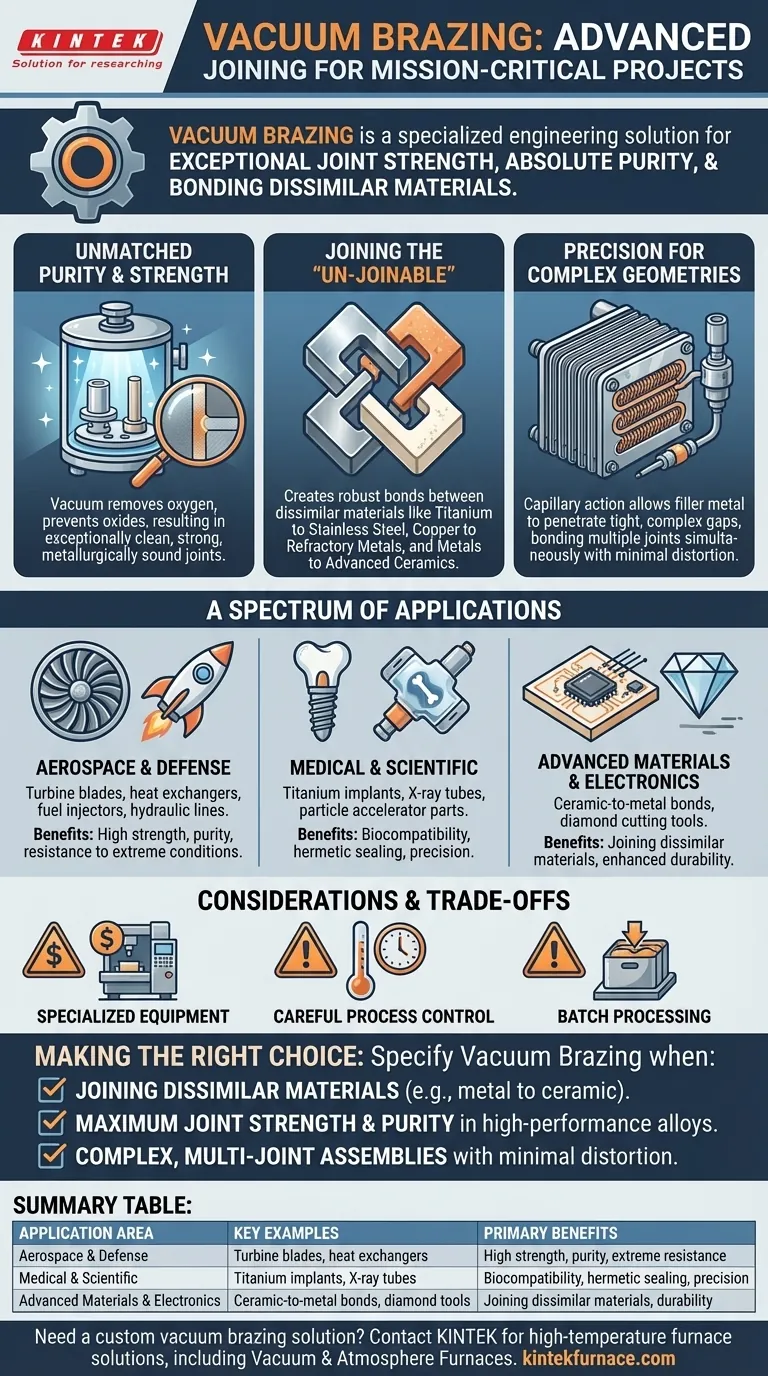
In practice, vacuum brazing projects range from manufacturing mission-critical aerospace components like turbine blades and heat exchangers to producing advanced medical implants and scientific instruments. The process is also central to joining dissimilar materials that cannot be welded, such as bonding ceramics to metal for high-power electronics or brazing diamond cutting tools for industrial applications.
The core takeaway is that vacuum brazing is not merely a joining method; it is a specialized engineering solution. It is selected when the project demands exceptional joint strength, absolute purity, and the ability to bond complex or fundamentally different materials that other processes cannot handle.
Why Vacuum Brazing is the Chosen Method
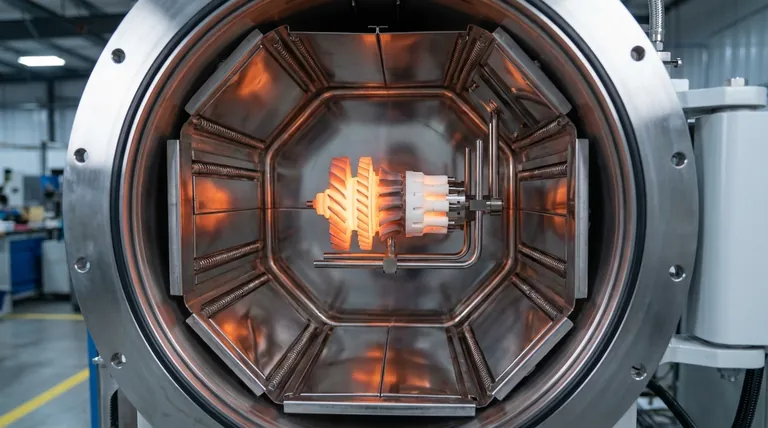
Vacuum brazing is specified when the consequences of joint failure are high and the material properties must be preserved. The value is derived from the controlled environment in which the joining occurs.
Unmatched Purity and Strength
The process takes place within a vacuum furnace, which removes oxygen and other atmospheric gases. This prevents the formation of oxides on the component surfaces during heating.
The result is an exceptionally clean, strong, and metallurgically sound joint. Without oxides to create weak spots or inclusions, the brazed bond is often as strong as the parent materials themselves.
Joining the "Un-joinable": Dissimilar Materials
Perhaps the most significant advantage of vacuum brazing is its ability to create robust bonds between materials with vastly different properties.
This includes joining metals like titanium to stainless steel, copper to refractory metals, or, most notably, metals to advanced ceramics. This capability is impossible with conventional welding and is critical for many high-tech devices.
Precision for Complex Geometries
The filler metal, drawn into the joint by capillary action, can penetrate extremely tight and complex gaps. This allows for the assembly of intricate parts with multiple joints that can all be brazed simultaneously.
This method is ideal for components like plate-fin heat exchangers or delicate sensor assemblies where a welding torch could not reach or would cause unacceptable thermal distortion.
A Spectrum of Applications: From Production to R&D
The principles of purity, strength, and material versatility make vacuum brazing essential across several demanding industries.
Aerospace and Defense
Components in this sector operate under extreme temperatures, pressures, and vibrations. Vacuum brazing is used for fuel injectors, turbine blades, hydraulic lines, and sensor packages where joint integrity is a matter of safety and performance.
Medical and Scientific Instruments
The need for biocompatibility and hermetic sealing makes vacuum brazing the go-to process for medical implants (like those made from titanium) and diagnostic equipment like X-ray tubes. It is also used to construct components for particle accelerators and other high-vacuum research tools.
Advanced Materials and Electronics
Active metal brazing, a subset of vacuum brazing, is used to join ceramics directly to metal for high-power electronic packages and insulators. The process is also used to securely bond industrial diamonds and other superhard materials to tool bodies for cutting and drilling applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a deliberate and specialized process with distinct requirements.
The Need for Specialized Equipment
Vacuum brazing requires a significant capital investment in a vacuum furnace and associated control systems. The process cannot be performed with general-purpose equipment and demands a clean, controlled environment.
Careful Process Control is Paramount
Success depends entirely on a precisely engineered thermal cycle, the correct selection of a filler alloy, and maintaining the integrity of the vacuum. Any deviation in temperature, time, or pressure can compromise the entire batch of parts, making it a less forgiving process than others.
Batch Processing and Cycle Times
Unlike welding, which is a continuous process, vacuum brazing is a batch process. An entire assembly must be loaded into the furnace, run through a lengthy heating and cooling cycle, and then unloaded. This makes it less suitable for high-volume, low-complexity fabrication.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting vacuum brazing should be a strategic decision based on the non-negotiable requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (e.g., metal to ceramic): Vacuum brazing is often the only reliable and robust solution available.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and purity in a high-performance alloy: Vacuum brazing prevents oxidation and embrittlement, ensuring the metallurgical properties of the joint are flawless.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, multi-joint assemblies with minimal distortion: The uniform heating and capillary action of vacuum brazing provide unmatched precision for intricate designs.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, simple fabrication of common metals: Conventional welding or mechanical fastening will almost always be a more economical choice.
Ultimately, specifying vacuum brazing is a commitment to achieving the highest possible quality for components that simply cannot be allowed to fail.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Examples | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace and Defense | Turbine blades, heat exchangers, fuel injectors | High strength, purity, resistance to extreme conditions |
| Medical and Scientific | Titanium implants, X-ray tubes, particle accelerator parts | Biocompatibility, hermetic sealing, precision |
| Advanced Materials and Electronics | Ceramic-to-metal bonds, diamond cutting tools | Joining dissimilar materials, enhanced durability |
Need a custom vacuum brazing solution for your high-performance project? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering unmatched joint strength, purity, and material versatility. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and achieve flawless results for your critical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















