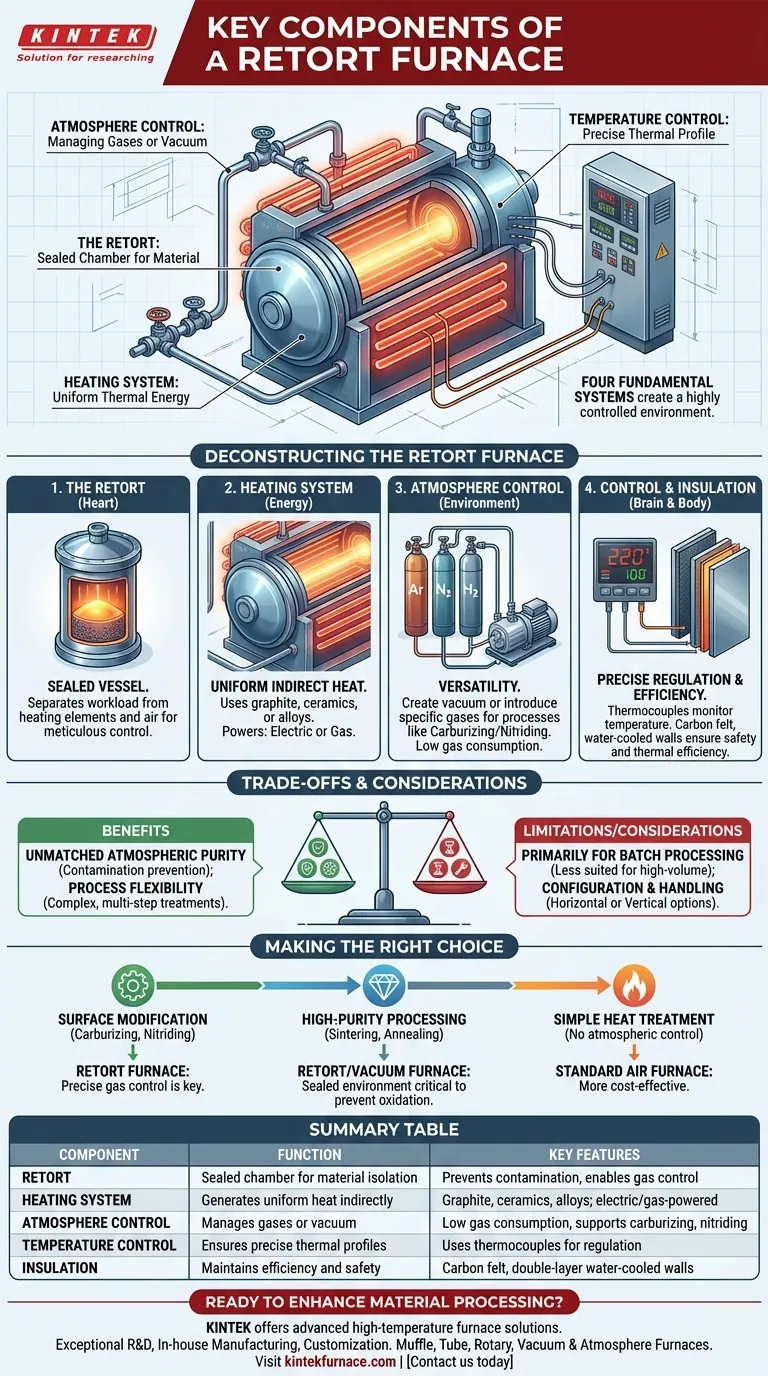
At its core, a retort furnace is built around four fundamental systems. These are the retort itself, which is a sealed chamber for the material; a heating system to generate high temperatures; a temperature control system for process precision; and an atmosphere control system to manage the specialized gases or vacuum inside the retort. Together, these components create a highly controlled environment for advanced material processing.
The defining characteristic of a retort furnace is not just its ability to generate heat, but its use of a sealed vessel—the retort—to completely isolate the material being processed. This separation is what enables the precise control over the internal atmosphere, which is the key to specialized heat treatments.

Deconstructing the Retort Furnace: How the Components Work Together
Understanding a retort furnace requires looking at how its individual systems interact to create a unique processing environment. The magic happens in the synergy between containment, heating, and atmospheric management.
The Retort: The Heart of the Process
The retort is the central component. It is a sealed, often cylindrical vessel typically made of metal that holds the material, or "workload."
Its primary function is to serve as a barrier, separating the workload from the furnace's heating elements and the outside air. This creates a closed system where the internal environment can be meticulously controlled.
The Heating System: Generating Precise Thermal Energy
Surrounding the retort are the heating elements. These can be made from various materials like graphite, ceramics, or specialized metal alloys, and can be powered by electricity or gas.
The system is designed to provide uniform heat that radiates through the retort walls to the material inside. This indirect heating ensures the workload reaches the target temperature without being directly exposed to the heat source.
The Atmosphere Control System: Engineering the Environment
This system is what makes a retort furnace so versatile. It consists of gas inlets, outlets, and often a vacuum pump.
It allows operators to remove air to create a vacuum or introduce specific gases like argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen. This control is essential for processes like carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen) and preventing oxidation during sintering or annealing. Because the retort is sealed, gas consumption is very low.
The Control & Insulation System: Ensuring Stability and Efficiency
The final piece is the brain and body of the furnace. The temperature control system uses thermocouples to monitor the internal temperature and regulate the power to the heating elements, ensuring the process follows a precise thermal profile.
The furnace body itself provides structural support and insulation. Modern designs often use high-grade carbon felt insulation and double-layer, water-cooled steel walls to maximize thermal efficiency and maintain safe external temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
While powerful, retort furnaces are not a universal solution. Their design brings specific benefits and limitations that you must weigh for your application.
Benefit: Unmatched Atmospheric Purity
The sealed design is the furnace's greatest strength. It provides absolute control over the atmosphere, preventing contamination from oxygen or other elements, which is critical for processing reactive or high-purity materials.
Benefit: Process Flexibility
A single retort furnace can perform vastly different processes. Operators can alter atmospheric conditions during a single firing cycle, enabling complex, multi-step treatments that would be impossible in a standard furnace.
Limitation: Primarily for Batch Processing
The nature of loading, sealing, and unloading a retort means these furnaces are best suited for batch processing. For high-volume, continuous production, other furnace types like conveyor belt furnaces may be more efficient.
Consideration: Configuration and Material Handling
Retort furnaces can be built in horizontal or vertical configurations. The choice depends on the product being processed and the desired method for loading and unloading, such as suspending parts from a fixture in a vertical retort.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your end goal. The unique capabilities of a retort furnace make it the ideal choice for specific, demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is surface modification (carburizing, nitriding): A retort furnace is ideal due to its precise control over reactive gas atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (sintering, annealing): The sealed environment of a retort or vacuum furnace is critical to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment without atmospheric control: A less complex and more cost-effective standard air-atmosphere furnace is the appropriate tool.
By understanding how these core components enable precise environmental control, you can determine if a retort furnace is the right solution for your material processing challenge.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Retort | Sealed chamber for material isolation | Prevents contamination, enables gas control |
| Heating System | Generates uniform heat indirectly | Uses graphite, ceramics, or alloys; electric or gas-powered |
| Atmosphere Control | Manages gases or vacuum | Low gas consumption, supports carburizing, nitriding |
| Temperature Control | Ensures precise thermal profiles | Uses thermocouples for regulation |
| Insulation | Maintains efficiency and safety | Carbon felt, double-layer water-cooled walls |
Ready to enhance your material processing with a custom retort furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity



















