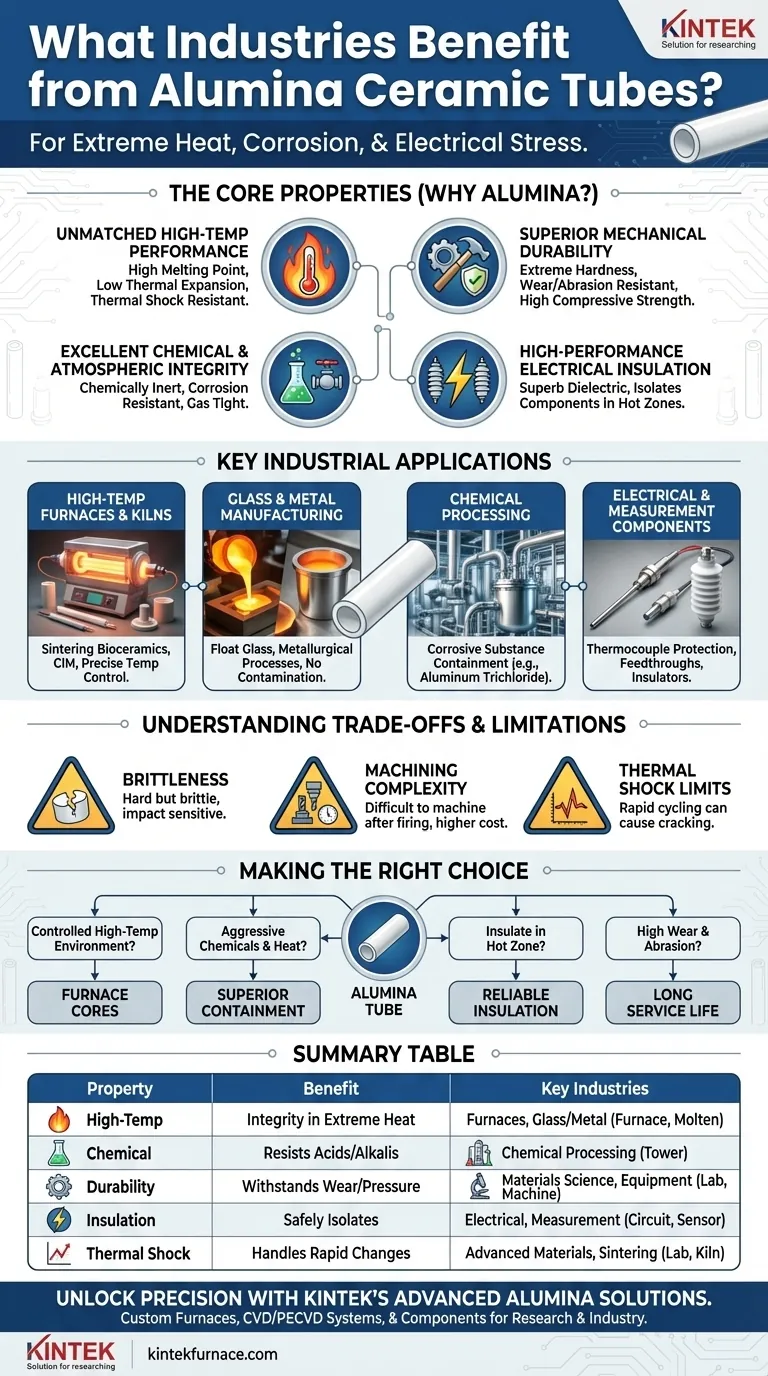
In short, any industry operating under extreme conditions of heat, corrosion, and electrical stress benefits from alumina ceramic tubes. This includes high-temperature furnace operations, glass and metal manufacturing, chemical processing, and advanced materials science, where the unique properties of alumina are essential for process stability and component longevity.
The critical takeaway is that alumina ceramic is not chosen for a single trait, but for its unique combination of extreme heat resistance, chemical inertness, mechanical durability, and electrical insulation. This makes it an indispensable engineering material for creating controlled, harsh environments that would destroy most metals and plastics.

Why Alumina? The Core Properties Driving Adoption
To understand which industries benefit from alumina tubes, you must first understand the fundamental material properties that make them so effective. These properties solve specific engineering challenges that other materials cannot.
Unmatched Performance at High Temperatures
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) has an exceptionally high melting point, allowing it to maintain structural integrity at temperatures where most metals would weaken or melt.
It also possesses low thermal expansion, meaning it does not significantly change size when heated. This stability prevents stress and cracking in applications with high thermal gradients.
Furthermore, its resistance to thermal shock allows it to withstand relatively rapid temperature changes without fracturing, a critical feature for furnace cycling.
Superior Mechanical Durability
Alumina is an extremely hard material, giving it excellent wear and abrasion resistance. Components last longer in environments with particulate flow or physical contact.
It also exhibits very high compressive strength, meaning it can withstand immense pressure without deforming. This is vital for structural components within industrial equipment.
Excellent Chemical and Atmospheric Integrity
Alumina is chemically inert and demonstrates remarkable corrosion resistance against most acids and alkalis, even at elevated temperatures. This is essential for industries like chemical processing.
High-purity alumina tubes can be made gas tight, preventing leakage and enabling the creation of high-vacuum or controlled-atmosphere environments crucial for materials science and semiconductor processing.
High-Performance Electrical Insulation
Unlike metals, alumina is a superb dielectric, meaning it is an electrical insulator. This property is crucial for safely isolating electrical components in high-temperature zones.
It allows for the construction of components like thermocouple sheaths and electrical cable lead-outs that must operate reliably inside a hot furnace without short-circuiting.
Key Industrial Applications in Practice
The combination of these properties makes alumina ceramic tubes a go-to solution in several demanding fields.
High-Temperature Furnaces and Kilns
This is the most common application. Alumina tubes form the core chamber of electric tube furnaces, vacuum furnaces, and gas atmosphere furnaces used in laboratories and for industrial production.
They are used for sintering bioceramics and Ceramic Injection Molding (CIM) components, where precise temperature control in a clean, non-reactive environment is mandatory.
Glass and Metal Manufacturing
In the float glass industry, alumina components are used in contact with molten glass. Their ability to withstand extreme heat without contaminating the product is paramount.
Similarly, they are used in various metallurgical processes that require containment and handling of materials at very high temperatures.
Chemical Processing
For producing chemicals like aluminum trichloride, the process vessel must withstand highly corrosive substances at elevated temperatures. Alumina's chemical inertness makes it an ideal choice over specialty metal alloys.
Electrical and Measurement Components
Alumina tubes serve as protective sheaths for thermocouples, which are used to measure temperature inside furnaces. The tube shields the delicate sensor from the harsh environment while allowing for accurate heat transfer.
Their dielectric properties make them perfect for fabricating electrical insulators and feedthroughs that must operate in extreme heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. To use alumina effectively, you must be aware of its limitations.
Brittleness and Impact Sensitivity
Like most ceramics, alumina is hard but brittle. It has excellent compressive strength but poor tensile strength and can fracture easily from a sharp impact or being dropped. This requires careful handling during installation and maintenance.
Machining and Fabrication Complexity
While alumina tubes can be made to custom specifications, machining them after they are fired is a difficult and expensive process due to their hardness. This can affect the cost and lead time for highly complex geometries compared to metals.
Thermal Shock Limits
While alumina has good thermal shock resistance, it is not immune to failure. Extremely rapid heating or cooling cycles, especially in thick-walled tubes, can induce stress that leads to cracking. Proper process control is necessary to manage thermal gradients.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine if alumina is the right fit.
- If your primary focus is creating a controlled high-temperature environment: Alumina tubes are the default choice for furnace cores due to their thermal stability and gas-tight nature.
- If your application involves aggressive chemicals at high heat: The exceptional corrosion resistance of alumina makes it superior to most metals for containment and processing.
- If you need to insulate electrical components in a hot zone: Alumina's high dielectric strength combined with its thermal resistance provides a reliable solution where polymers and other insulators would fail.
- If your environment involves high wear and abrasion: The hardness of alumina offers a long service life for components like material guides or nozzles.
By understanding these core properties, you can confidently leverage alumina ceramic to solve engineering challenges where conventional materials fall short.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Resistance | Maintains integrity in extreme heat | Furnaces, Glass/Metal Manufacturing |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from acids/alkalis | Chemical Processing |
| Mechanical Durability | Withstands wear, abrasion, and pressure | Materials Science, Industrial Equipment |
| Electrical Insulation | Isolates components safely in hot zones | Electrical, Measurement Systems |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Handles rapid temperature changes | Advanced Materials, Sintering Processes |
Unlock Precision and Durability with KINTEK's Advanced Alumina Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, chemical processing, or high-temperature manufacturing, our alumina ceramic tubes and custom systems ensure reliable performance under extreme conditions. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















