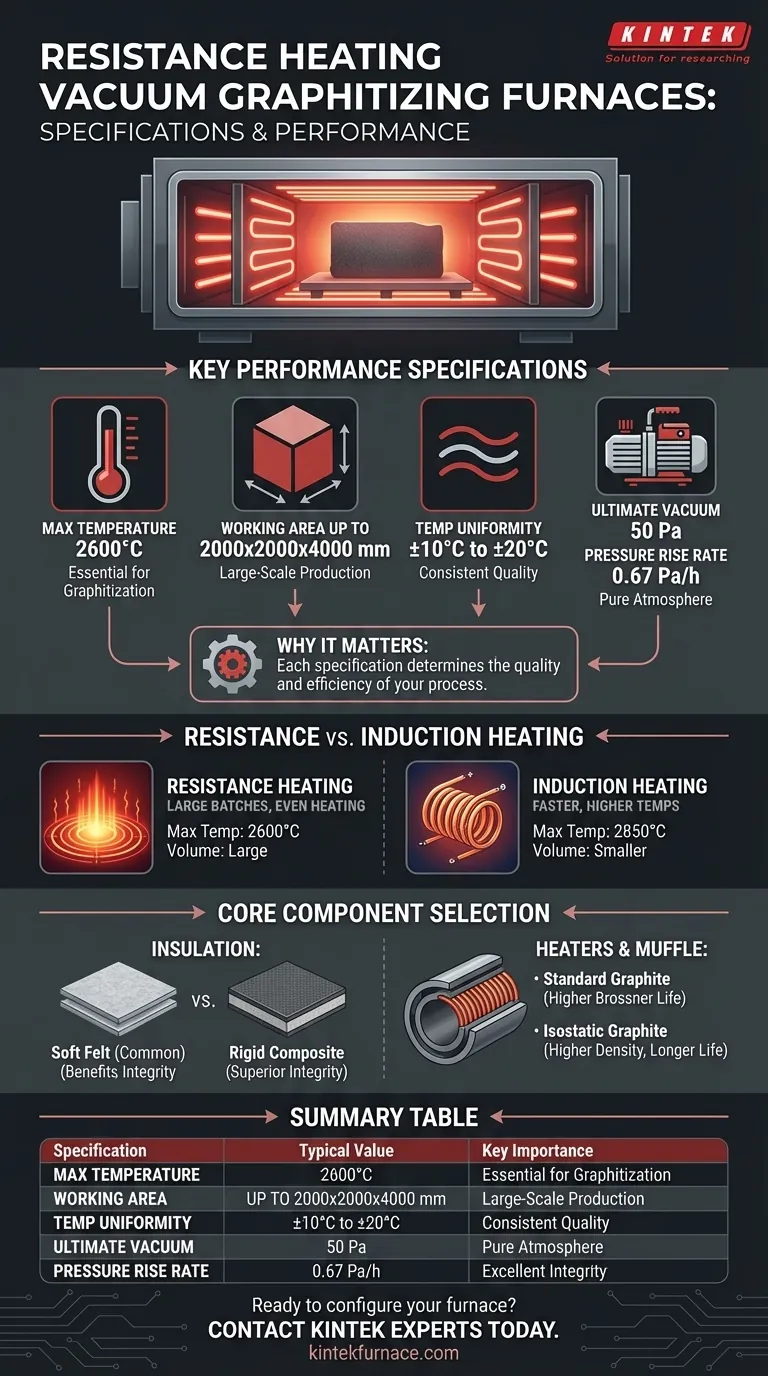
In short, a typical resistance heating vacuum graphitizing furnace offers a maximum temperature of 2600°C with a working area as large as 2000x2000x4000 mm. Key performance metrics include a temperature uniformity of ±10 to ±20°C, an ultimate vacuum of 50 Pa, and a pressure rise rate of 0.67 Pa/h, indicating a highly stable and controlled processing environment.
Understanding furnace specifications is not just about memorizing numbers. It's about recognizing that each specification is a piece of a larger system, where heating method, component materials, and construction all interact to determine the final quality and efficiency of your graphitization process.
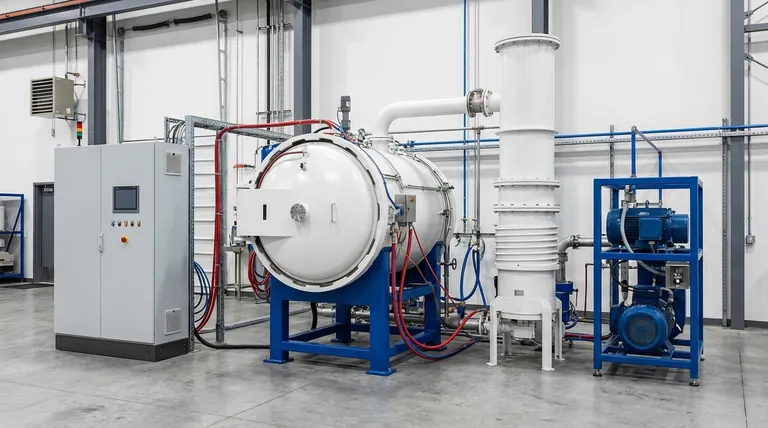

Key Performance Specifications Explained
Each specification defines a critical boundary for your process. Understanding what they mean is the first step toward selecting the right equipment.
Working Area Dimensions
Resistance heating furnaces are designed for large-scale production. Common working area sizes include:
- 1300 x 1300 x 2000 mm
- 1500 x 1500 x 3000 mm
- 2000 x 2000 x 4000 mm
These large volumes are a key advantage of resistance heating, allowing for the processing of large individual parts or high-volume batches of smaller components.
Maximum Operating Temperature
The specified maximum temperature is 2600°C. This high-temperature capability is essential for the graphitization process, which involves transforming amorphous carbon or graphite precursors into a highly ordered crystalline graphite structure.
Temperature Uniformity
A uniformity of ±10°C to ±20°C across the entire working area is standard. This is arguably one of the most critical parameters for quality control.
Excellent uniformity ensures that all parts in the batch, regardless of their position in the furnace, experience the same thermal profile. This leads to consistent material properties, predictable performance, and minimal part rejection.
Ultimate Vacuum Level
The ultimate vacuum is rated at 50 Pa (Pascals). The purpose of the vacuum is to remove atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, which would otherwise react with the carbon at high temperatures, causing oxidation and compromising the final product.
Pressure Rise Rate
The pressure rise rate of 0.67 Pa/h is a measure of the furnace's integrity. It quantifies how quickly pressure increases in a sealed, evacuated chamber over one hour.
A low rate like this indicates excellent seals and minimal leakage, which is crucial for maintaining the pure, controlled atmosphere required for a successful graphitization cycle.
Resistance vs. Induction Heating: A Critical Comparison
While you asked about resistance heating, it's vital to understand its place relative to the other common method, medium frequency induction heating. The choice between them is a fundamental decision based on your specific goals.
Heating Method and Use Case
Resistance heating uses graphite heating elements that radiate heat throughout the chamber. This method excels at heating large, voluminous spaces evenly, making it ideal for large batch production.
Induction heating uses an electromagnetic coil to induce eddy currents directly within a graphite crucible or the material itself. It is faster and can achieve higher temperatures, but is generally limited to smaller working volumes.
Performance Differences
The key differences are clear from the specifications:
- Temperature: Resistance furnaces max out around 2600°C, while induction furnaces can reach 2850°C.
- Volume: Resistance furnaces offer significantly larger working areas (e.g., 2000x2000x4000 mm) compared to the smaller volumes of induction units (e.g., 1000x1000x2000 mm).
- Uniformity: Both methods offer comparable temperature uniformity, typically within a ±15 to ±20°C range.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Core Component Selection
A furnace's headline specifications are the result of choices made in its construction. Understanding these component trade-offs is essential for specifying a furnace that meets your operational and budgetary needs.
Insulation Materials (Soft Felt vs. Rigid Composite)
Insulation is critical for thermal efficiency and temperature stability. Graphite soft felt is a common choice. However, rigid composite felt offers superior structural integrity, reduced particle shedding (cleanliness), and longer service life, making it a better investment for high-purity applications.
Heater and Muffle Materials (Isostatic vs. Standard Graphite)
The graphite heaters and muffle (the inner process chamber) are core to performance. Isostatic graphite is molded under high pressure, resulting in higher density, purity, and strength. This translates to longer element life and better temperature uniformity.
Less expensive options like "three-high" or fine-grain graphite are functional but may have a shorter lifespan and slightly less uniform heating characteristics.
Furnace Shell and Door Configuration
The furnace body can be made of full carbon steel, have a stainless steel inner shell, or be constructed entirely of stainless steel. All-stainless steel offers maximum corrosion resistance and cleanliness but at a higher cost.
Door mechanisms range from manual hinge types to fully automated, trolley-mounted doors. Automation reduces operator burden and improves cycle-to-cycle consistency, which is a key factor in high-throughput environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your ideal furnace configuration depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing batch size and part volume: A resistance heating furnace is the clear choice, as it offers the largest available working dimensions.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (>2600°C): An induction heating furnace is the more suitable technology for your needs.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and material quality: Prioritize a tight temperature uniformity specification (±10°C) and invest in high-grade insulation (rigid composite) and heater materials (isostatic graphite).
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and low contamination: Specify a full stainless steel shell and an automated vacuum and process gas system to ensure integrity and minimize operator error.
Understanding these interconnected specifications empowers you to configure a furnace that precisely matches your material, production, and quality goals.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Typical Value | Key Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | 2600°C | Essential for high-quality graphitization process |
| Working Area (LxWxH) | Up to 2000x2000x4000 mm | Enables large batch production and processing of large parts |
| Temperature Uniformity | ±10°C to ±20°C | Critical for consistent material properties and quality |
| Ultimate Vacuum | 50 Pa | Prevents oxidation and ensures a pure processing atmosphere |
| Pressure Rise Rate | 0.67 Pa/h | Indicates excellent vacuum integrity and system stability |
Ready to configure a vacuum graphitizing furnace that perfectly matches your production scale and quality goals?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether your primary focus is maximizing batch size with a large-volume resistance furnace or achieving ultra-high temperatures with an induction system, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can build a reliable, high-performance furnace solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the primary application of vacuum heat treating furnaces in aerospace? Enhance Component Performance with Precision
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency



















