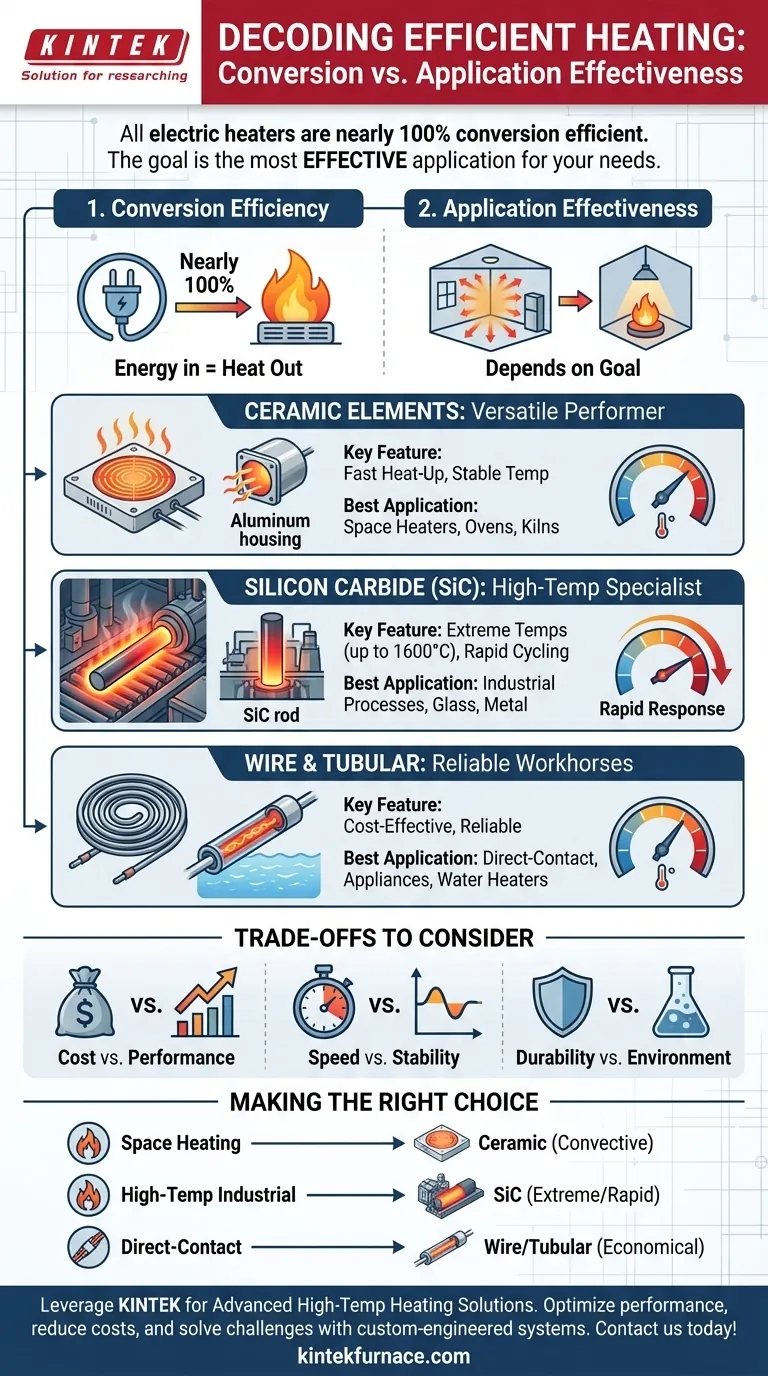
In practice, all electric resistance heaters are nearly 100% efficient at converting electricity into heat. However, the most effective heating element for transferring that heat usefully depends entirely on the application. For common uses like space heating, ceramic elements are a top choice due to their ability to produce and distribute heat quickly and consistently.
The search for the "most efficient" heating element is a misunderstanding of how electric heat works. The real goal is to find the most effective system for your specific need, as efficiency is more about how well heat is delivered, not just how it's created.

Deconstructing "Efficiency" in Heating
The term "efficiency" can be misleading. While nearly all electric heaters convert energy to heat with near-perfect efficiency, the method of heat transfer—conduction, convection, or radiation—determines how useful that heat is for your goal.
Conversion Efficiency vs. Application Effectiveness
A simple wire coil and an advanced ceramic plate both turn 1,000 watts of electricity into 1,000 watts of heat. This is their conversion efficiency.
The difference lies in application effectiveness. The ceramic element may be designed to heat up quickly and push warm air into a room (convection), while a wire element might be designed to heat water by direct contact (conduction). One is not inherently more "efficient," but it is more effective for its intended task.
The Role of System Design
The element is just one part of a system. A heater's housing, fans, and reflectors play a critical role. For example, a polished aluminum housing can direct infrared heat precisely where it's needed, minimizing waste and improving the system's overall effectiveness.
A Breakdown of Key Heating Element Technologies
The best choice is dictated by the required temperature, speed, and environment. Each material and design offers a distinct advantage.
Ceramic Elements: The Versatile Performer
Ceramic elements are prized for their balance of speed and stability. They heat up quickly and maintain a consistent temperature, making them ideal for space heaters, kilns, and ovens.
They are often housed in aluminum, which is a strong, lightweight, and excellent heat conductor, helping to distribute the generated heat effectively.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The High-Temperature Specialist
For extreme industrial applications like glass manufacturing or metal treatment, Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a superior choice. It can operate at incredibly high temperatures (up to 1600°C).
SiC's key advantage is its ability to heat and cool rapidly. This minimizes energy consumed during ramp-up and cool-down periods, directly lowering operational costs in demanding, cyclical processes.
Wire and Tubular Elements: The Reliable Workhorses
Configurations like nichrome wire coils and sheathed tubular elements are the foundation of many heating applications. You find them in everything from toasters and electric stovetops to industrial furnaces and water heaters.
While they may seem basic, they are exceptionally effective and cost-efficient for direct-contact heating, where the element is in physical touch with the object or substance being heated.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" option without considering the context.
Cost vs. Performance
An advanced Silicon Carbide system is a significant investment. This cost is justified by long-term energy savings and process speed in an industrial setting, but it would be complete overkill for a simple home appliance.
Speed vs. Stability
Some elements, like infrared quartz tubes, provide instant, intense radiant heat. This is perfect for targeted heating but may not be as effective as a ceramic convection heater for raising the ambient temperature of an entire room.
Durability vs. Environment
The element must be able to withstand its operating environment. A sealed ceramic element is durable and safe for long-duration use in a space heater. However, a different element type might be required in a corrosive chemical environment, where durability is the primary concern.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the most effective heating element, stop asking which one is "most efficient" and start by defining your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is home or office space heating: A ceramic element is an excellent choice for its ability to deliver stable, even, and responsive convective heat.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processes: A Silicon Carbide (SiC) element offers unparalleled performance and operational savings due to its rapid cycling and extreme temperature tolerance.
- If your primary focus is direct-contact heating in an appliance: Traditional tubular or wire elements are often the most effective and economical solution for tasks like heating water or a cooking surface.
Ultimately, the most efficient heating element is the one that is perfectly matched to the specific demands of your task.
Summary Table:
| Element Type | Key Feature | Best Application |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | Fast heat-up, stable temperature | Space heaters, ovens, kilns |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Extreme temperatures (up to 1600°C), rapid cycling | High-temperature industrial processes |
| Wire/Tubular | Cost-effective, reliable | Direct-contact heating (appliances, water heaters) |
Struggling to Select the Right Heating Element for Your Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and industries with advanced high-temperature heating solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique thermal processing requirements.
We can help you:
- Optimize performance by matching the ideal element technology (like SiC for high-temp cycling) to your application.
- Reduce operational costs through efficient system design that minimizes energy waste.
- Solve unique challenges with custom-engineered heating systems built for durability and precision.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let our experts engineer the most effective heating solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















