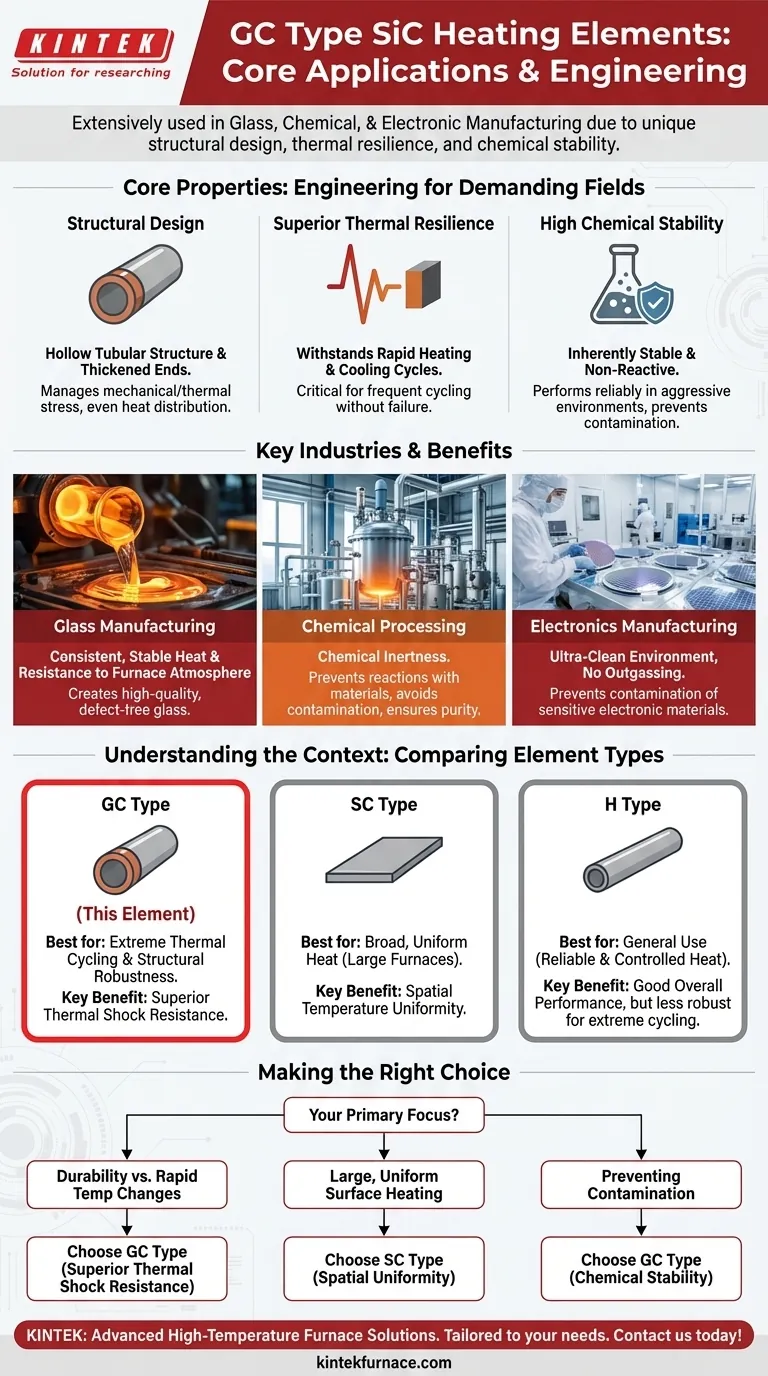
At their core, GC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are most extensively used in the manufacturing of glass, chemicals, and electronic materials. Their selection for these demanding fields is not arbitrary; it is a direct result of their unique structural design, which provides exceptional thermal resilience and chemical stability under extreme industrial conditions.
The decision to use a GC Type element goes beyond the industry name. It is driven by process requirements that demand robust performance, specifically the ability to withstand rapid temperature changes and resist chemical attack without failure.
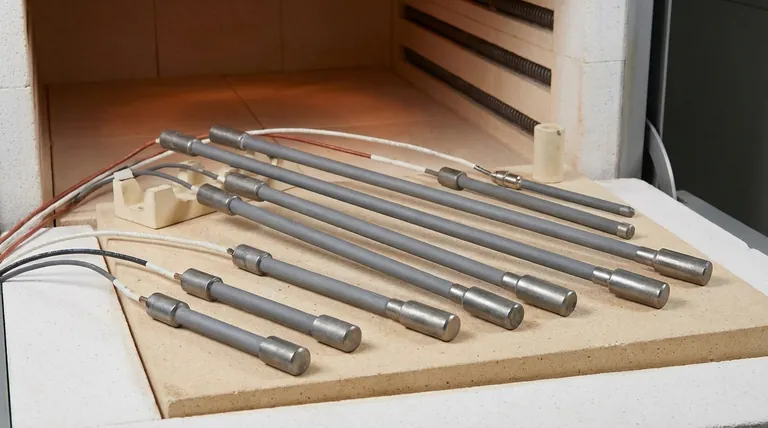

The Core Properties of GC Type Elements
To understand why these elements are chosen for such critical applications, we must first examine their fundamental engineering. Their value is derived from a specific combination of structural design and material properties.
Structural Design for Durability
GC Type elements feature a distinctive hollow tubular structure. This is often complemented by thickened ends.
This design is not for aesthetics; it is engineered to manage mechanical and thermal stress effectively. The tubular shape allows for even heat distribution, while the thickened ends provide robust connection points and added strength where it is most needed.
Superior Thermal Resilience
A key advantage of the GC Type is its ability to handle rapid heating and cooling cycles without deformation or cracking.
This property, often called thermal shock resistance, is critical in processes where furnaces are frequently cycled. Elements lacking this resilience would fail prematurely, leading to costly downtime and maintenance.
High Chemical Stability
Silicon carbide is an inherently stable and non-reactive material. The GC Type leverages this property to perform reliably in chemically aggressive environments.
This makes it an ideal choice for heating processes involving corrosive vapors or direct contact with materials that would degrade lesser elements, ensuring process purity and element longevity.
Why These Properties Matter in Key Industries
The engineering of the GC Type directly solves the core heating challenges within its primary industries. The connection between property and application is clear.
In Glass Manufacturing
Glass production involves extremely high temperatures and a chemically active environment. The GC Type's ability to provide consistent, stable heat while resisting the furnace atmosphere is paramount for creating high-quality, defect-free glass.
In Chemical Processing
Many chemical synthesis and refinement processes require precise temperature control in the presence of corrosive agents. The GC Type's chemical inertness prevents it from reacting with the process materials, which avoids contamination and ensures the element itself is not consumed.
In Electronics Manufacturing
Producing semiconductors and other electronic components demands an ultra-clean heating environment and precise temperature profiles. The stability of GC Type elements ensures there is no outgassing or material shedding that could contaminate sensitive electronic materials during production.
Understanding the Context: Other Element Types
To fully appreciate the GC Type's role, it is useful to compare it with other SiC element designs. The choice of element is always a matter of matching the right tool to the specific job.
The SC Type for Broad, Uniform Heat
The SC Type is often used for bottom or side heating in large furnaces, such as those in metal treatment or ceramics. Its design prioritizes spatial temperature uniformity across a very large surface area, which is a different engineering goal than the thermal shock resistance of the GC Type.
The H Type for General Use
The H Type is also used in the glass, chemical, and electronics sectors. While it provides reliable and controlled heat, the GC Type's specific tubular design gives it a distinct advantage in applications where extreme thermal cycling and structural robustness are the most critical factors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element requires a clear understanding of your primary operational challenge. Your choice should be based on the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is durability against rapid temperature changes: The GC Type's hollow tubular design offers superior thermal shock resistance, making it the most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is heating a large, uniform surface with minimal temperature variance: An SC Type element may be better suited to your furnace's design and goals.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination in a chemically aggressive environment: The GC Type's inherent chemical stability provides the process purity and element longevity you need.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element requires matching its core engineering strengths to your specific operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Application | GC Type Element Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Manufacturing | High-temperature heating in furnaces | Exceptional thermal resilience, uniform heat distribution, chemical stability |
| Chemical Processing | Corrosive environment heating | High chemical inertness, prevents contamination, long-lasting performance |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Precise heating for semiconductors | No outgassing, stable temperature control, process purity |
Ready to enhance your industrial heating processes with reliable, high-performance solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in glass, chemicals, or electronics, our GC Type Silicon Carbide Heating Elements can deliver the durability and precision your operations demand. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor our solutions to your specific needs and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















