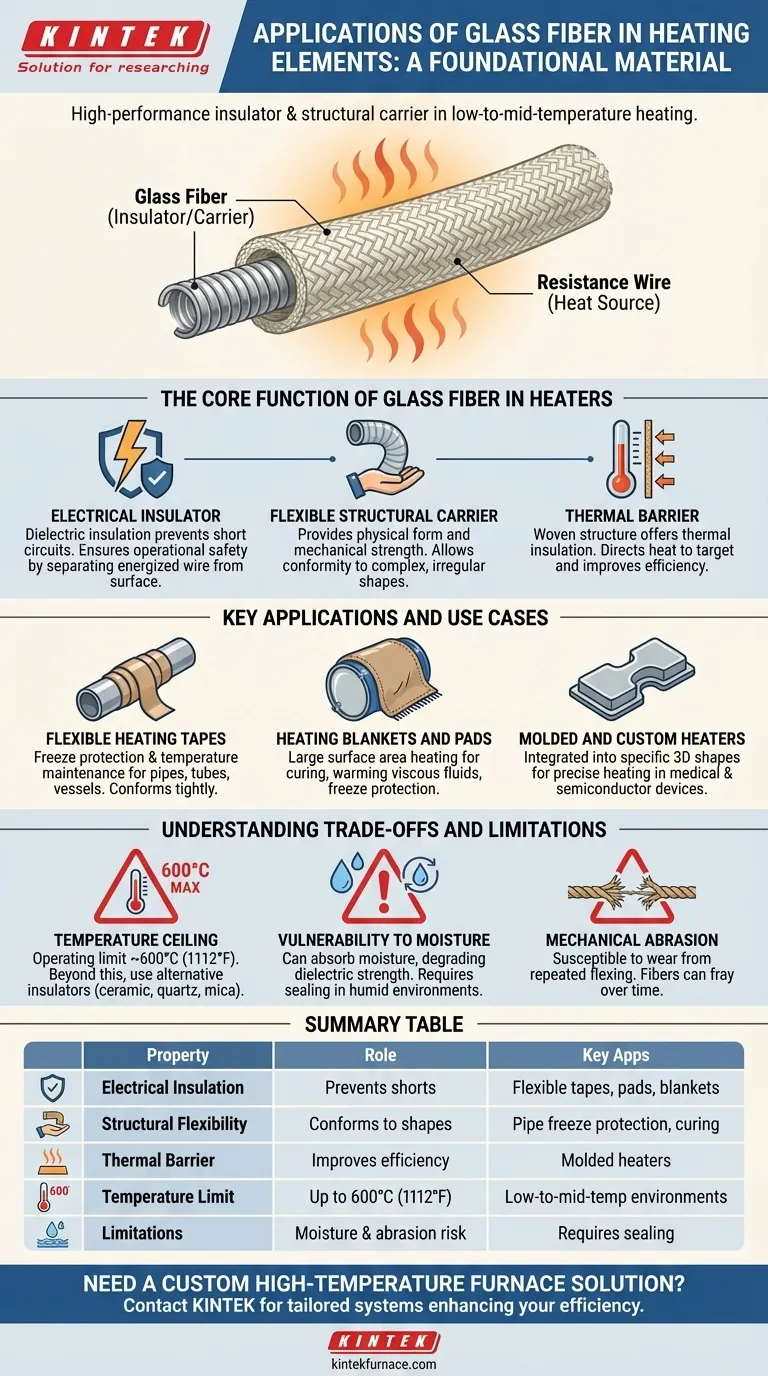
At its core, glass fiber is a foundational material used as a high-performance insulator and structural carrier in a specific class of heating elements. Its primary applications are in flexible heating tapes, pads, and blankets designed for low-to-mid-temperature environments where conformity to a surface is critical. The glass fiber itself does not generate heat; it supports and insulates the metallic resistance wire that does.
The crucial takeaway is that glass fiber is not the heating source, but the enabling framework. Its value lies in providing electrical insulation, mechanical flexibility, and thermal efficiency for heating elements operating in applications up to approximately 600°C (1112°F).
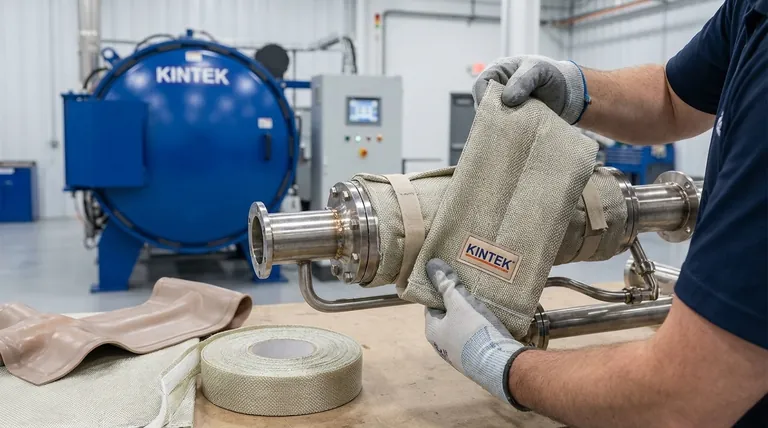

The Core Function of Glass Fiber in Heaters
To understand its applications, you must first understand the multiple roles glass fiber plays within a heating element assembly. It is a multi-purpose material chosen for its unique combination of properties.
As an Electrical Insulator
The most critical function of glass fiber is to serve as a dielectric insulator. It is woven into a fabric or sleeve that encases the resistive heating wire (typically a nickel-chromium alloy).
This insulation prevents the energized wire from making electrical contact with the conductive surface it is heating, preventing short circuits and ensuring operational safety.
As a Flexible Structural Carrier
Glass fiber provides the physical form and mechanical strength for the heating element. Its inherent flexibility is what allows for the creation of products like tapes and blankets.
This enables heaters to be wrapped around pipes, valves, and complex, irregular shapes, ensuring intimate contact for efficient heat transfer where a rigid heater would fail.
As a Thermal Barrier
While its primary role is electrical insulation, the woven structure of glass fiber also provides a degree of thermal insulation.
This helps direct more of the generated heat toward the target object and minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment, improving the overall efficiency of the heating system.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The properties of glass fiber make it the ideal choice for specific industrial, commercial, and laboratory heating scenarios.
Flexible Heating Tapes
Heating tapes are one of the most common applications. These are used to wrap pipes, tubes, and vessels to provide freeze protection or maintain process temperatures.
The flexibility of the glass fiber carrier allows the tape to conform tightly to the surface, delivering uniform heat across complex geometries.
Heating Blankets and Pads
For larger surface areas, glass fiber is used to construct heating blankets. These are used for tasks like curing composite materials in aerospace, warming drums of viscous fluids, or providing freeze protection for tanks.
The blanket can be laid over or wrapped around an object, providing broad, even heat distribution.
Molded and Custom Heaters
Glass fiber can be integrated with silicone or other polymers to create custom-molded heaters. These can be manufactured into specific, three-dimensional shapes to fit perfectly onto or inside a piece of equipment.
This is common in medical devices, semiconductor processing equipment, and food service appliances where precise, repeatable heating of a specific component is necessary.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, glass fiber is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is critical for proper material selection and safe design.
The Temperature Ceiling
The primary limitation is temperature. Standard E-glass fiber has a continuous operating limit around 600°C (1112°F). Beyond this, the fiber will soften and lose its structural and insulating properties.
For applications requiring higher temperatures, you must use alternative insulators like ceramic fiber, quartz, or mica.
Vulnerability to Moisture
Untreated glass fiber can absorb moisture, which can significantly degrade its dielectric strength and lead to electrical leakage or failure.
In applications with potential exposure to humidity or liquids, the glass fiber element must be sealed, coated with silicone, or otherwise encapsulated to maintain its insulating integrity.
Mechanical Abrasion
While flexible, glass fiber is susceptible to wear from repeated, sharp-radius flexing or mechanical abrasion. In dynamic applications, the fibers can fray and break down over time, compromising the heater's structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material depends entirely on your operational parameters and design goals.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and complex shapes: Glass fiber is the default choice for wrapping pipes or conforming to irregular surfaces, provided the temperature remains below 600°C.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation (above 600°C): You must specify an alternative insulator, such as a ceramic fiber-based heating element, to ensure safety and longevity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective surface heating in a dry environment: Glass fiber-based tapes and blankets offer an excellent balance of performance and price for a vast range of industrial heating tasks.
Understanding these distinct capabilities and limits allows you to design and implement effective, reliable, and safe flexible heating solutions.
Summary Table:
| Property | Role in Heating Elements | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Prevents short circuits, ensures safety | Flexible heating tapes, pads, blankets |
| Structural Flexibility | Allows conformity to complex shapes | Pipe freeze protection, composite curing |
| Thermal Barrier | Improves efficiency by reducing heat loss | Molded heaters for medical, semiconductor devices |
| Temperature Limit | Up to 600°C (1112°F) | Low-to-mid-temperature environments |
| Limitations | Vulnerable to moisture and abrasion | Requires sealing in humid conditions |
Need a Custom High-Temperature Furnace Solution?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
If you're working with heating elements or other thermal processes, contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace systems can enhance your efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why might a vacuum furnace maintain vacuum during cooling? Protect Workpieces from Oxidation and Control Metallurgy
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- How are parts loaded into a vacuum furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency in Your Process
- What role does a vacuum sintering furnace play in the formation of the 'core-rim' structure in Ti(C,N)-FeCr cermets?
- What additional processes can a vacuum heat treatment furnace carry out? Unlock Advanced Material Processing



