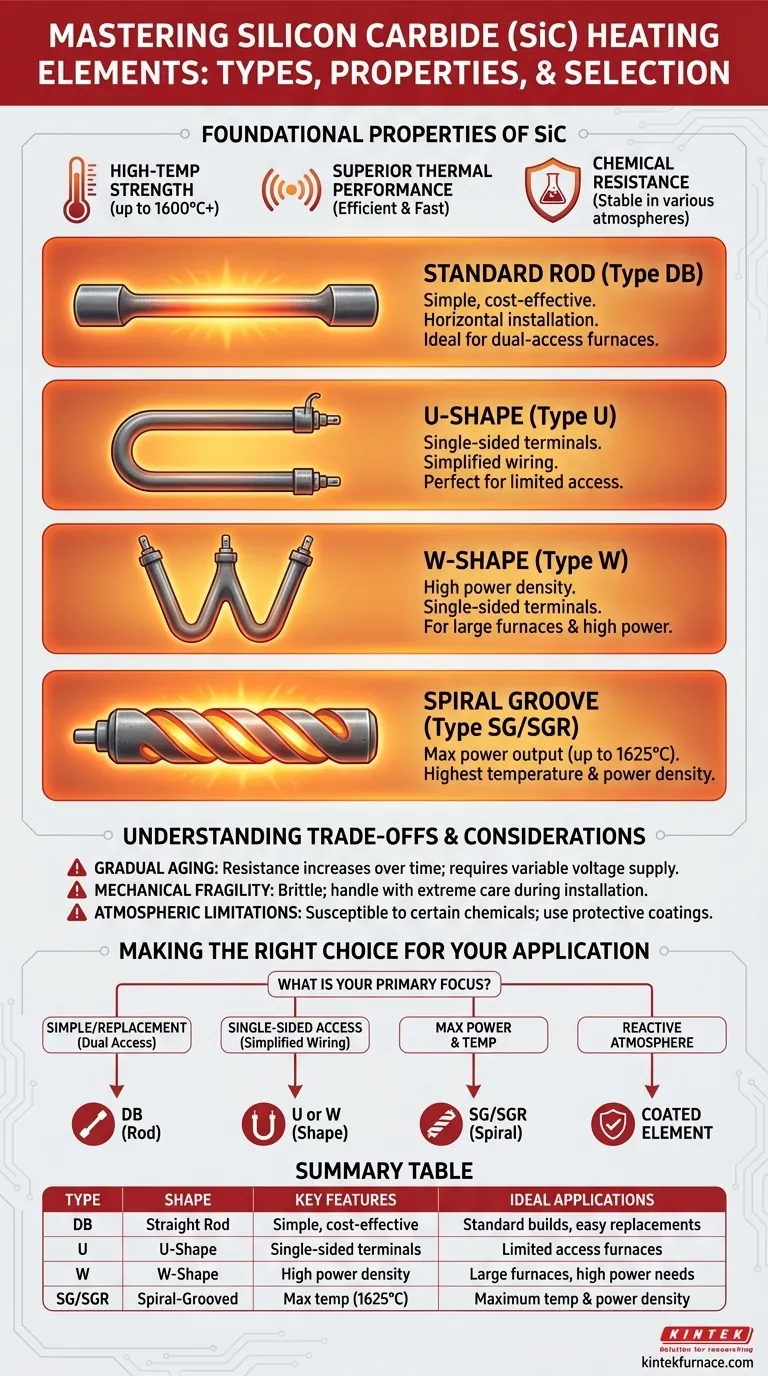
In short, the most common types of silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are defined by their shape, including straight rods (Type DB), U-shapes (Type U), W-shapes (Type W), and spiral-grooved rods (Type SG/SGR). These elements are prized for their ability to operate at very high temperatures, up to 1600°C (2912°F) or even higher for specialized types, while offering excellent thermal stability and strength.
The specific shape of a silicon carbide element is not an arbitrary detail; it is the primary factor that dictates furnace design, wiring configuration, and heat distribution. Understanding the practical implications of each shape is the key to selecting the correct element for your application.

The Foundational Properties of SiC Elements
Before examining the different shapes, it's essential to understand why silicon carbide is the material of choice for demanding high-temperature applications. Its properties dictate its performance and limitations.
High-Temperature Strength
Silicon carbide is a ceramic material that maintains its high strength at extreme temperatures. Unlike many metals that soften or deform, SiC remains rigid and stable.
This structural integrity allows it to function as both the heat source and its own support within a furnace.
Superior Thermal Performance
SiC elements possess excellent thermal conductivity and a high emissivity (radiancy) of around 0.85. This means they transfer heat very efficiently, primarily through thermal radiation.
Their ability to withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles without damage makes them reliable for industrial processes.
Chemical Resistance
SiC is inherently resistant to oxidation and performs particularly well in reducing atmospheres compared to other high-temperature elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2).
For applications involving specific chemicals or atmospheres, specialized protective coatings are also available to prevent corrosion and extend service life.
A Practical Guide to SiC Element Shapes
The "type" of a SiC element almost always refers to its physical geometry. Each shape is designed to solve a specific installation or heating challenge. The key dimensions for any type include the hot zone length (L1), the terminal or cold end length (L2), the hot zone diameter (d), and the terminal diameter (D).
The Standard Rod (Type DB)
This is the most common and fundamental design, often called a dumbbell (DB) or rod element. It consists of a central high-resistance hot zone and two lower-resistance cold ends that serve as terminals.
These elements are simple, cost-effective, and typically installed horizontally, passing straight through the furnace chamber. They are ideal for straightforward designs where access to both sides of the furnace is available for electrical connections.
The U-Shape (Type U)
A U-shaped element is a single piece of SiC bent into a "U." Its primary advantage is that both terminals are on the same side.
This design drastically simplifies wiring and is perfect for furnaces where access is limited to one side. They can be mounted vertically, hanging from the roof, or horizontally from a side wall.
The W-Shape (Type W)
The W-shape is a three-leg element, essentially an extension of the U-shape. It provides a greater heating surface area and higher power output from a single element with terminals located on one side.
This is often used in large furnaces or applications requiring high power density, where installing many individual rod elements would be impractical.
The Spiral Groove (Type SG & SGR)
Spiral groove elements feature a helical cut along the hot zone. The SG type has a single spiral, while the SGR is a double spiral, with the two spirals connected at one end.
This spiral design increases the electrical resistance and surface area in the hot zone, allowing for a much higher power output (watt loading) from a single rod. The SGR type is particularly effective, offering the highest temperatures, with some reaching up to 1625°C (2957°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SiC elements have specific characteristics that must be managed for optimal performance and longevity.
Gradual Aging and Resistance Increase
Over its operational life, a SiC element will slowly oxidize. This process causes its electrical resistance to gradually increase. This phenomenon is known as aging.
Power supply systems must be able to compensate for this change, typically by using a variable voltage transformer or a phase-angle fired SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) that can increase the voltage over time to maintain constant power output.
Mechanical Fragility
Like most ceramics, SiC is hard but brittle. The elements are susceptible to damage from mechanical shock or impact, especially when they are cold.
Careful handling during installation is critical. Furthermore, they should be protected from any objects that might fall on them or from thermal expansion stresses within the furnace structure.
Atmospheric Limitations
While generally robust, SiC elements can be attacked by certain atmospheres, particularly water vapor and alkali chemicals at high temperatures.
In such environments, using elements with a specialized protective glaze or coating is essential to prevent rapid degradation and ensure a reasonable service life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct element requires matching its shape and properties to your furnace's design and your process goals.
- If your primary focus is a simple new build or a like-for-like replacement: The standard rod (Type DB) is the most direct and cost-effective solution, assuming you have access to both sides of the furnace.
- If your primary focus is single-sided access or simplified wiring: The U-shape or W-shape elements are the ideal choice, allowing all connections to be made from the top or one side of the furnace.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum power density or the highest possible temperatures: A spiral groove element (Type SG or SGR) will deliver the most heat from a single element footprint.
- If your primary focus is operating in a reactive chemical atmosphere: You must specify an element with a protective coating designed to resist the specific contaminants in your process.
By matching the element's physical form to your functional requirements, you ensure an efficient, reliable, and long-lasting heating system.
Summary Table:
| Type | Shape | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| DB | Straight Rod | Simple, cost-effective, horizontal installation | Standard builds, easy replacements |
| U | U-Shape | Single-sided terminals, simplified wiring | Limited access furnaces |
| W | W-Shape | High power density, single-sided terminals | Large furnaces, high power needs |
| SG/SGR | Spiral-Grooved Rod | High power output, up to 1625°C | Maximum temperature and power density |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced silicon carbide heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored heating elements can optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















