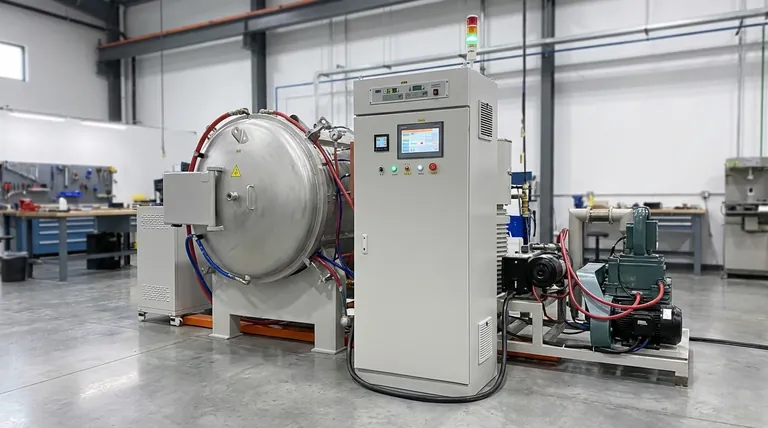
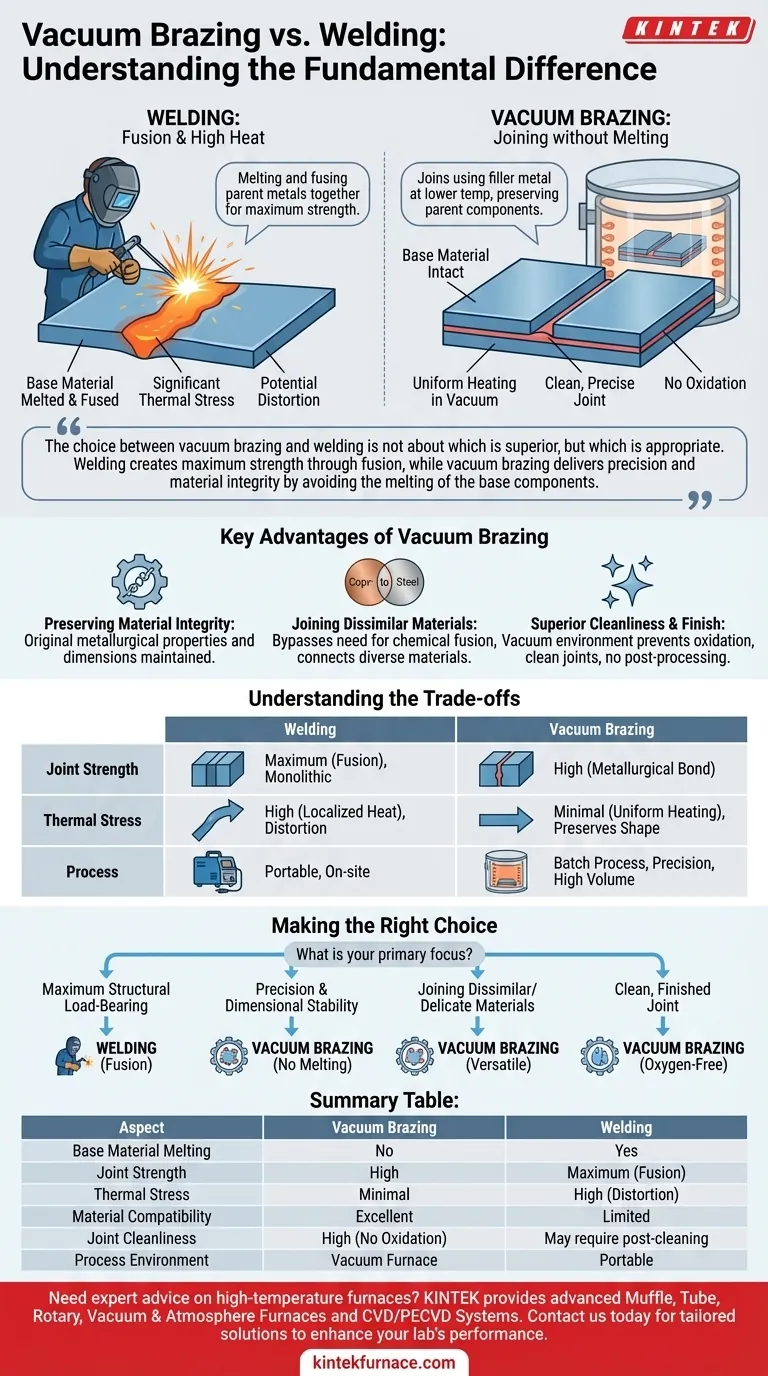
The fundamental difference between vacuum brazing and welding lies in how they treat the base materials being joined. While welding works by melting and fusing the parent metals together, vacuum brazing joins them using a separate filler metal that melts at a lower temperature, leaving the parent components completely intact.
The choice between vacuum brazing and welding is not about which is superior, but which is appropriate. Welding creates maximum strength through fusion, while vacuum brazing delivers precision and material integrity by avoiding the melting of the base components.

The Fundamental Distinction: Melting vs. Joining
The core of the comparison comes down to temperature and its effect on the materials. One method fuses, while the other bonds.
How Welding Works: Fusion and High Heat
Welding uses a highly concentrated heat source (like an electric arc or gas flame) to melt the edges of the parent materials. A filler material is often added to the molten pool.
As this pool cools and solidifies, it forms a single, continuous piece of metal. This process creates a very strong, monolithic joint but introduces significant thermal stress, which can lead to distortion and changes in the material's properties.
How Vacuum Brazing Works: Capillary Action in a Controlled Environment
Vacuum brazing involves assembling the components with a specialized filler metal (a braze alloy) placed at the joint. The entire assembly is then heated uniformly inside a vacuum furnace.
The temperature is raised above the melting point of the filler metal but stays safely below the melting point of the parent materials. The molten filler is then drawn into the tight gap between the components by capillary action, creating a strong metallurgical bond upon cooling. The vacuum environment prevents oxidation, resulting in a perfectly clean joint.
Key Advantages of the Brazing Process
Because it doesn't melt the base components, vacuum brazing offers unique benefits that are impossible to achieve with welding.
Preserving Material Integrity
The primary advantage is the preservation of the parent metals. Since they are never melted, their original metallurgical properties, heat treatment, and dimensional stability are maintained. This is critical for delicate or high-precision parts.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
Welding is often limited to joining similar or metallurgically compatible metals. Vacuum brazing excels at joining dissimilar materials, such as copper to steel or stainless steel to ceramics, because it bypasses the need for chemical fusion.
Superior Cleanliness and Finish
The vacuum furnace removes atmospheric contaminants, primarily oxygen. This prevents the formation of oxides during heating, resulting in extremely clean, bright joints that typically require no post-process cleaning or finishing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct method requires an objective look at the limitations and specific demands of your project.
Joint Strength
A properly executed weld joint is generally stronger than a brazed joint because it is a single, fused piece of the parent material. For applications where the joint will be under extreme load or stress, welding is often the preferred method for its absolute structural strength.
Thermal Stress and Distortion
Welding's intense, localized heat creates significant thermal gradients, which almost always lead to warping and distortion. Vacuum brazing uses uniform heating and cooling cycles, drastically minimizing thermal stress and preserving the part's original shape and dimensions.
Process Suitability
Welding can be a portable process suitable for large structures and on-site repairs. Vacuum brazing is a batch process that requires a specialized furnace, making it ideal for smaller, complex, or high-volume production runs where precision is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by the non-negotiable requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum structural load-bearing: Welding is the clear choice for its ability to create a monolithic, fused joint.
- If your primary focus is precision and dimensional stability: Vacuum brazing is superior, as it eliminates the distortion caused by melting.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar or delicate materials: Vacuum brazing provides a reliable solution where welding is often not feasible.
- If your primary focus is a clean, finished joint with no post-processing: The oxygen-free environment of vacuum brazing delivers an unmatched finish.
Ultimately, select the joining technology that best protects the most critical characteristics of your components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Brazing | Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material Melting | No | Yes |
| Joint Strength | High, but generally lower than welding | Maximum, due to fusion |
| Thermal Stress | Minimal, uniform heating | High, localized heat causes distortion |
| Material Compatibility | Excellent for dissimilar materials | Limited to similar or compatible metals |
| Joint Cleanliness | High, no oxidation in vacuum | May require post-cleaning |
| Process Environment | Vacuum furnace, batch process | Portable, various environments |
Need expert advice on selecting the right high-temperature furnace for your vacuum brazing or welding applications? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering precision, efficiency, and material integrity. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your lab's performance and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















