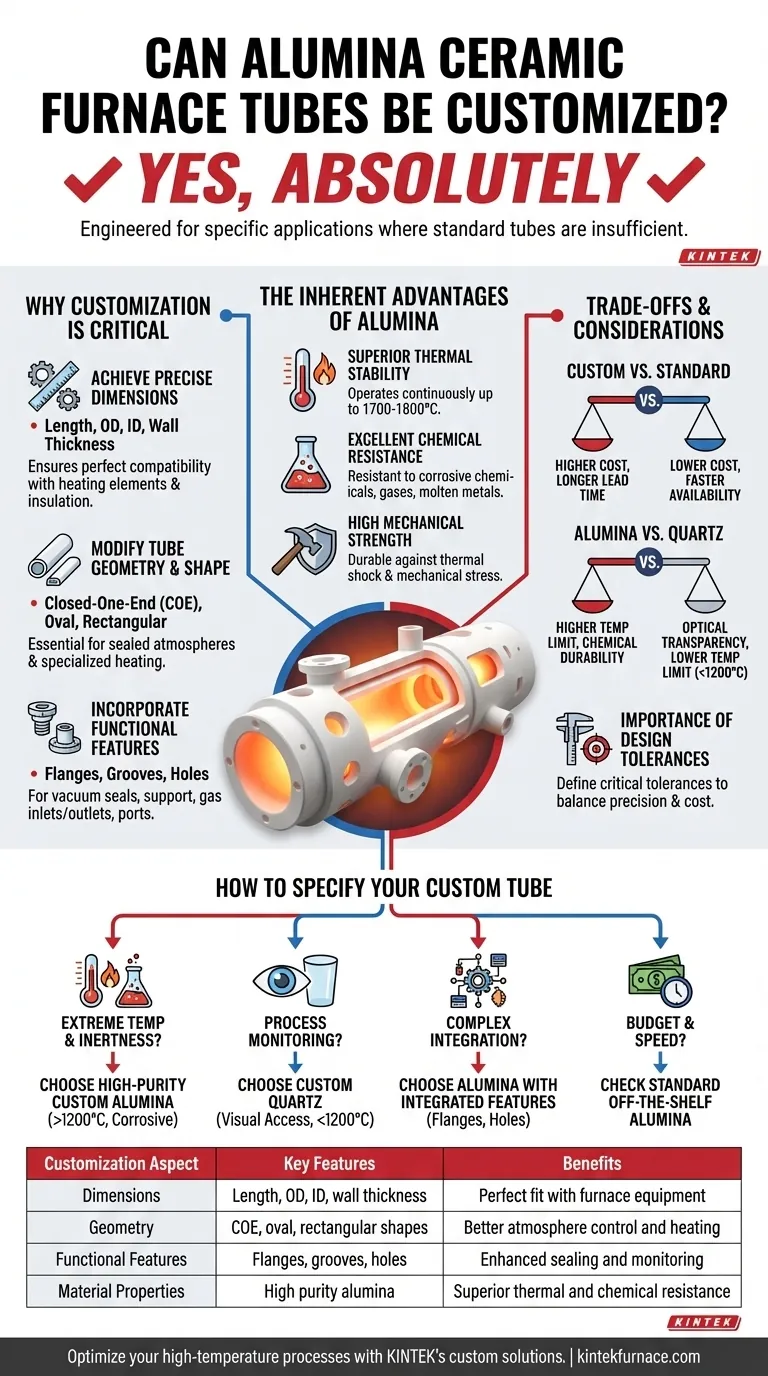
Yes, absolutely. Alumina ceramic furnace tubes are not only customizable, but they are frequently engineered for specific applications where standard off-the-shelf tubes are insufficient. Customization moves beyond simple dimensions to include modified shapes and integrated functional features, ensuring the tube is a perfect fit for your process equipment and experimental requirements.
Choosing a custom alumina tube is not just about fitting a physical space; it's about precisely engineering a core component to enhance the thermal stability, chemical inertness, and overall integrity of your high-temperature process.

Why Customization is Critical for Your Process
A furnace tube is not a passive container; it is an active part of your process environment. When a standard tube doesn't meet your needs, it can compromise gas flow, temperature uniformity, and data accuracy, forcing you to adapt your process to the equipment instead of the other way around.
Achieving Precise Dimensions
The most common customization involves tailoring the tube's dimensions. This includes its length, outer diameter (OD), inner diameter (ID), and resulting wall thickness. Getting this right ensures perfect compatibility with your furnace's heating elements, insulation, and end-seals.
Modifying Tube Geometry and Shape
Standard tubes are simple open-ended cylinders. Customization allows for more complex geometries, such as closed-one-end (COE) tubes, which are essential for creating a sealed, controlled atmosphere without requiring two end caps. Other shapes, like oval or rectangular tubes, can be fabricated for specialized heating profiles.
Incorporating Functional Features
This is where customization delivers the most value for complex setups. Features can be machined into the ceramic before its final firing, including:
- Flanges: For creating robust vacuum or positive-pressure seals.
- Grooves: To hold heating elements or secure support structures.
- Holes: For gas inlets/outlets, thermocouple insertion, or viewing ports.
The Inherent Advantages of Alumina
Before considering alternatives, it's important to remember why alumina is a premier choice for high-temperature work. Its fundamental material properties are what make it so reliable.
Superior Thermal Stability
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) exhibits an exceptionally high melting point and can operate continuously at extreme temperatures (often up to 1700-1800°C) without losing structural integrity.
Excellent Chemical Resistance
This material is highly inert and resistant to attack from a wide range of corrosive chemicals, gases, and molten metals. This is critical for processes in metallurgy, chemical processing, and semiconductor manufacturing.
High Mechanical Strength
Alumina is a hard, wear-resistant material that stands up well to thermal shock and mechanical stress, ensuring a long service life even in demanding industrial or research cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While customization offers significant advantages, it's crucial to make an informed decision based on a clear understanding of the trade-offs involved.
Custom vs. Standard: Cost and Lead Time
The most significant trade-off is cost and time. A custom-fabricated tube will always be more expensive and have a longer lead time than a standard, in-stock tube due to the need for custom tooling and dedicated production runs.
Alumina vs. Quartz: A Key Decision
For many applications below ~1200°C, quartz is a viable alternative that can also be customized. Alumina is superior for its higher temperature limit and chemical durability, but quartz offers optical transparency, allowing you to visually monitor your process. If you don't need to exceed the temperature limits of quartz and visual access is important, it may be a more practical choice.
The Importance of Design Tolerances
When specifying a custom part, you must be clear about your required dimensional tolerances. Highly precise features or dimensions increase manufacturing complexity and cost, so it's vital to define what is truly critical for your application to function correctly.
How to Specify Your Custom Tube
To ensure you get the right component, approach the specification process with a clear goal in mind.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature and chemical inertness: A high-purity (99.5%+) custom alumina tube is the definitive choice for processes above 1200°C or involving corrosive materials.
- If your primary focus is process monitoring and moderate temperatures: A custom quartz tube may be a more effective solution, providing direct visual access to your sample.
- If your primary focus is complex system integration: Specify a custom alumina tube with integrated features like flanges and access holes to ensure a leak-tight and functional setup from the start.
- If your primary focus is budget and speed for a standard process: Always check if a standard, off-the-shelf alumina tube can meet your needs before committing to the cost and lead time of a custom part.
A well-specified custom tube is a foundational investment in the reliability and repeatability of your high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Customization Aspect | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | Length, OD, ID, wall thickness | Perfect fit with furnace equipment |
| Geometry | COE, oval, rectangular shapes | Better atmosphere control and heating |
| Functional Features | Flanges, grooves, holes | Enhanced sealing and monitoring |
| Material Properties | High purity alumina | Superior thermal and chemical resistance |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes with a custom alumina furnace tube? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















