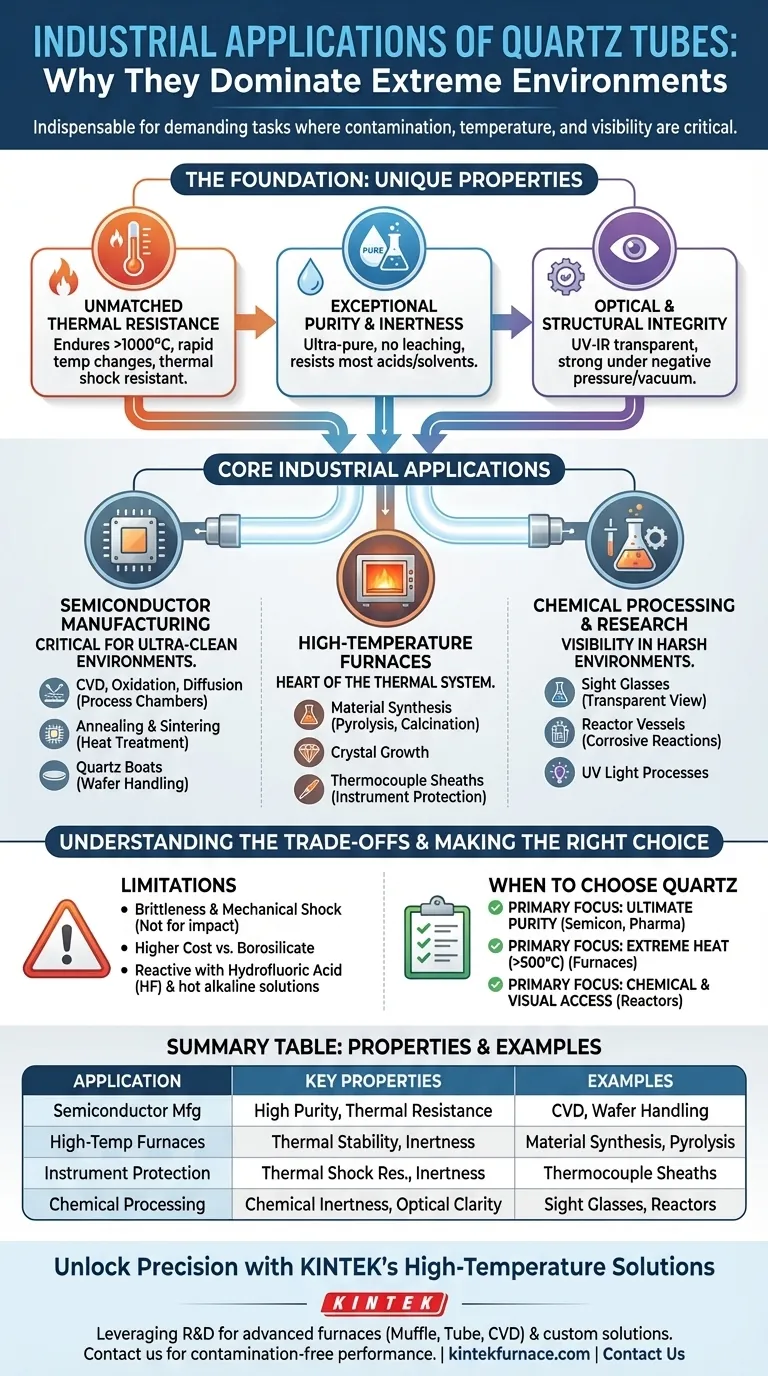
In industrial settings, quartz tubes are indispensable components used for a wide range of demanding tasks. Their most common applications are in semiconductor manufacturing for wafer processing, inside high-temperature tube furnaces for material synthesis, as protective sheaths for thermocouples, and as transparent sight glasses in harsh chemical or thermal environments.
The widespread use of quartz tubes is not due to a single feature, but to a unique combination of properties. Their ability to withstand extreme heat, resist chemical corrosion, and maintain exceptional purity makes them the default choice for processes where contamination, temperature, or visibility are critical concerns.
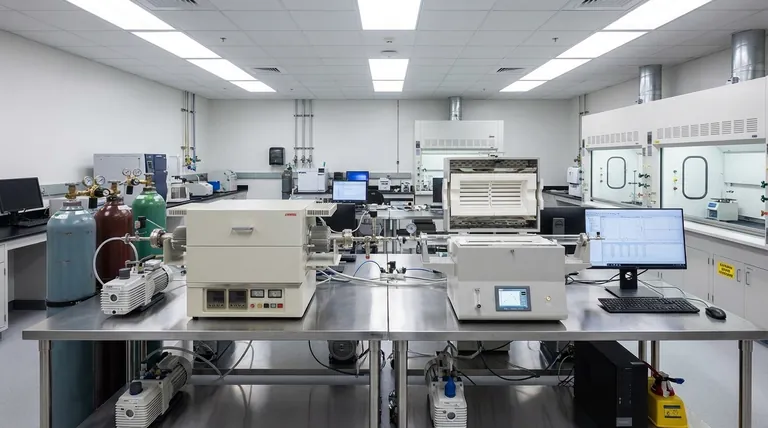

The Foundation: Why Quartz Dominates Extreme Environments
To understand where quartz tubes are used, you must first understand the fundamental properties that make them so valuable. These characteristics work in concert to solve specific engineering challenges.
Unmatched Thermal Resistance
Quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. This allows it to endure very high temperatures—often over 1000°C—and survive rapid temperature changes without cracking from thermal shock.
This stability is why quartz is the material of choice for components that are repeatedly heated and cooled.
Exceptional Purity and Chemical Inertness
High-purity fused quartz is one of the purest materials commercially available. It will not leach impurities into a process, which is a non-negotiable requirement in semiconductor manufacturing.
Furthermore, it is highly inert and does not react with most acids, solvents, or other chemicals, ensuring the integrity of chemical reactions.
Optical and Structural Integrity
Quartz is transparent from the ultraviolet through the visible and into the infrared spectrum. This optical clarity makes it perfect for use as sight glasses and for processes that utilize UV light.
It also maintains its structural integrity under negative pressure, making it a reliable material for chambers in vacuum systems.
Core Application: Semiconductor Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry relies heavily on quartz tubes because even microscopic contamination can ruin an entire batch of microchips. Its high purity is paramount.
Processing and Heat Treatment
Quartz tubes form the process chambers for critical steps like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), oxidation, and diffusion. They create an ultra-clean environment for creating thin films on silicon wafers.
They are also used for annealing and sintering, where materials are heated to alter their physical properties in a controlled, contamination-free atmosphere.
Wafer Handling
Specialized quartz components, known as quartz boats or wafer carriers, are used to hold and transport silicon wafers into and out of these high-temperature furnaces.
Their thermal stability and purity ensure the wafers are handled without being damaged or contaminated during the process.
Broad Use in High-Temperature Furnaces
Tube furnaces are a staple in materials science, research, and industrial production, and the quartz tube is often the heart of the system.
Material Synthesis and Treatment
Industries from metallurgy to battery development use quartz tube furnaces for processes like pyrolysis, calcination, and crystal growth. The tube contains the reaction and provides a stable thermal environment.
This includes the manufacturing of specialty glasses, ceramics, and advanced materials that require precise thermal profiles.
Protecting Sensitive Instruments
In many high-temperature applications, precise temperature measurement is critical. A quartz tube acts as a protective sheath for a thermocouple, shielding the sensitive instrument from the harsh chemical or thermal environment while still allowing for an accurate temperature reading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly capable, quartz is not without its limitations. A true technical evaluation requires acknowledging its potential downsides.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
Quartz has excellent thermal shock resistance but is a brittle material. It can easily shatter from a direct physical impact or mechanical stress. It is not suitable for applications requiring high toughness or ductility.
Cost Considerations
High-purity fused quartz is significantly more expensive than other types of glass, like borosilicate. For applications where its extreme thermal performance and purity are not strictly necessary, a lower-cost alternative may be more appropriate.
Reaction with Specific Chemicals
Although highly inert, quartz will be etched and damaged by hydrofluoric acid (HF). It can also be attacked by hot alkaline solutions and certain metal oxides at very high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material depends entirely on your primary engineering challenge. Use these guidelines to determine if quartz is the correct solution.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity: For semiconductor, pharmaceutical, or sensitive chemical synthesis, the non-contaminating nature of high-purity quartz makes it the only viable choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat resistance: For furnace process tubes, thermocouple protection, or sight glasses above 500°C, the thermal stability of quartz is its most critical advantage.
- If your primary focus is chemical processing with visual access: For reactor vessels where you need to observe a reaction in a corrosive environment, the combination of quartz's clarity and inertness is unmatched.
Understanding these core properties empowers you to leverage quartz tubes not just as a component, but as a direct solution to a specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Properties Utilized | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | High purity, thermal resistance | CVD, oxidation, wafer handling |
| High-Temperature Furnaces | Thermal stability, chemical inertness | Material synthesis, pyrolysis |
| Instrument Protection | Thermal shock resistance, inertness | Thermocouple sheaths |
| Chemical Processing | Chemical inertness, optical clarity | Sight glasses, reactor vessels |
Unlock Precision with KINTEK's High-Temperature Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in semiconductor production, materials research, or chemical processing, our quartz tube-integrated systems ensure contamination-free, reliable performance under extreme conditions.
Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor our solutions to enhance your industrial applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What industrial and research applications are tube furnaces used for? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing Solutions
- What is the function of high-vacuum encapsulated quartz tubes for Ce2(Fe, Co)17? Ensure Phase Purity and Stability
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace essential for CVD graphene? Master Growth Control & Purity



















