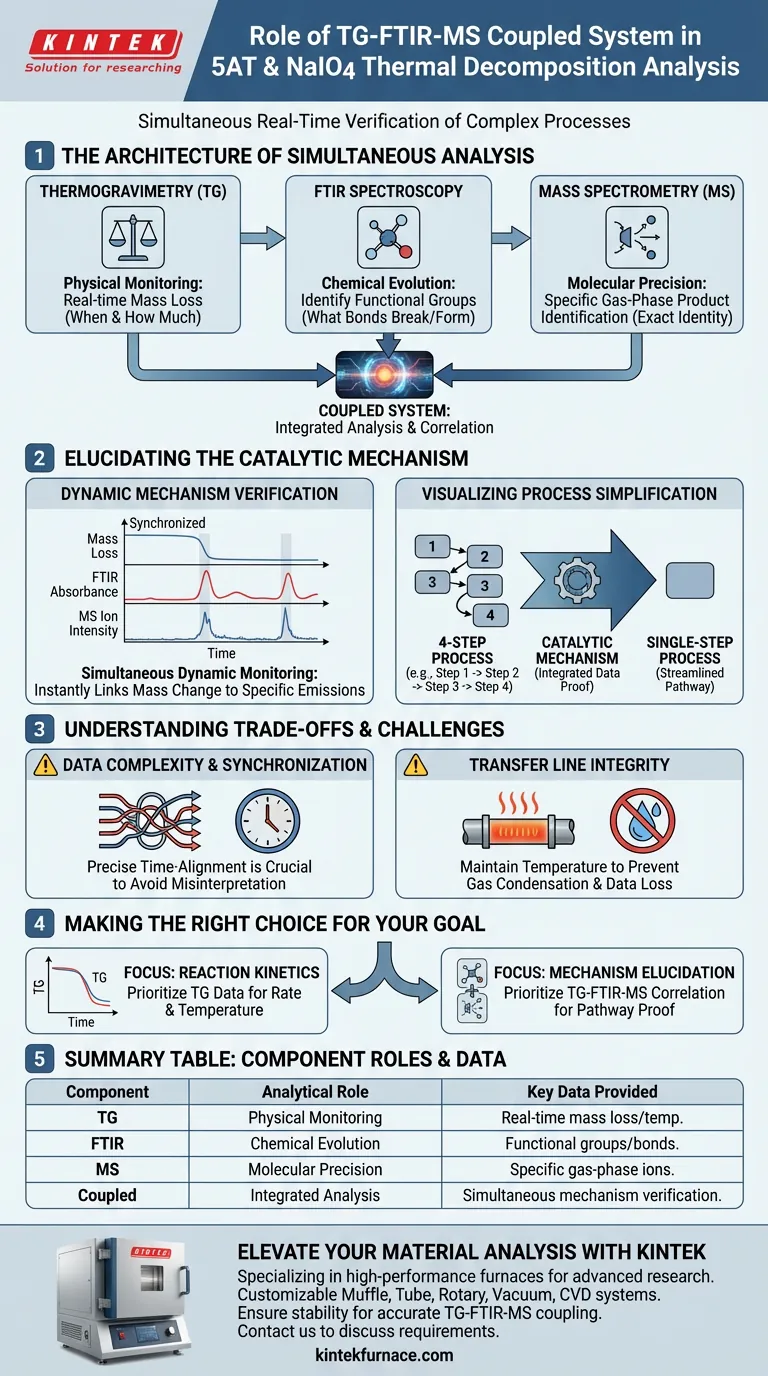
The role of a TG-FTIR-MS coupled system is to provide simultaneous, real-time verification of the thermal decomposition process for 5-aminotetrazole (5AT) and sodium periodate (NaIO4). This integrated setup correlates physical mass loss with chemical changes, specifically allowing researchers to identify how the decomposition mechanism simplifies from a complex four-step process into a single step.
By capturing mass changes, functional group evolution, and gas-phase products instantly and simultaneously, this system moves beyond simple observation. It provides the multi-dimensional data required to definitively explain the catalytic mechanisms driving the reaction.

The Architecture of Simultaneous Analysis
To fully understand the decomposition of energetic materials like 5AT, you cannot rely on a single data point. The coupled system functions as a cohesive unit where each component addresses a specific analytical blind spot.
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TG)
The TG component acts as the foundation of the experiment. Its primary function is to monitor the mass loss of the sample as the temperature changes.
By tracking weight changes, it identifies the exact temperature ranges where decomposition occurs. However, while TG tells you when a reaction happens, it cannot tell you what is reacting.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR bridges the gap between physical mass loss and chemical structure. As gases evolve from the decomposing sample, the FTIR analyzes them to identify changes in functional groups.
This allows you to see which chemical bonds are breaking or forming in real-time. It provides the chemical context necessary to interpret the mass loss steps recorded by the TG.
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
The MS adds the final layer of precision to the analysis. It captures gas-phase product ion fragments, offering a highly specific identification of the molecules being released.
While FTIR identifies functional groups, MS provides the molecular weight and fragmentation patterns needed to confirm the exact identity of the gaseous byproducts.
Elucidating the Catalytic Mechanism
The true value of this system is not just in the data it collects, but in the complex mechanisms it reveals.
Dynamic Mechanism Verification
For 5AT and NaIO4, the interaction is not static. The coupled system achieves simultaneous dynamic monitoring, meaning it captures the evolution of the reaction as it happens.
This synchronization ensures that a spike in mass loss can be immediately correlated with a specific gas emission, removing ambiguity from the analysis.
Visualizing Process Simplification
The most critical insight provided by this system is the observation of the decomposition pathway. In this specific context, the system provides the evidence that the decomposition of 5AT is simplified from four steps into a single step.
Without the integrated data from FTIR and MS verifying the products, it would be difficult to confirm that this simplification is due to a catalytic mechanism rather than a loss of data or experimental error.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a TG-FTIR-MS coupled system introduces specific challenges that you must manage to ensure data integrity.
Data Complexity and Synchronization
The volume of data generated by three simultaneous detectors is immense. You must ensure precise time-synchronization between the instruments to accurately correlate a TG event with an MS signal.
Misalignment by even a few seconds can lead to incorrect conclusions regarding which byproducts belong to which decomposition stage.
Transfer Line Integrity
The system relies on transfer lines to move evolved gases from the TG to the FTIR and MS. If these lines are not maintained at the correct temperature, gases can condense before analysis.
This "cold spotting" can result in the loss of critical data regarding high-boiling-point decomposition products.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a TG-FTIR-MS system, you should tailor your focus based on your specific analytical objectives.
- If your primary focus is defining reaction kinetics: Concentrate on the TG data to establish the rate and temperature of mass loss, using FTIR only to confirm the onset of reaction.
- If your primary focus is mechanism elucidation: Prioritize the correlation between the "single-step" TG profile and the MS/FTIR data to prove the catalytic simplification of the pathway.
The TG-FTIR-MS is the definitive tool for transforming a theoretical hypothesis about catalytic decomposition into a proven, observable fact.
Summary Table:
| Component | Analytical Role | Key Data Provided |
|---|---|---|
| Thermogravimetry (TG) | Physical Monitoring | Real-time mass loss and decomposition temperature |
| FTIR Spectroscopy | Chemical Evolution | Identification of functional groups and bond changes |
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Molecular Precision | Specific identification of gas-phase product ion fragments |
| Coupled System | Integrated Analysis | Simultaneous verification of catalytic mechanisms |
Elevate Your Material Analysis with KINTEK
Precise thermal decomposition studies require more than just standard equipment—they demand integrated, high-performance systems. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the foundation for advanced research.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for your unique analytical needs. Whether you are analyzing energetic materials or complex catalytic reactions, our solutions ensure the stability and temperature control necessary for accurate TG-FTIR-MS coupling.
Ready to optimize your thermal analysis? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Investigation on thermal kinetic behavior of 5 aminotetrazole/sodium periodate gas generator. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00820-x
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How does a high-precision laboratory oven ensure the performance of large-scale halide perovskite catalyst plates?
- Why is an air-ventilated oven necessary for GFPP surface modification? Achieve Maximum Solar Reflectance
- What is the function of a precise heating system during the hydrolysis of palm kernel oil? Optimize Your Fatty Acid Yield
- How do high-temperature quenching and tempering furnaces treat AISI 304 stainless steel? Enhance Core Toughness
- Why is a laboratory constant temperature drying oven necessary for biomass adsorbents? Ensure Precision & Integrity
- How does a laboratory oven contribute to the hydrothermal treatment of graphene aerogels? Master High-Strength Synthesis
- How does diamond benefit 5G technology? Unlock Peak Performance with Superior Thermal Management
- How does the secondary heat treatment process improve battery performance? Optimize SHPC/N-CNT Composites Today

