At its core, the chemical inertness of quartz is critical because it ensures the material does not react with the substances it contains. This non-reactive nature is the primary reason quartz tubes are indispensable in sensitive scientific and industrial processes, as it guarantees the purity of the sample and the integrity of the equipment itself.
The importance of chemical inertness extends beyond simple non-reaction. It is the bedrock property that enables process purity, experimental repeatability, and long-term reliability in a way few other materials can, especially under extreme temperatures.

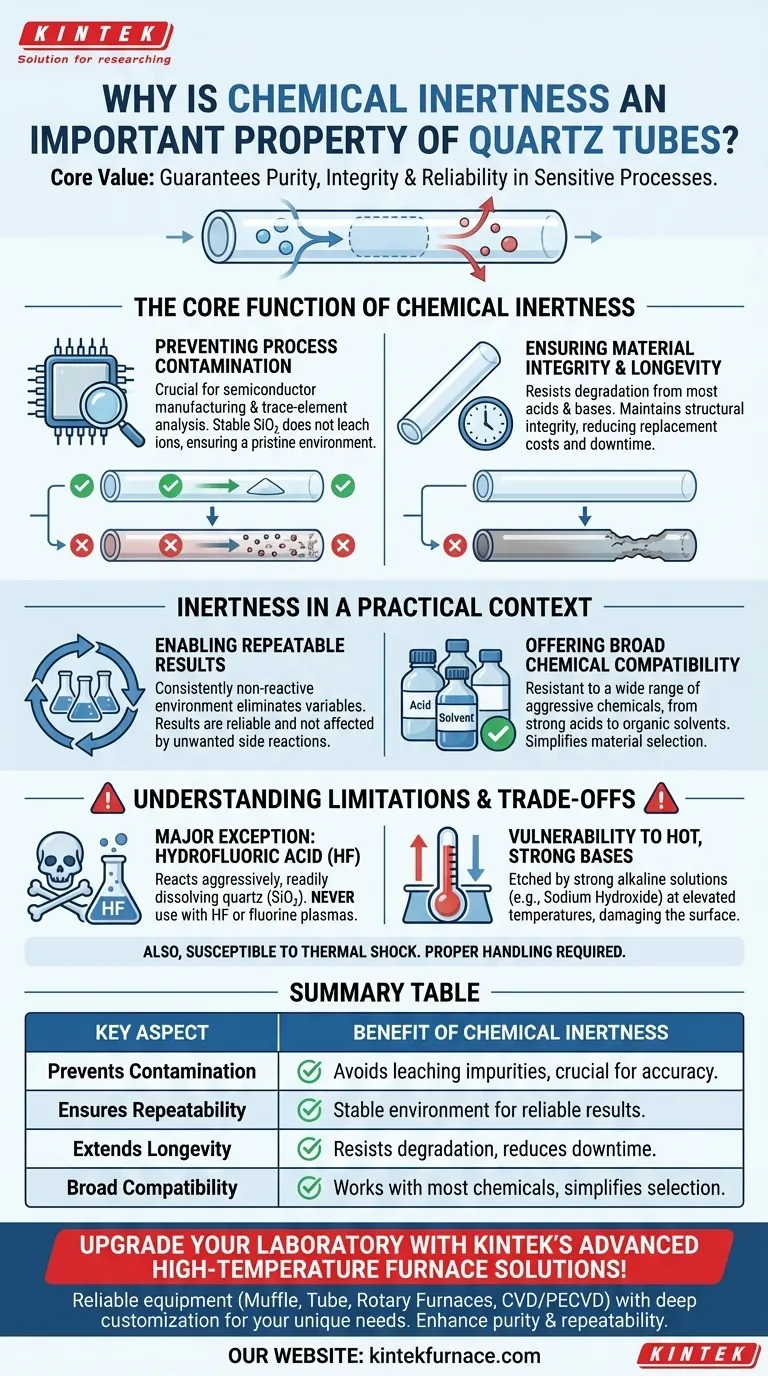
The Core Function of Chemical Inertness
The value of a quartz tube in a high-stakes environment comes from its ability to be a passive observer—a container that does not interfere with the process happening inside it. This is what inertness delivers.
Preventing Process Contamination
In applications like semiconductor manufacturing or trace-element analysis, even minuscule contamination can be catastrophic. A reactive tube would leach ions or other impurities into the system.
Because quartz (high-purity silicon dioxide) is so stable, it does not release contaminants into a chemical sample, gas, or molten material. This preserves the pristine environment necessary for creating flawless microchips or obtaining accurate analytical results.
Ensuring Material Integrity and Longevity
Chemical inertness is directly linked to the lifespan and safety of the tube. A material that reacts with its contents will degrade over time.
This degradation takes the form of etching, corrosion, or structural weakening, which can lead to equipment failure. The resistance of quartz to nearly all acids, bases, and solvents means it maintains its structural integrity for far longer, reducing replacement costs and downtime.
Inertness in a Practical Context
The theoretical stability of quartz translates directly into tangible benefits for operators, researchers, and manufacturers.
Enabling Repeatable Results
The scientific method and industrial quality control both hinge on repeatability. If your container changes the experiment or process each time, your results become unreliable.
By providing a consistently non-reactive environment, quartz tubes eliminate a major variable. This ensures that any observed changes are due to the intended process, not due to an unwanted side reaction with the container wall.
Offering Broad Chemical Compatibility
Quartz is famously resistant to a wide range of aggressive chemicals. This includes everything from strong acids to organic solvents.
This versatility makes it a default choice for laboratories and factories that handle many different types of processes. It simplifies material selection and reduces the need for a wide inventory of specialized containers.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While exceptionally inert, quartz is not universally unreactive. Understanding its specific limitations is crucial for safe and effective use.
The Major Exception: Hydrofluoric Acid
Quartz is composed of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). Hydrofluoric acid (HF) reacts aggressively with SiO₂, readily dissolving the material. Quartz tubes must never be used with HF or fluorine-containing plasmas that can generate it.
Vulnerability to Hot, Strong Bases
While generally resistant to bases, quartz can be etched by strong alkaline solutions (like sodium hydroxide), especially at elevated temperatures. Over time, this exposure will damage the tube's surface and compromise its integrity.
Balancing Inertness with Physical Properties
It's important to remember that chemical inertness is just one of quartz's key properties. It is also a brittle ceramic. While it has excellent thermal stability, it can be susceptible to thermal shock—cracking if heated or cooled too rapidly. Proper handling protocols are essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity for electronics: The extreme inertness of quartz is non-negotiable to prevent parts-per-billion contamination that ruins semiconductor wafers.
- If your primary focus is accurate chemical analysis: Quartz ensures your measurements reflect the sample itself, not a reaction byproduct from a less-inert container.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis: Quartz's blend of thermal stability and chemical inertness is ideal, but you must confirm its non-reactivity with your specific reagents.
Ultimately, the chemical inertness of quartz is the foundation of trust for any sensitive, high-stakes process.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit of Chemical Inertness |
|---|---|
| Prevents Contamination | Avoids leaching impurities, crucial for semiconductor manufacturing and analytical accuracy. |
| Ensures Repeatability | Provides a stable environment for reliable scientific and industrial results. |
| Extends Longevity | Resists degradation from acids and bases, reducing replacement costs and downtime. |
| Broad Compatibility | Works with most chemicals except hydrofluoric acid and hot strong bases, simplifying material selection. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing purity, repeatability, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-stakes processes with tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What industrial and research applications are tube furnaces used for? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing Solutions
- What is the primary function of high-purity quartz sealed tubes? Master Sb-Te Alloy Synthesis with Precision Isolation
- What is the significance of porcelain furnaces in academic and scientific research? Unlock Innovation with Precise High-Temperature Control
- Why is a high-precision vacuum tube furnace essential for CVD graphene? Master Growth Control & Purity
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab



















