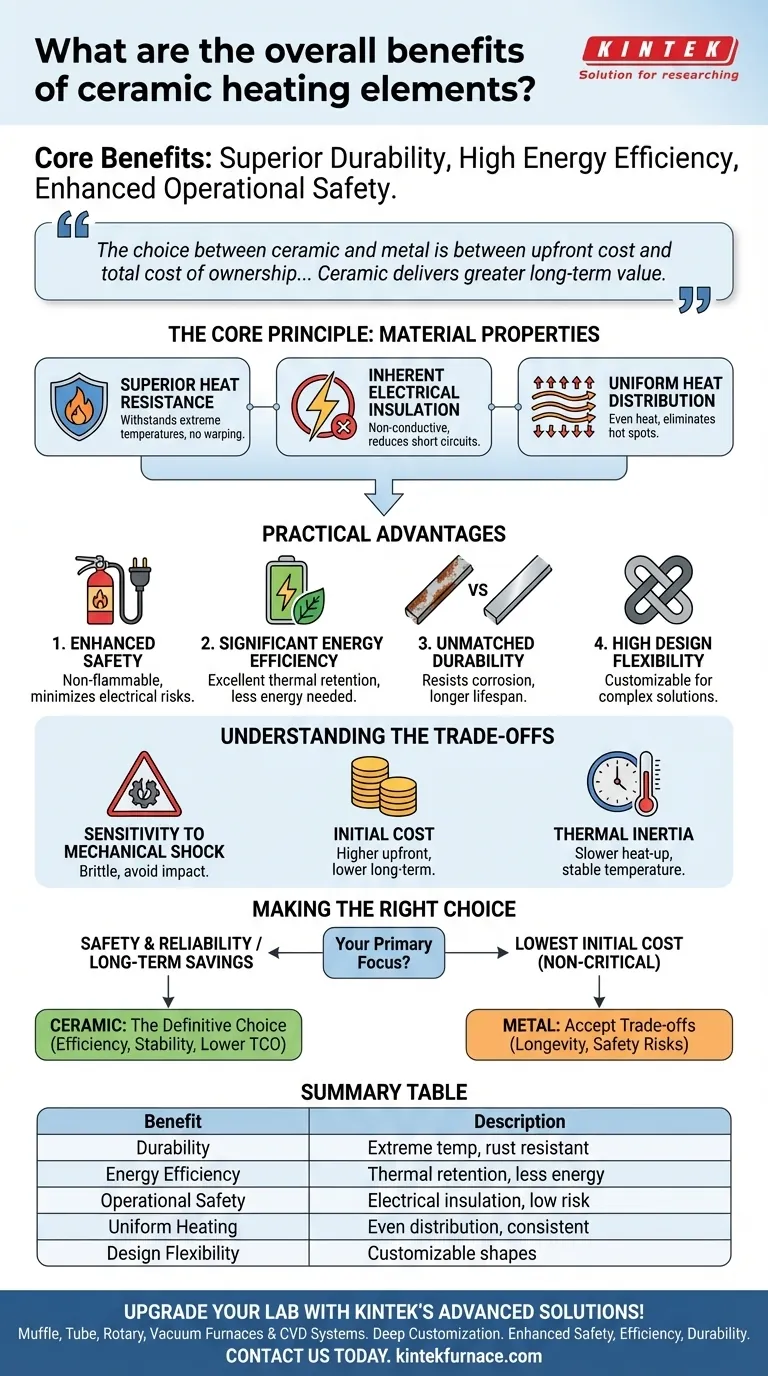
In short, the primary benefits of ceramic heating elements are superior durability, high energy efficiency, and enhanced operational safety. They can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading, and their inherent properties as an electrical insulator significantly reduce the risk of short circuits and other electrical hazards.
The choice between a ceramic and a traditional metal heater is a choice between upfront cost and total cost of ownership. While metal may be cheaper initially, ceramic's combination of efficiency, longevity, and safety delivers greater long-term value and reliability in demanding applications.

The Core Principle: Why Material Properties Matter
The advantages of ceramic heaters are not features that have been added on; they are a direct result of the fundamental properties of the ceramic material itself. Understanding this is key to appreciating their value.
Superior Heat Resistance and Stability
Ceramic elements are engineered to endure extremely high temperatures without melting, warping, or oxidizing. Unlike metal coils that can become brittle and fail over time, ceramics maintain their structural integrity, ensuring consistent performance.
Inherent Electrical Insulation
Perhaps the most critical property of ceramic is that it is an excellent electrical insulator. The material itself does not conduct electricity. This drastically reduces the risk of short circuits or electrical shocks, even if the element is damaged.
Uniform Heat Distribution
Ceramic elements are known for providing even and consistent heat across their entire surface. This eliminates hot spots and ensures a uniform heating process, which is critical in both industrial furnaces and household appliances.
Translating Properties into Practical Advantages
These core material properties translate directly into tangible benefits for both industrial and consumer applications, impacting everything from safety to your energy bill.
Enhanced Operational Safety
Because ceramics are non-conductive and non-flammable, they are inherently safer. This design minimizes the risk of electrical fires and thermal runaway incidents that can occur with traditional resistance wires.
Significant Energy Efficiency
Ceramics possess excellent thermal retention. Once they reach the target temperature, they hold that heat effectively. This means the heating system needs to cycle on less frequently to maintain the desired temperature, consuming less energy over time.
Unmatched Durability and Longevity
Ceramic elements do not rust or corrode like their metal counterparts. This resistance to chemical and environmental degradation means they last significantly longer, especially in harsh or humid conditions, leading to lower maintenance and replacement costs.
High Design Flexibility
Advanced ceramic materials, like Silicon Carbide (SiC), can be manufactured in a wide variety of complex shapes and sizes. This allows engineers to create highly customized heating solutions tailored to the specific needs of a furnace, kiln, or appliance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its compromises. To make an informed decision, you must also consider the potential downsides.
Sensitivity to Mechanical Shock
While thermally robust, ceramics can be more brittle than metals. A sharp impact or physical shock can cause them to crack or shatter. They are best suited for stationary applications where they are protected from mechanical stress.
Initial Cost
The manufacturing process for high-quality ceramic heaters is more complex than that for simple metal coil elements. This often results in a higher upfront purchase price, though this is typically offset by a lower total cost of ownership.
Thermal Inertia
The same property that gives ceramics excellent heat retention (their thermal mass) also means they may take slightly longer to heat up from a cold start compared to a thin metal wire. However, this also means their temperature is more stable once it's reached.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific priorities of your project or application.
- If your primary focus is safety and reliability: Ceramic is the definitive choice due to its inherent electrical insulation and long-term stability.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost savings: Ceramic's superior energy efficiency and durability will lead to lower operational and replacement costs over the heater's lifespan.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible initial cost for a non-critical task: A simple metal element may be sufficient, but you must accept the trade-offs in longevity, efficiency, and safety.
Understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select a heating solution that aligns not just with your temperature needs, but with your long-term operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Durability | Withstands extreme temperatures without degrading; resistant to rust and corrosion. |
| Energy Efficiency | Excellent thermal retention reduces energy consumption over time. |
| Operational Safety | Inherent electrical insulation minimizes risks of short circuits and shocks. |
| Uniform Heating | Provides even heat distribution, eliminating hot spots for consistent results. |
| Design Flexibility | Can be manufactured in complex shapes for customized solutions. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, delivering enhanced safety, efficiency, and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heating processes and reduce long-term costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















