle times; precise joint design required |
| Best For | Aerospace, medical, automotive industries where reliability is critical |
Elevate your manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced furnace brazing solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering superior joint integrity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your brazing processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control



















