For any high-temperature furnace application, the surface finish of an alumina ceramic tube is a foundational parameter that directly dictates its performance and lifespan. A smoother, cleaner surface minimizes the risk of process contamination and enhances the efficiency of heat transfer. These two factors are fundamental to achieving reliable and repeatable results in controlled thermal environments.
The choice of surface finish is not merely cosmetic; it is an engineering decision. The right finish ensures process purity, improves thermal efficiency, and preserves the mechanical integrity of the tube, ultimately protecting your investment and ensuring the success of your application.
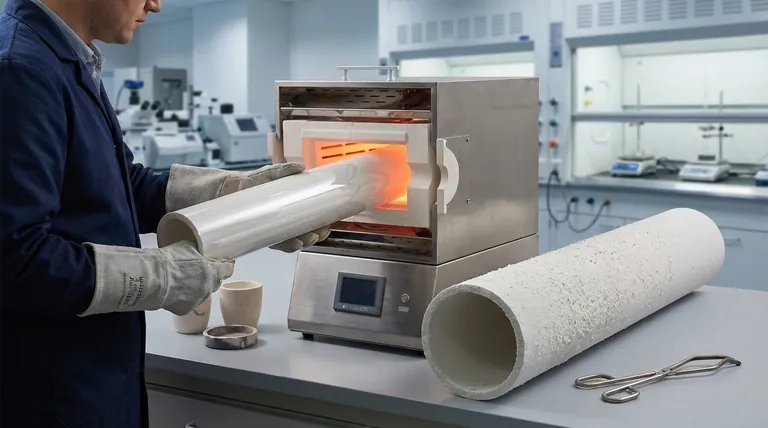

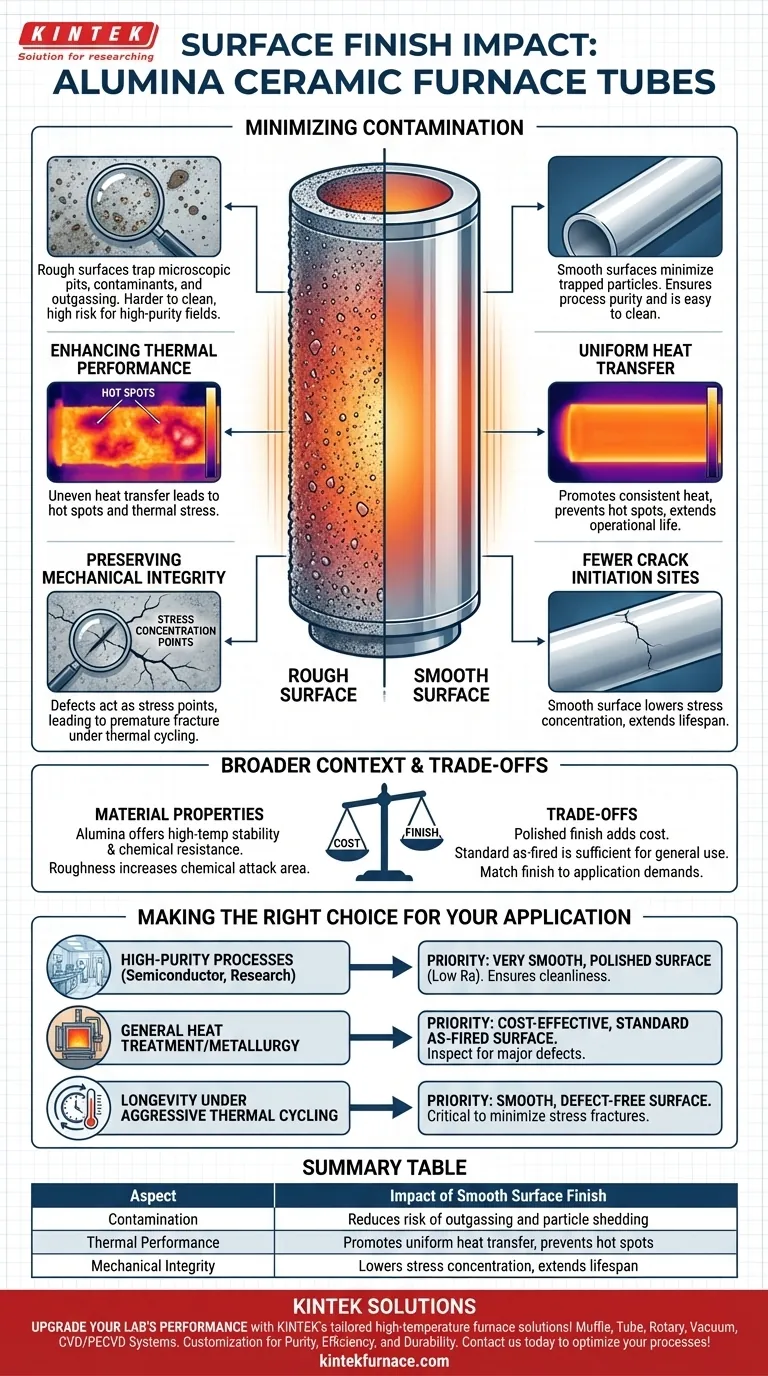
The Performance Impact of Surface Finish
A tube's surface condition influences three critical areas: its cleanliness, its thermal behavior, and its structural durability. Understanding these connections is key to selecting the right component.
Minimizing Process Contamination
A primary role of a furnace tube is to create a controlled, isolated environment. A rough surface finish directly undermines this goal.
Rougher surfaces have a higher effective surface area and contain microscopic pits and valleys where contaminants can become trapped. This makes the tube significantly harder to clean and increases the risk of outgassing or particle shedding during operation, which is unacceptable in high-purity fields like semiconductor manufacturing.
Enhancing Thermal Performance
Alumina tubes are prized for their thermal stability, and surface finish plays a key role in how efficiently they manage heat.
A smooth, uniform surface promotes more consistent heat transfer across the tube wall. This reduces the likelihood of "hot spots," which can induce thermal stress and lead to cracking over time. Efficient thermal transfer is essential for both process control and extending the tube's operational life.
Preserving Mechanical Integrity
The mechanical strength of a ceramic component is highly sensitive to surface defects.
Scratches, pits, and even the microscopic texture of a rough finish can act as stress concentration points. When the tube is subjected to thermal cycling (expansion and contraction) or mechanical loads, these points are where fractures are most likely to initiate, leading to premature failure. A smoother surface has fewer initiation sites for cracks.
Understanding the Broader Context
While surface finish is critical, it is one of several interconnected properties. Choosing the right tube means balancing these factors against your specific application and budget.
Material Properties Define the Baseline
Alumina is chosen for its excellent combination of high-temperature stability and chemical resistance. It stands up well to most acids, alkalis, and corrosive environments where metals or quartz would fail.
However, this inherent resistance can be compromised. A rougher surface increases the total area exposed to chemical attack, which can accelerate degradation even in a material as robust as alumina.
The Trade-off Between Finish and Cost
Achieving a highly polished, mirror-like surface requires additional manufacturing steps, such as grinding and lapping. These processes add significant cost.
It is crucial to match the surface finish to the demands of the application. Not every process requires the expense of a perfectly polished tube. A standard, as-fired surface is often sufficient for general heat treatment applications, provided it is free of significant flaws.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The most common mistake is to treat all alumina tubes as identical. Failing to specify a surface finish appropriate for your process can lead to contamination, inconsistent results, and unexpected equipment failure.
Another pitfall is ignoring the interaction between thermal and mechanical stress. A tube that seems strong enough for the load can easily fail if a poor surface finish creates weak points that are then exploited by repeated thermal cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your selection. This ensures you are investing in the performance characteristics that matter most to your work.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processes (e.g., semiconductor, research): You must prioritize a very smooth, polished surface with a low surface roughness (Ra) value to ensure cleanliness and minimize contamination.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment or metallurgy: A cost-effective, standard "as-fired" surface is often perfectly adequate, as long as it is inspected for major defects like cracks or chips.
- If your primary focus is longevity under aggressive thermal cycling: A smooth, defect-free surface is critical to minimize stress concentration points and reduce the risk of fracture over time.
By treating surface finish as a key engineering parameter, you directly enhance the performance, reliability, and lifespan of your entire high-temperature system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Smooth Surface Finish |
|---|---|
| Contamination | Reduces risk of outgassing and particle shedding |
| Thermal Performance | Promotes uniform heat transfer, prevents hot spots |
| Mechanical Integrity | Lowers stress concentration, extends lifespan |
Upgrade your lab's performance with KINTEK's tailored high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing purity, efficiency, and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and protect your investment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















