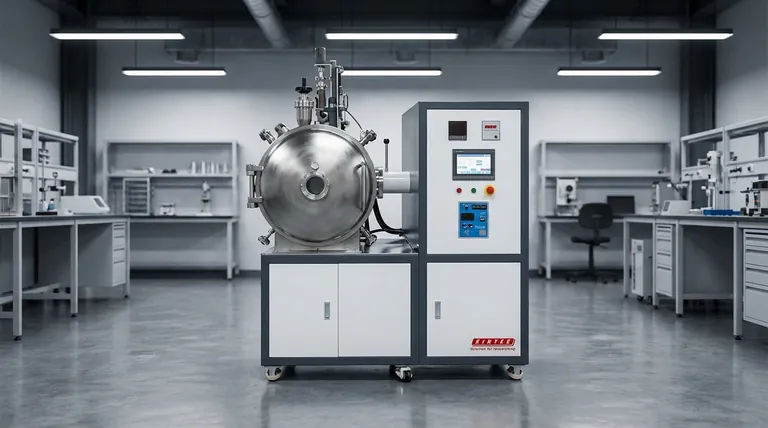
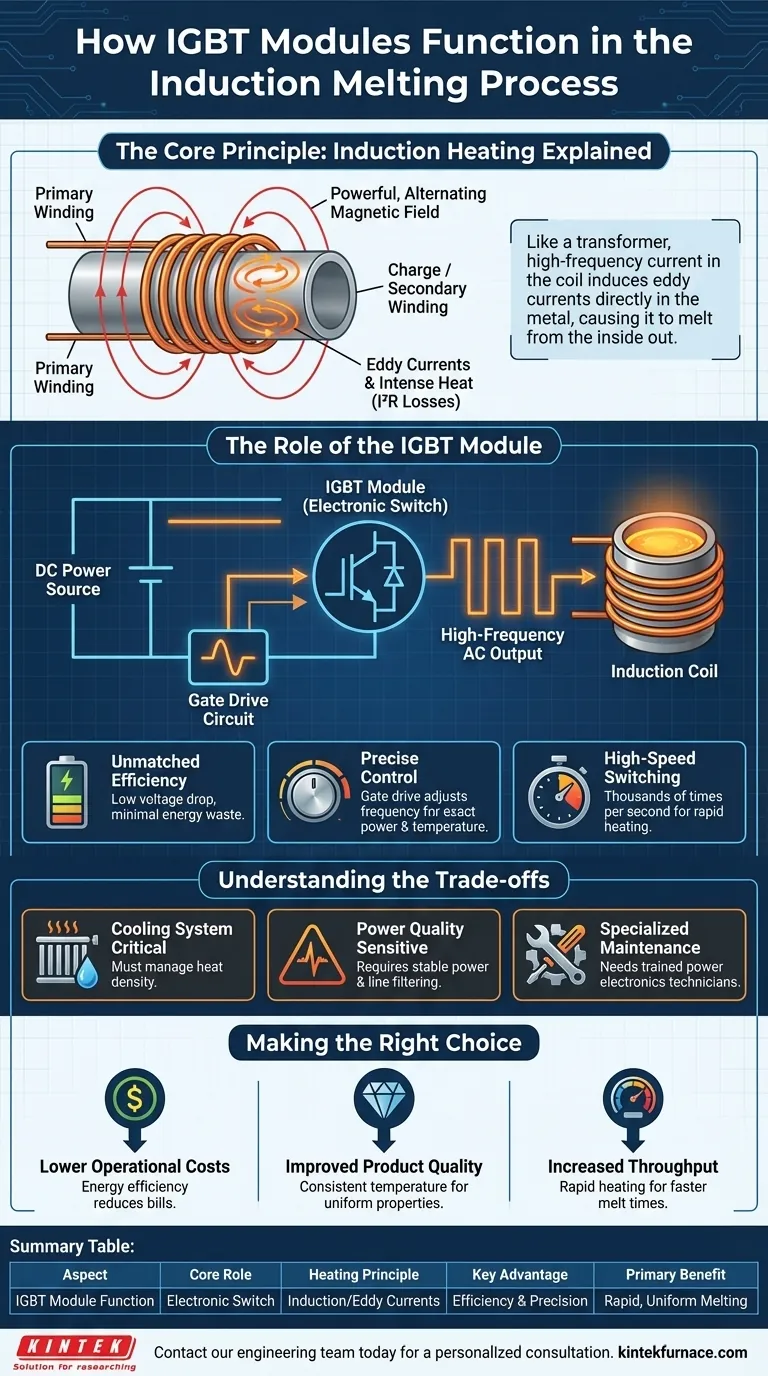
At its core, an IGBT module functions as an ultra-fast, high-power electronic switch in the induction melting process. Controlled by a gate drive circuit, it rapidly turns on and off, allowing a massive current to flow through a work coil. This creates a powerful, alternating magnetic field that induces electrical "eddy" currents directly within the metal, generating intense heat and causing it to melt efficiently from the inside out.
The central challenge in industrial melting is converting electrical energy into heat with maximum efficiency and control. IGBT technology solves this by enabling high-frequency induction heating, a method that transforms the metal itself into the source of heat, eliminating intermediate transfer steps and providing unparalleled speed and precision.

The Core Principle: Induction Heating Explained
Modern melting relies on the principle of electromagnetic induction. An IGBT-powered system is simply a highly refined and controlled way to apply this principle at an industrial scale.
The Transformer Analogy
Think of the system as a specialized transformer. The induction coil, through which the high-frequency current flows, acts as the primary winding.
The piece of metal to be melted (the "charge") acts as a single-turn secondary winding that is effectively short-circuited.
Generating Heat with Eddy Currents
As the IGBTs switch and drive alternating current through the coil, a fluctuating magnetic field is created. This field penetrates the metal charge and, according to Faraday's Law of Induction, induces powerful electrical currents within it.
These are known as eddy currents. The inherent electrical resistance of the metal opposes the flow of these eddy currents, resulting in intense resistive heating (I²R losses). This heat is generated directly inside the metal, leading to rapid and uniform melting.
The Role of the IGBT Module
The IGBT (Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor) does not generate heat itself; it is the critical component that precisely controls the power that does.
The High-Speed Switch
The primary function of the IGBT module is to switch massive DC currents on and off at very high frequencies, often thousands of times per second.
This rapid switching action is what "chops" a stable DC voltage into the high-frequency alternating current required by the induction coil to generate the magnetic field.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
IGBTs are exceptionally efficient switches. They have a very low on-state voltage drop and minimal power dissipation, meaning very little energy is wasted as heat within the control electronics.
This high efficiency ensures that the maximum amount of electrical energy is converted into useful heat within the metal, dramatically reducing overall energy consumption.
Precise Control via the Gate Drive
The IGBTs are commanded by a gate drive circuit. This circuit tells the IGBTs precisely when to switch and for how long.
By adjusting the switching frequency and duration, an operator gains exact control over the power delivered to the coil. This translates directly into precise temperature control, ensuring consistent melt quality and preventing overheating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While IGBT-based induction systems offer significant advantages, a complete technical assessment requires acknowledging their operational characteristics.
Sensitivity to Operating Conditions
The high power density and fast switching of IGBTs generate significant heat within the module itself. An effective and well-maintained cooling system (typically water-based) is absolutely critical. Failure to manage thermals is a primary cause of module failure.
Power Quality Requirements
High-frequency switching circuits can be sensitive to fluctuations and harmonics on the incoming power line. Robust line filtering and a stable power source are necessary to ensure reliable operation and prevent damage to the electronics.
Specialized Maintenance Knowledge
While the systems are reliable, troubleshooting them requires a different skillset than older, electromechanical technologies. Diagnosing issues with gate drives, control logic, or the IGBT modules themselves requires technicians trained in power electronics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Adopting IGBT-based melting is a strategic decision based on specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is reducing operational costs: The superior energy efficiency of IGBT systems directly lowers electricity consumption, while their reliability reduces maintenance expenses.
- If your primary focus is improving product quality: The precise and uniform temperature control ensures consistent metallurgical properties, helping you meet the most demanding quality standards for alloys and finished materials.
- If your primary focus is increasing throughput: The ability of IGBTs to enable rapid heating leads to significantly faster melt times, directly increasing the output of your melting operation.
Ultimately, integrating IGBT technology into your melting process is a decisive step toward a more efficient, controllable, and productive future.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | IGBT Module Function |
|---|---|
| Core Role | Acts as a high-speed, high-power electronic switch |
| Heating Principle | Generates alternating magnetic field to induce eddy currents in metal |
| Key Advantage | High energy efficiency and precise temperature control |
| Primary Benefit | Rapid, uniform melting from the inside out |
Upgrade your melting process with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature solutions.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether you need to improve energy efficiency, achieve precise temperature control, or increase melting throughput, our experts can help you integrate the right heating technology for your specific application.
Contact our engineering team today for a personalized consultation and discover how our solutions can transform your melting operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity



















