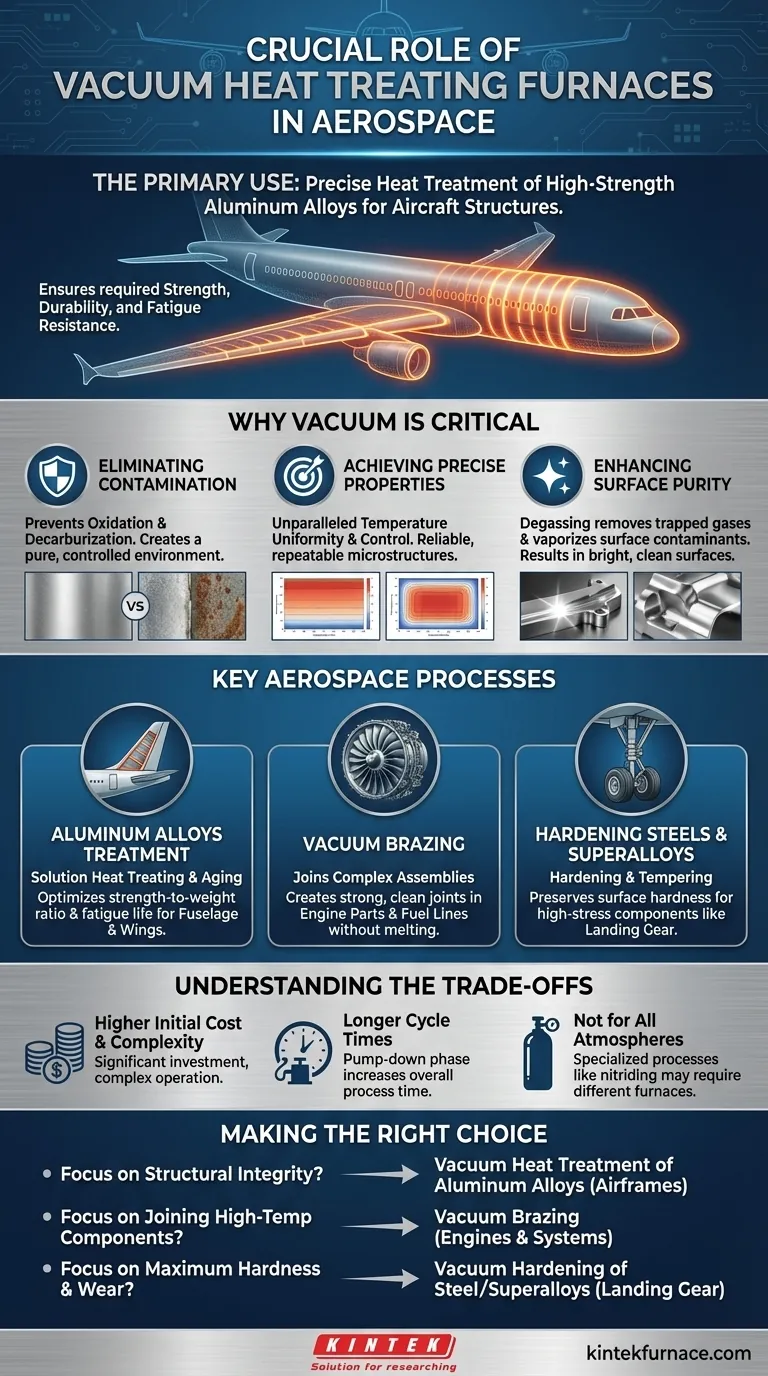
In aerospace manufacturing, one of the most important uses of a vacuum heat treating furnace is the precise heat treatment of high-strength aluminum alloys. These alloys form the structural backbone of modern aircraft, and this process is absolutely critical for ensuring their required strength, durability, and fatigue resistance over decades of service.
The core value of vacuum furnaces in aerospace is not just heating metal, but creating a perfectly controlled, contamination-free environment. This level of control is non-negotiable for producing materials that meet the industry's extreme safety and performance standards.

Why Vacuum is Critical for Aerospace Metals
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need to eliminate variables that could compromise material integrity. In aerospace, even microscopic imperfections can have catastrophic consequences.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
When metals are heated in the open air, the oxygen and other gases in the atmosphere react with the metal's surface. This process, known as oxidation, can create a weak, brittle surface layer.
A related issue is decarburization, where carbon is stripped from the surface of steel alloys, reducing their hardness and wear resistance. A vacuum removes these reactive gases, ensuring the material's surface remains pure and its properties are consistent throughout.
Achieving Precise and Repeatable Properties
Aerospace components must meet incredibly strict specifications. Vacuum furnaces offer unparalleled temperature uniformity and control over heating and cooling rates.
This precision allows manufacturers to reliably hit the exact microstructural targets that define a material's strength and toughness. The process is highly repeatable, ensuring that the first part and the thousandth part have the exact same properties.
Enhancing Surface Purity
The vacuum environment has a cleaning effect. It helps pull out trapped gases within the metal (degassing) and vaporize surface contaminants like oils.
The result is a bright, clean surface that is free of impurities that could otherwise become initiation points for cracks or corrosion.
Key Aerospace Processes in Vacuum Furnaces
While aluminum treatment is a primary application, vacuum furnaces are essential for a range of other critical aerospace processes.
Heat Treatment of Aluminum Alloys
This is the quintessential example. Components for the fuselage and wings undergo processes like solution heat treating and aging in a vacuum. This multi-stage process optimizes the alloy's strength and internal stress, making it resistant to fatigue.
Vacuum Brazing of Complex Assemblies
Brazing is a process for joining metal parts. In a vacuum, it can create exceptionally strong, clean joints without melting the base components. This is vital for assembling complex parts like engine turbine blades, fuel lines, and heat exchangers where joint integrity is paramount.
Hardening of High-Strength Steels and Superalloys
Components that face extreme stress and wear, such as landing gear or high-pressure engine parts, are often made from specialty steels or nickel-based superalloys.
Vacuum hardening and tempering these parts prevents the surface degradation (decarburization) that would occur in a conventional furnace, preserving the hardness needed for safe operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum technology is not a universal solution. It involves specific considerations and is chosen deliberately for its benefits.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are a significant capital investment and are more complex to operate and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Longer Process Cycle Times
Each cycle requires a "pump-down" phase to create the vacuum, which adds time compared to simply heating a part in an atmospheric furnace. This can impact throughput for high-volume production.
Not Ideal for All Atmospheres
Some specialized heat treatment processes, such as certain types of nitriding, require the introduction of specific active gases. While some vacuum furnaces can accommodate this, these processes are often performed in dedicated controlled-atmosphere furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice of heat treatment process is dictated entirely by the component's function and the material it is made from.
- If your primary focus is the structural integrity of airframes: Vacuum heat treatment of aluminum alloys is the industry standard for achieving optimal strength-to-weight ratios and fatigue life.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, high-temperature components: Vacuum brazing is essential for creating strong, pure, and void-free joints in critical engine and fluid systems.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance for dynamic parts: Vacuum hardening of steel and superalloys is crucial for components like landing gear and bearings to ensure surface integrity.
Ultimately, the control afforded by vacuum furnaces is what enables engineers to push the boundaries of material science, ensuring the safety and performance of modern aircraft.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Precise heat treatment of high-strength aluminum alloys for aircraft structures |
| Critical Benefits | Eliminates oxidation and decarburization, ensures uniform heating, and enhances surface purity |
| Key Processes | Solution heat treating, aging, vacuum brazing, hardening of steels and superalloys |
| Ideal For | Aerospace components like fuselage, wings, engine parts, and landing gear |
Ready to elevate your aerospace manufacturing with precision heat treatment solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for aerospace applications. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your material performance and ensure compliance with stringent aerospace standards!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control



















