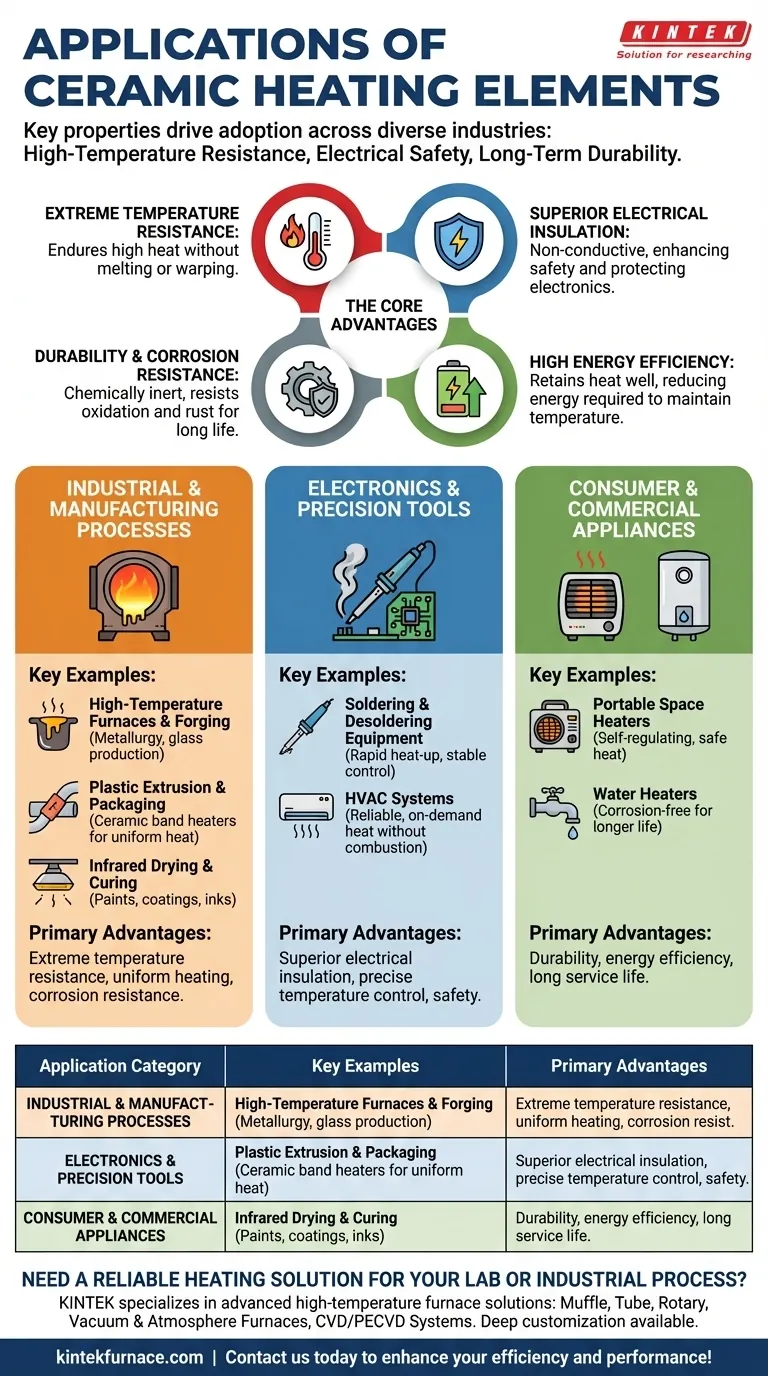
In short, ceramic heating elements are used in an incredibly wide range of applications, from industrial furnaces and manufacturing processes to precision tools like soldering irons and common household appliances such as space heaters and water heaters. Their adoption is driven by a unique combination of high-temperature resistance, electrical safety, and long-term durability.
The versatility of ceramic heating elements is not an accident. They are selected when a process requires stable, uniform heat at very high temperatures, combined with excellent electrical insulation and resistance to corrosion, making them a superior choice for both heavy industry and sensitive electronics.

Industrial and Manufacturing Processes
Ceramic heaters are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing because they provide reliable, controlled heat in demanding environments. Their ability to operate at extreme temperatures without degrading is critical.
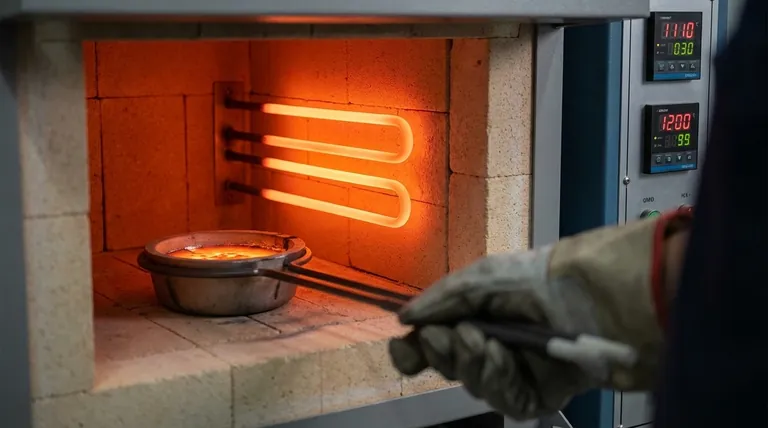
High-Temperature Furnaces and Forging
Ceramic elements are essential in furnaces used for metallurgy, material testing, and glass production. They can reach and maintain the extreme temperatures needed to melt, treat, or forge metals and other materials without risk of element failure.
Plastic Extrusion and Packaging
In machinery for plastic extrusion and packaging, uniform temperature is critical for product quality. Ceramic band heaters wrap around cylindrical parts, providing consistent heat that ensures materials flow smoothly and seals are made perfectly.
Infrared Drying and Curing
Ceramic infrared emitters are used for industrial drying and curing of paints, coatings, and inks. They radiate heat efficiently onto a surface, speeding up production lines by providing targeted energy without directly contacting the product.
Electronics and Precision Tools
In applications where electrical safety and precise temperature are paramount, ceramic heaters provide unmatched performance and safety. Their inherent insulating properties are a major advantage.
Soldering and Desoldering Equipment
Soldering irons rely on ceramic heaters for their rapid heat-up time and stable temperature control. Because the ceramic is an excellent electrical insulator, it eliminates the risk of a short circuit damaging sensitive electronic components.
HVAC Systems
In certain Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, ceramic elements are used for their safety and efficiency. They provide reliable, on-demand heat without the combustion risks associated with other fuel sources.
Consumer and Commercial Appliances
The durability and efficiency of ceramic heaters make them a popular choice for appliances we use every day, where safety and longevity are key concerns.
Portable Space Heaters
Ceramic space heaters are common because they are self-regulating and safe. The ceramic material holds heat well, providing a steady stream of warmth, and its properties reduce the risk of overheating or fire compared to older element types.
Water Heaters
In water heaters, the primary enemy of a heating element is corrosion. Ceramic elements do not rust or corrode, giving them a significantly longer service life in direct contact with water compared to many traditional metal-sheathed elements.
Understanding the Core Advantages
The widespread use of ceramic heaters is not based on a single feature, but on the powerful combination of several key properties. Understanding these attributes explains why they are chosen for such diverse applications.
Extreme Temperature Resistance
Ceramic materials can endure exceptionally high temperatures without melting, warping, or oxidizing. This makes them the only viable choice for many high-temperature industrial processes.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Unlike metal elements, ceramics do not conduct electricity. This property is crucial for safety, as it dramatically reduces the risk of electrical shorts and protects both operators and sensitive equipment.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramics are chemically inert and resistant to oxidation and corrosion. This leads to a much longer service life, especially in harsh chemical environments or applications involving direct contact with water.
High Energy Efficiency
Ceramic elements have a high thermal mass, meaning they retain heat exceptionally well. Once at temperature, they require less energy to maintain it, leading to greater overall energy efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a ceramic heater is based on the specific demands of the task.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processing: The unmatched thermal stability of ceramics makes them ideal for furnaces, forging, and drying.
- If your primary focus is precision and operational safety: The combination of stable temperature control and electrical insulation is perfect for soldering irons and electronics manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and efficiency: The corrosion resistance and durability of ceramics make them a superior choice for appliances like water heaters and space heaters.
Ultimately, the unique properties of ceramic materials make them one of the most versatile and reliable solutions for generating controlled heat across nearly every industry.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Examples | Primary Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial & Manufacturing | High-temperature furnaces, plastic extrusion, infrared drying | Extreme temperature resistance, uniform heating, corrosion resistance |
| Electronics & Precision Tools | Soldering irons, HVAC systems | Superior electrical insulation, precise temperature control, safety |
| Consumer & Commercial Appliances | Space heaters, water heaters | Durability, energy efficiency, long service life |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What ceramic materials are commonly used for heating elements? Discover the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- What types of molybdenum disilicide heating elements are available? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance
- What are the key differences between SiC and MoSi2 heating elements in sintering furnaces? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs



















