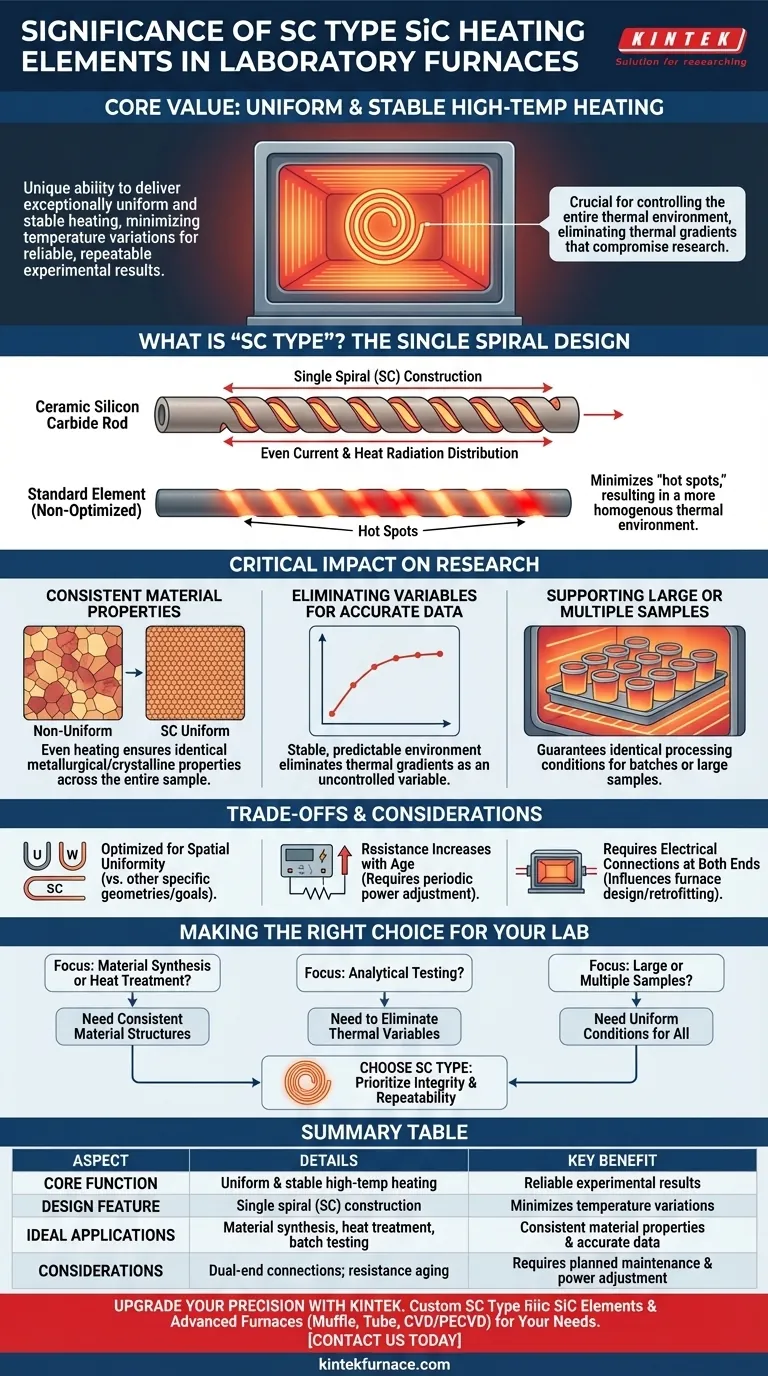
At its core, the significance of SC Type Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements in laboratory furnaces lies in their unique ability to deliver exceptionally uniform and stable high-temperature heating. This is a direct result of their "Single Spiral" (SC) design, which is engineered to minimize temperature variations across the furnace chamber, a critical requirement for producing reliable and repeatable experimental results.
The choice of a heating element is not merely about reaching a target temperature; it is about controlling the entire thermal environment. The SC Type's single spiral construction is specifically optimized to ensure every part of your sample is heated evenly, eliminating thermal gradients that can compromise research data.

What "SC Type" Actually Means: The Single Spiral Design
The designation "SC" directly refers to the physical construction of the heating element. Understanding this design is key to understanding its performance.
Defining the Single Spiral
The SC Type element consists of a ceramic silicon carbide rod with a single, continuous spiral cut along its heating section. This distinguishes it from other designs like simple straight rods or more complex double-spiral (SGR) types.
How the Spiral Creates Uniformity
This single spiral configuration is not an arbitrary choice. It is engineered to distribute electrical current and, consequently, heat radiation more evenly across the element's entire surface area.
This design effectively minimizes "hot spots" that can occur in less optimized elements, resulting in a more homogenous thermal environment within the furnace.
The Critical Impact of Thermal Uniformity in Research
In a laboratory setting, inconsistent heating is not a minor inconvenience—it is an uncontrolled variable that can invalidate an entire experiment. The uniformity provided by SC Type elements is therefore a foundational requirement for good science.
Ensuring Consistent Material Properties
For research involving heat treatment—such as annealing, tempering, or crystal growth—even small temperature differences can lead to vastly different outcomes.
If one side of a sample is hotter than the other, it will develop different metallurgical or crystalline properties. The SC Type's uniform heating ensures the entire sample experiences the exact same thermal conditions, leading to consistent and predictable results.
Eliminating Variables for Accurate Data
The scientific method demands the strict control of variables. A furnace's primary job is to create a predictable and stable environment.
Non-uniform heating introduces a significant variable that can obscure the true effects of your experiment. By providing a stable and homogenous heat source, SC elements help ensure that any observed changes are due to the intended variables, not a faulty thermal environment.
Supporting Large or Multiple Samples
Laboratory work often requires testing multiple samples simultaneously or using a single, large sample.
In these scenarios, the SC Type's ability to heat a large surface area evenly is paramount. It guarantees that every sample in a batch, regardless of its position, is subjected to identical processing conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While the SC Type's uniformity is a powerful advantage, a complete technical understanding requires acknowledging its operational context.
Design vs. Other Element Types
No single heating element is perfect for every application. The SC Type is optimized for spatial temperature uniformity.
Other designs, such as U-type or W-type elements, might be chosen for specific furnace geometries, ease of replacement from one side, or different power distribution requirements. The choice always depends on the primary goal of the application.
Power and Aging Characteristics
Like all silicon carbide elements, SC Types age over time. Their electrical resistance gradually increases with use, requiring periodic adjustments to the power supply to maintain a consistent temperature output.
This is a standard operational consideration for any high-temperature furnace and must be factored into the lab's maintenance procedures.
Physical and Electrical Requirements
The single spiral design necessitates electrical connections at both ends of the element. This influences the overall design of the furnace, including wiring and terminal placement.
This is often a straightforward consideration but must be accounted for during the initial furnace design or when retrofitting an existing system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Laboratory
Your choice of heating element should be directly informed by your primary research objectives.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or heat treatment: The SC Type's thermal uniformity is non-negotiable for achieving consistent and repeatable material structures.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing at high temperatures: Choose SC Type elements to eliminate thermal gradients as a variable, thereby ensuring the fundamental accuracy of your data.
- If you are running experiments with large or multiple samples: The SC Type's ability to heat large areas evenly makes it the superior choice for ensuring all samples experience identical conditions.
Ultimately, selecting an SC Type element is a decision to prioritize the integrity and repeatability of your experimental work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Key Benefit | Uniform and stable high-temperature heating for reliable experimental results |
| Design Feature | Single spiral (SC) construction minimizes temperature variations |
| Ideal Applications | Material synthesis, heat treatment, analytical testing with large or multiple samples |
| Considerations | Requires electrical connections at both ends; resistance increases with age |
Upgrade your laboratory's precision with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure SC Type SiC heating elements and other components perfectly meet your unique experimental needs for uniform heating and reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















