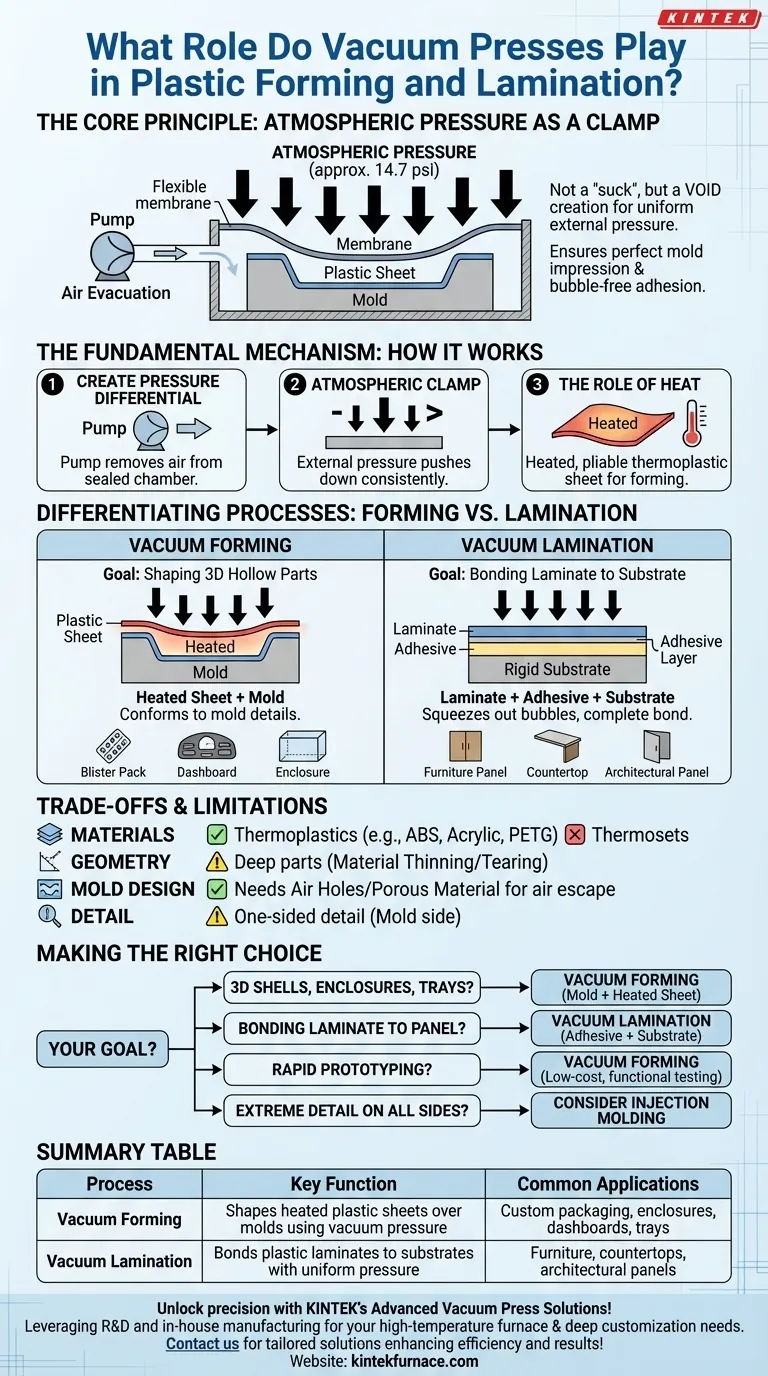
At its core, a vacuum press uses atmospheric pressure as a powerful and uniform clamp. For plastics, it plays a critical role by evacuating air between a heated, pliable plastic sheet and a mold or substrate, allowing the weight of the atmosphere to press the material into a precise shape or bond it perfectly to a surface.
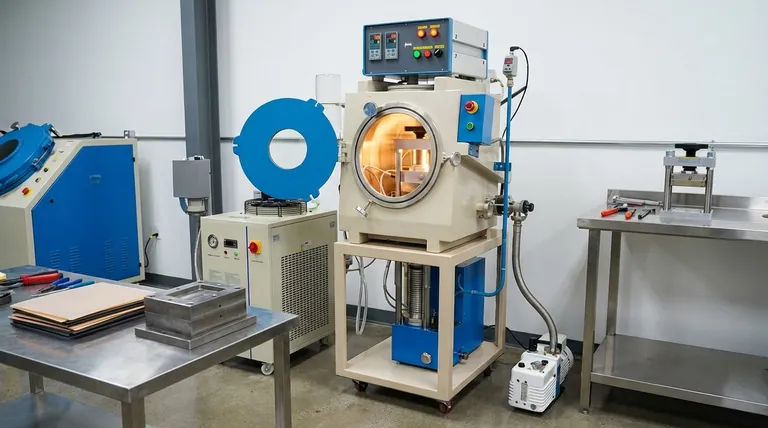
The primary role of a vacuum press is not to "suck" material into place, but to create a void, allowing immense and evenly distributed atmospheric pressure (approximately 14.7 psi at sea level) to do the work of shaping or laminating. This ensures a perfect impression of a mold and bubble-free adhesion.

The Fundamental Principle: How Vacuum Pressure Shapes and Bonds
A vacuum press is a simple yet elegant system that harnesses the power of physics. Understanding the mechanism is key to appreciating its role in fabrication.
Creating the Pressure Differential
The process begins when a pump removes the air from a sealed chamber or bag containing the workpiece and a mold. This evacuation creates a low-pressure environment, or a vacuum.
Atmospheric Pressure as the "Clamp"
Once the air is removed, the external atmospheric pressure is no longer counteracted by pressure inside the chamber. This imbalance results in a net force pushing down on the flexible membrane of the press, applying consistent pressure across the entire surface of the material inside.
The Role of Heat
For plastic forming, the sheet of plastic must first be heated to its specific forming temperature. At this temperature, the material becomes soft and pliable, allowing the relatively low force of atmospheric pressure to stretch and shape it over a mold.
Differentiating Key Processes: Forming vs. Lamination
While both processes use the same principle, their goals are distinct. The term "vacuum press" is often used for lamination, while "vacuum former" is used for shaping, but the underlying technology is identical.
Vacuum Forming Explained
In vacuum forming, a single sheet of heated plastic is draped over a mold. The vacuum pulls the air out from between the sheet and the mold, forcing the plastic to conform perfectly to the mold's every detail. This is ideal for creating three-dimensional, hollow parts.
Common applications include custom packaging (blister packs), equipment enclosures, vehicle dashboards, and product trays.
Lamination Explained
In lamination, the goal is to bond materials together. A vacuum press is used to glue a thin sheet of plastic (a laminate) onto a rigid or curved substrate, such as MDF or plywood.
The uniform pressure ensures a complete bond across the entire surface, squeezing out all air bubbles and excess adhesive. This is essential for creating durable, decorative surfaces for furniture, countertops, and architectural panels.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the vacuum press process has important constraints that dictate its suitability for a given project.
Material Constraints
This method works primarily with thermoplastics—plastics that become malleable when heated and solid when cooled. Common examples include ABS, acrylic (PMMA), polystyrene (HIPS), PETG, and polycarbonate (PC). Thermosetting plastics, which cure irreversibly, cannot be vacuum formed.
Geometric Challenges
Extremely deep parts or those with sharp internal corners can be difficult to form. The material stretches as it is drawn into the mold, and it can become excessively thin or even tear in deep sections. This is known as material thinning.
Mold Design Requirements
The mold (or "buck") must be designed to allow air to escape. This is typically achieved by drilling small vacuum holes in the low points of the mold or by making the entire mold from a porous material.
One-Sided Detail
In vacuum forming, only the side of the plastic touching the mold receives a high-fidelity finish. The outer side will be less detailed, as it is not in direct contact with a shaping surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a vacuum press is the right tool, consider your final goal.
- If your primary focus is creating 3D shells, enclosures, or custom trays: Your process is vacuum forming, which requires a mold and a heated plastic sheet.
- If your primary focus is bonding a plastic finish to a flat or curved panel: Your process is vacuum lamination, which requires an adhesive and a substrate.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping: Vacuum forming is an excellent, low-cost method for testing designs and creating functional prototypes before investing in expensive injection molding tooling.
- If your primary focus is parts with extreme detail on all sides: You may need to investigate other processes like injection molding or pressure forming, which use positive pressure to achieve higher detail.
By leveraging the invisible force of the atmosphere, vacuum pressing provides a reliable and precise method for both shaping and bonding plastics.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Forming | Shapes heated plastic sheets over molds using vacuum pressure | Custom packaging, enclosures, dashboards, trays |
| Vacuum Lamination | Bonds plastic laminates to substrates with uniform pressure | Furniture, countertops, architectural panels |
Unlock precision in your plastic fabrication with KINTEK's advanced vacuum press solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for forming and lamination. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- High Performance Vacuum Bellows for Efficient Connection and Stable Vacuum in Systems
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum press and what are its primary uses? Unlock High-Performance Material Processing
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies
- In which fields is hot pressing technology applied? Essential for Aerospace, Defense, and Advanced Manufacturing
- How does automation enhance the hot pressing process? Boost Precision, Efficiency, and Quality
- How does tailored heat and pressure control benefit hot pressing? Achieve Superior Material Density and Strength



















