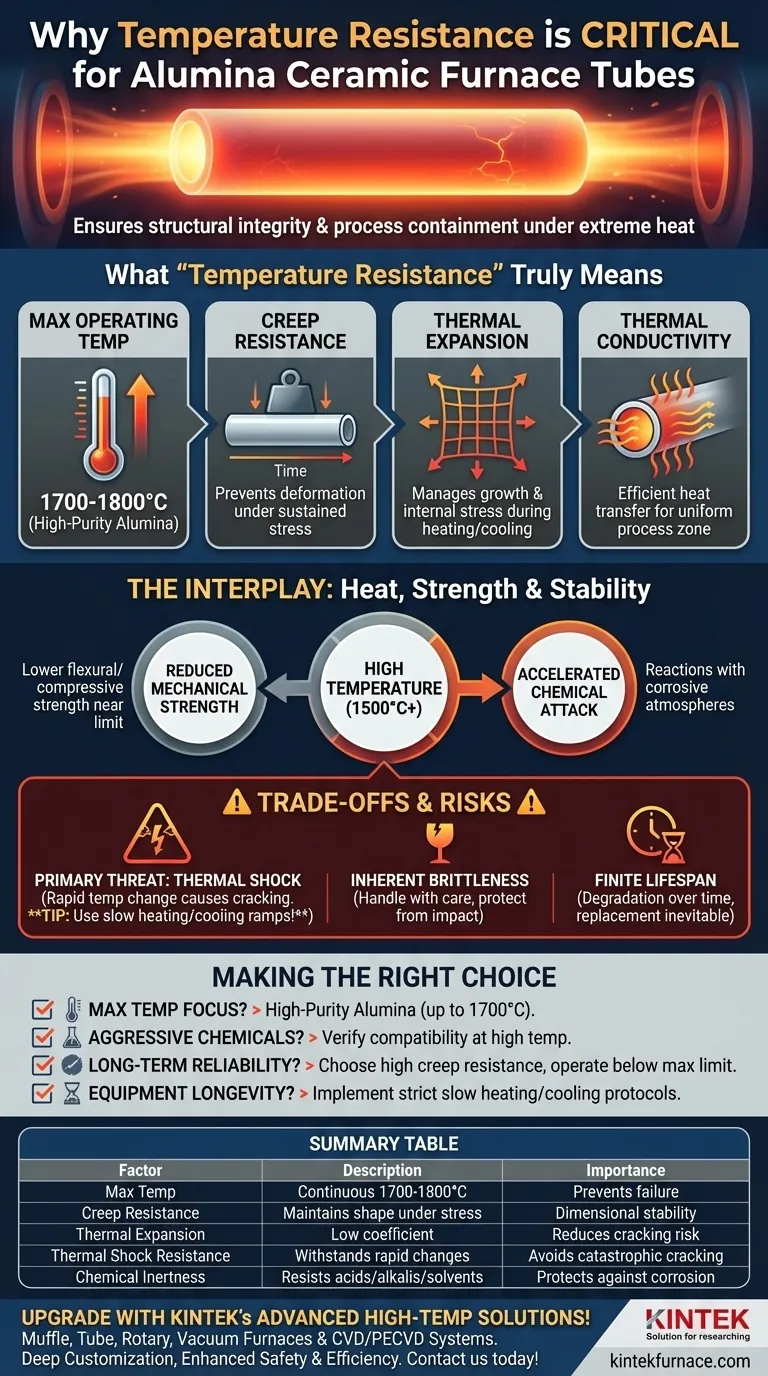
In high-temperature furnace applications, temperature resistance is the single most critical property for an alumina ceramic tube. It is the fundamental characteristic that ensures the tube can maintain its structural integrity and contain the process environment without failing under extreme heat. Choosing a tube rated significantly higher than your maximum operating temperature is the first line of defense for safety, performance, and equipment longevity.
Selecting the right furnace tube goes beyond matching a single temperature rating. True temperature resistance is a combination of factors—including maximum operating temperature, creep resistance, and thermal expansion—that collectively determine the tube's ability to perform reliably and safely under sustained thermal stress.

What "Temperature Resistance" Truly Means
The term "temperature resistance" encompasses several distinct physical properties. Understanding each one is key to diagnosing potential failures and selecting the right material.
Exceeding the Maximum Operating Temperature
The most straightforward metric is the maximum service temperature. High-purity alumina ceramics are valued for their exceptionally high limits, often capable of withstanding continuous use at temperatures up to 1700-1800°C.
This makes them a default choice for demanding laboratory and industrial processes like metal heat treating, crystal growth, and materials sintering, where lesser materials like quartz would fail.
Resisting Creep and Deformation
At high temperatures, materials can slowly deform under stress, even under their own weight. This phenomenon is known as creep.
Excellent creep resistance means the alumina tube will maintain its straightness and dimensional stability over hundreds or thousands of hours at temperature, preventing process failure or damage to the furnace.
Managing Thermal Expansion
All materials expand when heated. The coefficient of thermal expansion describes how much a material grows for each degree of temperature increase.
While alumina has a relatively low thermal expansion for a ceramic, this property is still the primary cause of failure. Heating or cooling the tube too quickly creates internal stress that can cause it to crack.
Conducting Heat
Thermal conductivity measures how well the tube transfers heat. Alumina has moderate thermal conductivity, which allows for relatively uniform heating of the process zone inside the tube. This property is defined by the material's purity and density.
The Interplay of Thermal, Mechanical, and Chemical Stability
A furnace tube does not exist in a vacuum. Its ability to resist heat is directly tied to its ability to withstand mechanical and chemical stresses, which are often amplified at high temperatures.
How Heat Impacts Mechanical Strength
A material's strength is not a constant. As an alumina tube approaches its maximum temperature limit, its flexural and compressive strength decreases.
Operating well below the stated maximum temperature provides a critical safety margin, ensuring the tube retains enough mechanical strength to support itself and resist any incidental stresses.
How Heat Accelerates Chemical Attack
High temperatures act as a catalyst for chemical reactions. A substance that is benign at room temperature might become highly corrosive to the ceramic at 1500°C.
Alumina is known for its excellent chemical inertness, resisting most acids, alkalis, and solvents. However, you must always verify its resistance against your specific process atmosphere at the target operating temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While alumina is a superior material for high-temperature work, it has specific vulnerabilities that you must manage to ensure a long service life.
The Primary Threat: Thermal Shock
The most common cause of failure in ceramic tubes is thermal shock. This occurs when the temperature changes too rapidly, causing different parts of the tube to expand or contract at different rates, leading to catastrophic cracks.
Implementing controlled, gradual heating and cooling ramps is not optional; it is essential for the survival of the tube.
Inherent Brittleness
Unlike metals, ceramics are brittle. They do not bend or deform before breaking. This means the tube must be handled carefully during installation and protected from mechanical impact or vibration, especially when hot and structurally weaker.
Lifespan Is Not Guaranteed
Even with perfect care, the lifespan of a furnace tube is finite. Factors like the specific temperature used, the duration of thermal cycles, and the chemical environment all contribute to the material's gradual degradation. Proper usage extends this lifespan, but eventual replacement is inevitable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace tube is about ensuring the integrity and success of your high-temperature process. Use these principles to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is maximizing operating temperature: High-purity alumina is the definitive choice, reliably performing in environments up to 1700°C or more.
- If your process involves aggressive chemicals at high heat: Verify the alumina's compatibility with your specific chemical environment at your target temperature, not just at room temperature.
- If you need long-term structural reliability for extended runs: Choose a tube with high-rated creep resistance and always operate at least 100-150°C below its absolute maximum temperature.
- If you are concerned about equipment longevity: You must implement and enforce strict, slow heating and cooling protocols to protect the tube from thermal shock.
Ultimately, understanding temperature resistance in all its dimensions empowers you to select a tube that will perform safely and reliably.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Continuous use up to 1700-1800°C | Prevents failure under extreme heat |
| Creep Resistance | Maintains shape under sustained thermal stress | Ensures dimensional stability over time |
| Thermal Expansion | Low coefficient reduces cracking risk | Manages internal stresses during heating/cooling |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Ability to withstand rapid temperature changes | Avoids catastrophic cracking |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists acids, alkalis, and solvents at high temps | Protects against corrosion in harsh environments |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable alumina ceramic tubes and custom furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing safety, efficiency, and longevity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs



















