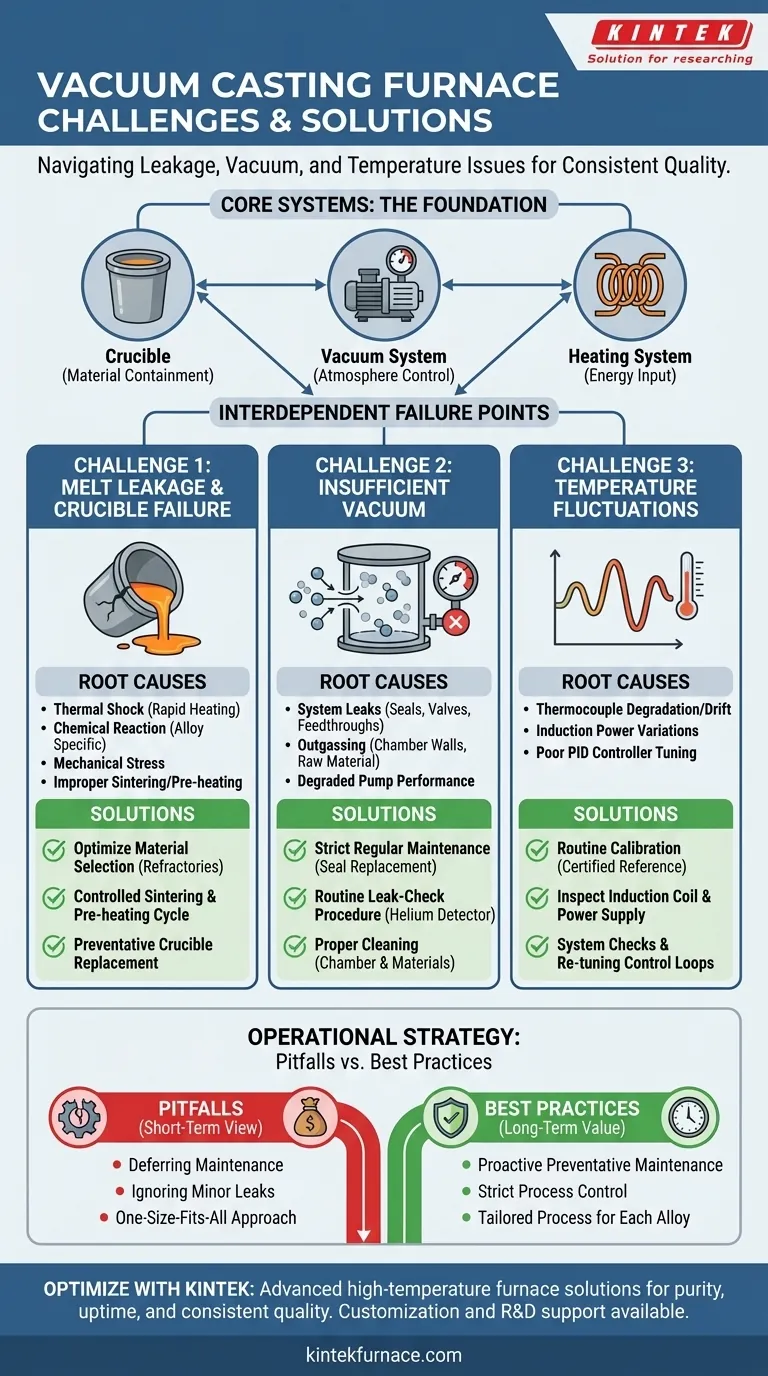
In vacuum casting furnace operations, the most common challenges are melt leakage, insufficient vacuum levels, and temperature fluctuations. These issues are typically solved through a combination of optimizing crucible selection and preparation, implementing a rigorous maintenance schedule for vacuum system components, and performing routine calibration of temperature control systems.
A reliable vacuum casting process is not about reacting to failures, but preventing them. The core challenges almost always stem from the gradual degradation of three critical systems: the material containment (crucible), the atmosphere control (vacuum), and the energy input (heating).
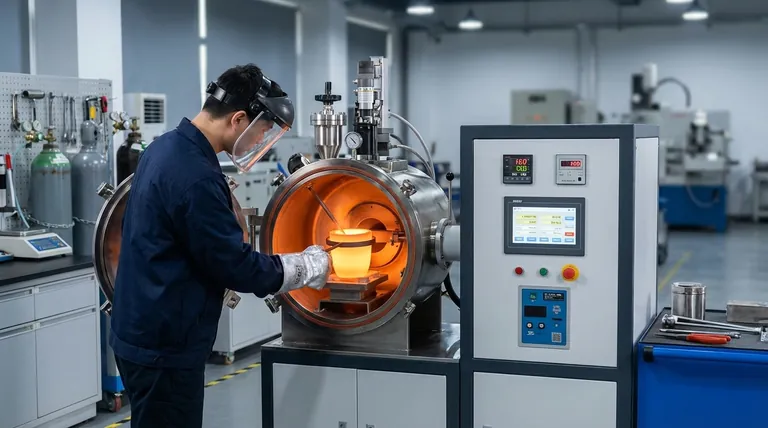

Deconstructing the Core Systems and Their Failures
To master the operation of a vacuum casting furnace, you must first understand its primary components and how they interact. The furnace is a system where a failure in one part cascades to others.
The Anatomy of a Vacuum Furnace
The key components include the vacuum chamber which houses the operation, a heating system (typically induction), a crucible to hold the molten metal, and the vacuum system itself (pumps and gauges). A control system orchestrates heating and pouring.
Each of these components is a potential point of failure that can compromise the final product.
Challenge 1: Melt Leakage and Crucible Failure
The crucible is the first line of defense, and its failure can be catastrophic, leading to equipment damage and significant downtime.
Root Causes: A crucible can fail due to thermal shock from rapid heating, chemical reaction with the specific alloy being melted, or simple mechanical stress. The sintering process used to prepare a new crucible is also critical; if done improperly, the crucible remains porous and weak.
Solutions: The solution is to optimize crucible material selection for the specific alloys you cast. Refractory materials like graphite or ceramics behave differently when in contact with various molten metals.
Equally important is a controlled sintering and pre-heating cycle. This process bakes out binders and moisture, properly hardens the crucible, and minimizes the risk of thermal shock during the first melt.
Challenge 2: Insufficient Vacuum
A poor vacuum level introduces contaminants like oxygen and nitrogen into the melt, leading to porosity and inclusions in the final casting.
Root Causes: The most common cause is a leak in the system, typically from degraded door seals, valve seats, or feedthroughs that have been stressed by thermal cycling. Another factor is outgassing, where gases are released from the chamber walls or the raw material itself when heated under vacuum.
Solutions: A strict, regular maintenance schedule is non-negotiable. This includes inspecting and replacing seals before they fail.
Implementing a routine leak-check procedure using a helium leak detector can identify and fix small leaks before they become major problems. Finally, proper cleaning of the chamber and raw materials minimizes outgassing.
Challenge 3: Temperature Fluctuations
Inconsistent melt temperature directly impacts the material's viscosity, solidification rate, and final grain structure, leading to inconsistent product quality.
Root Causes: Temperature control systems can drift over time. Thermocouples, the sensors that measure temperature, can degrade and provide inaccurate readings. The induction heating system itself can have variations in power delivery, or the PID controller may be poorly tuned for the thermal load.
Solutions: Routine calibration of the temperature control system against a certified reference instrument is essential. This ensures your setpoint is your actual temperature.
Regular inspection of the induction coil and power supply can preemptively identify issues. System checks and, if necessary, re-tuning the control loops ensure the system responds accurately to thermal changes.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Running a vacuum furnace involves a constant balance between cost, speed, and quality. Ignoring these trade-offs often leads to the very problems you are trying to solve.
Pitfall: Prioritizing Short-Term Cost Over Uptime
Deferring maintenance on vacuum pumps or using a "good enough" crucible to save immediate costs is a false economy. The eventual failure—a major melt leak or a scrapped batch of high-value parts—will invariably cost more in downtime and material waste.
Pitfall: Ignoring "Minor" Atmospheric Contamination
A small vacuum leak may not seem critical, but even trace amounts of oxygen can create oxides in reactive alloys like titanium or nickel-based superalloys. These microscopic inclusions can compromise the mechanical properties of the final part, leading to field failures.
Pitfall: The "One-Size-Fits-All" Approach
Using the same crucible material or heating profile for different alloys is a common mistake. Each alloy has a unique chemical and thermal behavior that requires a tailored process to achieve optimal, repeatable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational strategy should align with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is material purity and performance: Prioritize vacuum integrity above all else by investing in high-quality seals and rigorous leak-detection protocols.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment uptime: Implement a proactive, calendar-based preventative maintenance schedule for all mechanical and electrical systems, replacing components before they fail.
- If your primary focus is consistent, repeatable casting quality: Enforce strict process control through routine calibration of your temperature and vacuum measurement systems.
Ultimately, mastering your vacuum furnace comes from treating it as an integrated system where proactive maintenance and process discipline are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Root Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Leakage | Thermal shock, chemical reactions, improper sintering | Optimize crucible material, controlled pre-heating cycle |
| Insufficient Vacuum | System leaks, outgassing | Regular maintenance, leak checks, proper cleaning |
| Temperature Fluctuations | Thermocouple degradation, power variations | Routine calibration, inspect induction systems |
Struggling with vacuum casting furnace issues? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring purity, uptime, and consistent quality. Contact us today to optimize your operations and prevent costly downtime!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















