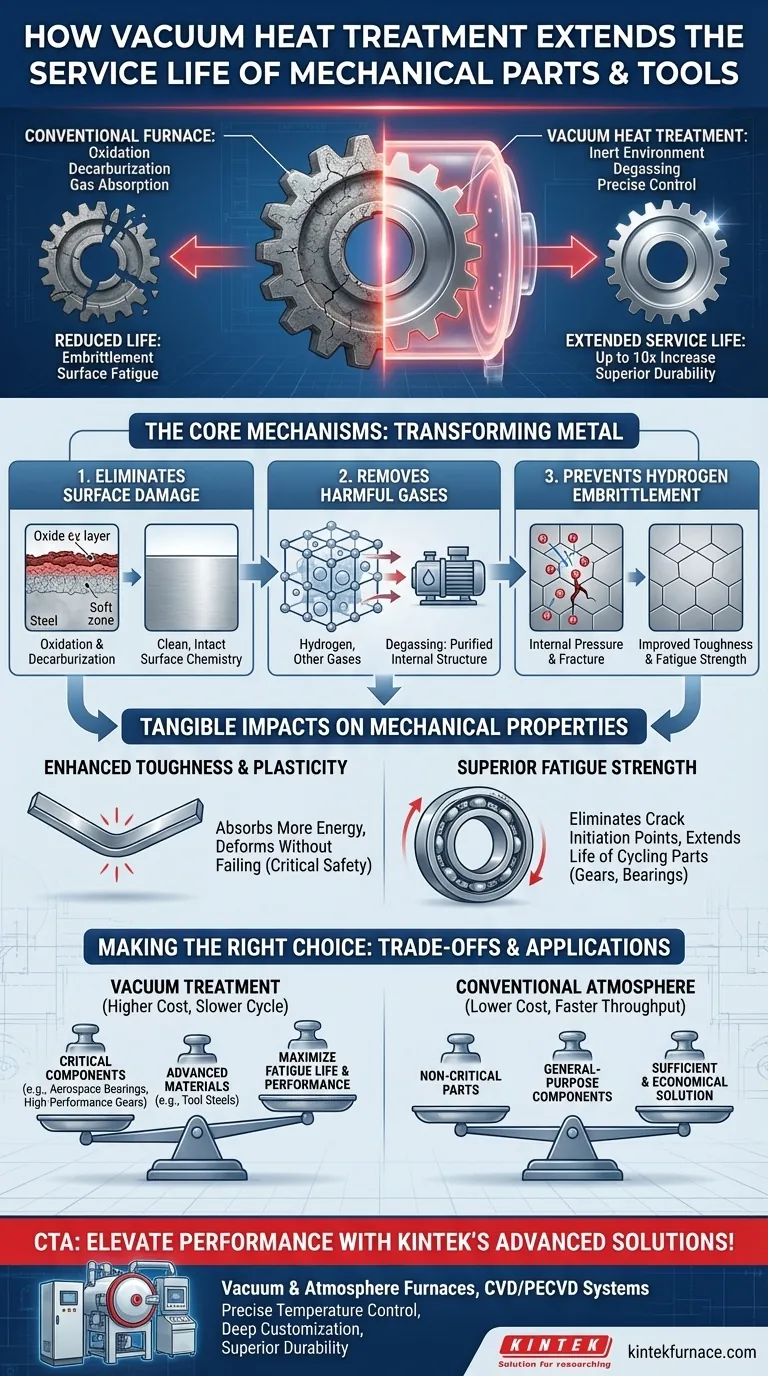
In essence, vacuum heat treatment enhances the service life of mechanical parts by fundamentally changing the environment in which they are heated. This process purifies the metal's surface and removes harmful internal gases, preventing common failure mechanisms like embrittlement and surface fatigue. By allowing the material to achieve its full theoretical performance potential, service life can often be doubled or even increased tenfold for critical components.
The primary advantage of vacuum heat treatment is not just what it does, but what it prevents. By eliminating reactions with atmospheric gases, it stops surface and subsurface damage before it can begin, resulting in a component that is internally cleaner and externally more durable than one treated in a conventional furnace.

The Core Mechanisms: How a Vacuum Transforms Metal
The "magic" of vacuum heat treatment lies in its ability to control the part's environment with extreme precision during its most vulnerable, high-temperature state. This prevents a host of negative reactions that degrade performance.
Eliminating Surface Oxidation and Decarburization
In a traditional furnace, the hot metal surface reacts with oxygen and other gases in the atmosphere. This creates a brittle, undesirable scale (oxidation) or can burn off carbon from the surface of steel (decarburization), leaving a soft outer layer.
A vacuum environment is inert. By removing the reactive gases, it ensures the part emerges from the furnace clean, bright, and with its surface chemistry perfectly intact.
Removing Harmful Dissolved Gases
Metals, particularly steel, can absorb gases like hydrogen during their manufacturing process. These dissolved gases act as internal impurities that create significant problems.
Vacuum heat treatment effectively degasses the material. The combination of high heat and low pressure draws these dissolved gases out of the metal, where they are then pumped away by the vacuum system.
Preventing Hydrogen Embrittlement
Hydrogen is especially damaging. Individual hydrogen atoms can migrate and become trapped within the metal's crystalline structure, creating immense internal pressure points.
This phenomenon, known as hydrogen embrittlement, dramatically reduces a material's ductility and toughness, making it prone to sudden, brittle fracture under load. By removing hydrogen, vacuum treatment directly improves the part's toughness and fatigue strength.
The Tangible Impact on Mechanical Properties
Eliminating these negative factors translates directly into measurable improvements in the properties that define a part's service life.
Enhanced Toughness and Plasticity
A cleaner, gas-free internal structure allows the metal to behave as intended. It will have higher toughness, meaning it can absorb more energy and impact before fracturing.
This also improves plasticity, the material's ability to deform slightly under extreme load without failing, which is a critical safety characteristic.
Superior Fatigue Strength
Fatigue failures—which account for the vast majority of mechanical failures in rotating or cycling parts—almost always begin at a microscopic surface imperfection.
Because vacuum heat treatment produces a perfectly clean surface free of oxide pits or soft decarburized spots, it eliminates the most common initiation points for fatigue cracks. This dramatically extends the life of components like bearings, gears, and shafts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making sound engineering decisions.
Higher Process Cost
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and expensive to build and operate than conventional atmosphere furnaces. This translates to a higher cost per part.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum takes time. The process of pumping down the chamber can result in longer overall cycle times compared to continuous atmosphere furnaces, affecting throughput.
Not Always Necessary
For simple, low-stress components or materials where surface finish and peak fatigue performance are not critical design drivers, the added cost of vacuum treatment may not provide a worthwhile return on investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heat treatment process requires aligning the method's benefits with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing fatigue life in critical components: The clean surface and removal of internal hydrogen make vacuum treatment the superior choice for parts like connecting rods, high-performance gears, and aerospace bearings.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced tool steels or high-alloy materials: The precise temperature control and prevention of decarburization are essential for achieving the required hardness, wear resistance, and toughness.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive production of non-critical parts: Traditional atmosphere heat treatment often provides a sufficient and more economical solution for general-purpose components.
By understanding these principles, you can specify a heat treatment process that doesn't just harden a part, but truly optimizes it for maximum durability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Key Benefit | Impact on Service Life |
|---|---|---|
| Eliminates surface oxidation and decarburization | Clean, intact surface | Reduces fatigue crack initiation, extends life |
| Removes harmful dissolved gases | Purified internal structure | Improves toughness and plasticity, prevents embrittlement |
| Prevents hydrogen embrittlement | Enhanced fatigue strength | Increases durability under cyclic loads |
Elevate your component performance with KINTEK's advanced vacuum heat treatment solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior durability and extended service life for critical parts. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















