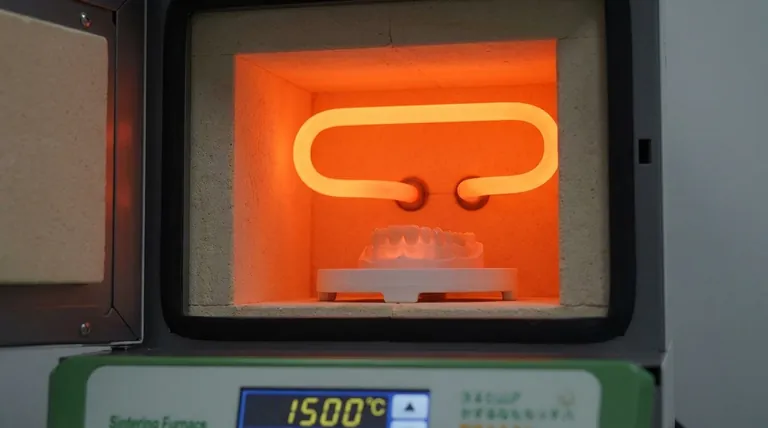
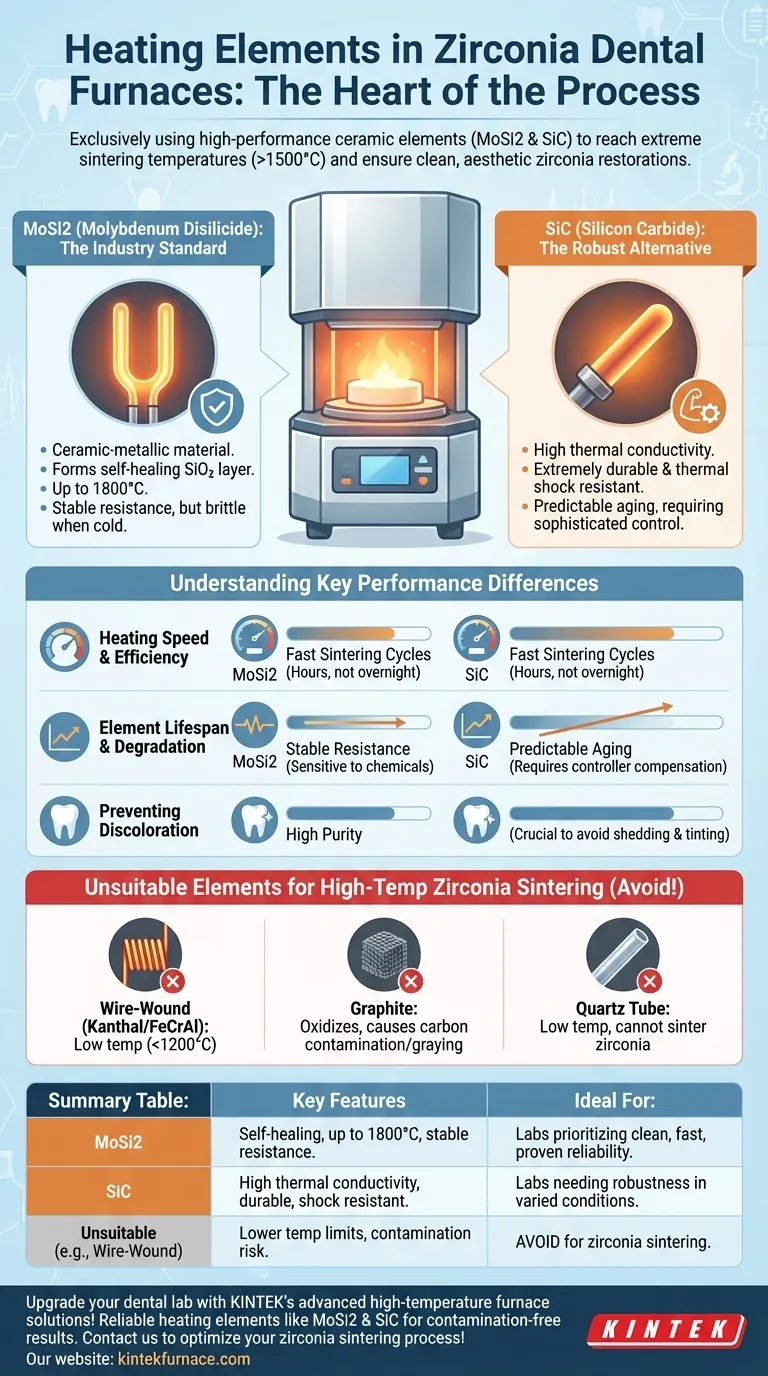
In essence, zirconia dental furnaces exclusively use high-performance ceramic heating elements, with the two dominant types being Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC). These materials are specifically chosen for their unique ability to rapidly reach and sustain the extreme sintering temperatures required for zirconia—often exceeding 1500°C (2732°F)—while minimizing the risk of contamination that could discolor the final restorations.
The choice of heating element is not a minor technical detail; it is the heart of the furnace. This component directly dictates the furnace's lifespan, the speed of its cycles, and most importantly, its ability to produce clean, esthetically pleasing zirconia restorations without discoloration.

The High-Temperature Champions: MoSi2 and SiC
Sintering zirconia is a thermally demanding process. The furnace chamber must reach incredibly high temperatures uniformly and maintain them with precision. Only a few materials can perform this task reliably over thousands of cycles.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): The Industry Standard
MoSi2 elements are the most common choice in modern, high-end zirconia furnaces. They are a cermet material, combining ceramic and metallic properties.
Their key advantage is the formation of a protective quartz-silica (SiO2) layer on their surface at high temperatures. This layer is "self-healing," reforming to cover any new cracks or exposure, which grants the elements a very long potential lifespan in a clean environment.
MoSi2 elements can operate at temperatures up to 1800°C, providing a comfortable margin for all types of zirconia sintering protocols.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The Robust Alternative
SiC elements are another high-performance ceramic material used in many industrial and dental furnaces. They are known for their exceptional strength and high thermal conductivity.
These elements are extremely durable and offer excellent resistance to thermal shock, making them less susceptible to damage from rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Like MoSi2, SiC elements can easily handle the temperature requirements for zirconia. Their primary mode of aging involves a gradual increase in electrical resistance over time, which the furnace's power controller must be designed to manage.
Understanding the Key Performance Differences
While both materials achieve the same primary goal, their operational characteristics create important distinctions for a dental lab.
Heating Speed and Efficiency
Both MoSi2 and SiC elements enable the fast sintering cycles that modern labs depend on. They can ramp up to temperature very quickly, allowing a full sintering cycle to be completed in a few hours rather than overnight.
Element Lifespan and Degradation
MoSi2 elements have a stable resistance throughout their life, but they are brittle at room temperature and can be sensitive to chemical contamination.
SiC elements are more mechanically robust but "age" predictably. This aging process requires a more sophisticated power controller to compensate for the changing resistance to ensure consistent power output.
The Critical Factor: Preventing Discoloration
The ultimate goal of sintering is a strong and esthetic restoration. The heating elements themselves can be a source of contamination that compromises aesthetics.
High-purity MoSi2 and SiC elements are manufactured specifically to prevent "shedding" or outgassing of microscopic particles at high temperatures. Cheaper, industrial-grade elements can release contaminants that cause a grayish or greenish tint in translucent zirconia, ruining the case.
Elements Not Suitable for High-Temp Zirconia Sintering
It is just as important to understand what doesn't work. Using a furnace with the wrong type of heating element for zirconia sintering will inevitably lead to failure.
Wire-Wound (Kanthal/FeCrAl) Elements
These metallic wire elements are common in porcelain furnaces designed for glazing or firing ceramics at lower temperatures. Their maximum service temperature is typically around 1200°C, far below what is needed to properly sinter a zirconia crown.
Graphite Elements
While graphite can achieve extremely high temperatures, it is completely unsuitable for zirconia furnaces used in dental labs. In the presence of oxygen (as in a standard, non-vacuum furnace), graphite will rapidly oxidize and release carbon particles, causing severe gray discoloration of the zirconia.
Quartz Tube Elements
Furnaces using quartz tubes wrapped with a heating coil are sometimes used for low-temperature staining and glazing. The quartz tube protects the restoration from direct contact with the heating wire, but these systems cannot produce the high temperatures necessary for the initial sintering process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Lab
Your choice of furnace—and its internal heating technology—should align directly with your lab's production goals for quality and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge performance and proven results: A furnace with high-purity Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements is the industry's gold standard for clean, fast, and reliable zirconia sintering.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and long-term robustness: A furnace equipped with high-quality Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements is an excellent choice, valued for its mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock.
- If you are evaluating any furnace: Always verify that the elements are specifically designed for dental zirconia to avoid the costly and frustrating problem of restoration discoloration.
Ultimately, understanding the heating element empowers you to evaluate a furnace based on its core ability to produce consistent and esthetic results for your clients.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Self-healing protective layer, up to 1800°C, stable resistance | Labs prioritizing clean, fast sintering and proven reliability |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High thermal conductivity, durable, resistant to thermal shock | Labs needing robustness and long-term performance in varied conditions |
| Unsuitable Elements (e.g., Wire-Wound, Graphite) | Lower temperature limits, risk of contamination and discoloration | Avoid for zirconia sintering to prevent restoration failure |
Upgrade your dental lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable heating elements like MoSi2 and SiC in our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise matching to your unique experimental needs, delivering fast cycles, contamination-free results, and enhanced productivity. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your zirconia sintering process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision
- What aspects of a dental restoration are directly impacted by the choice of a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Fit, Strength & Longevity
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- How often should dental furnaces be calibrated? Ensure Precision for Perfect Restorations



















