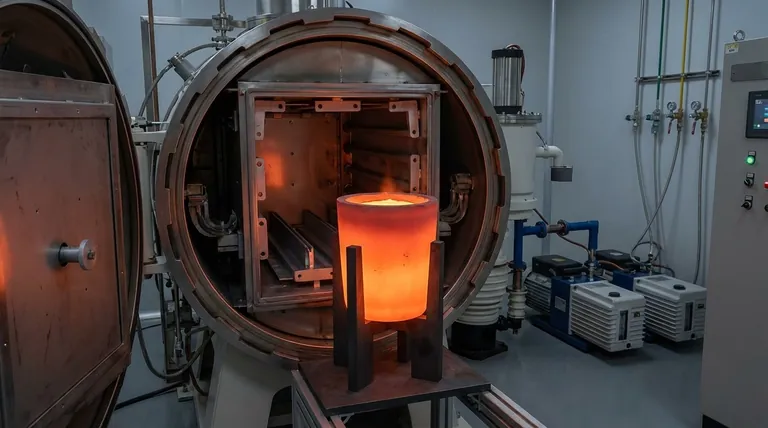
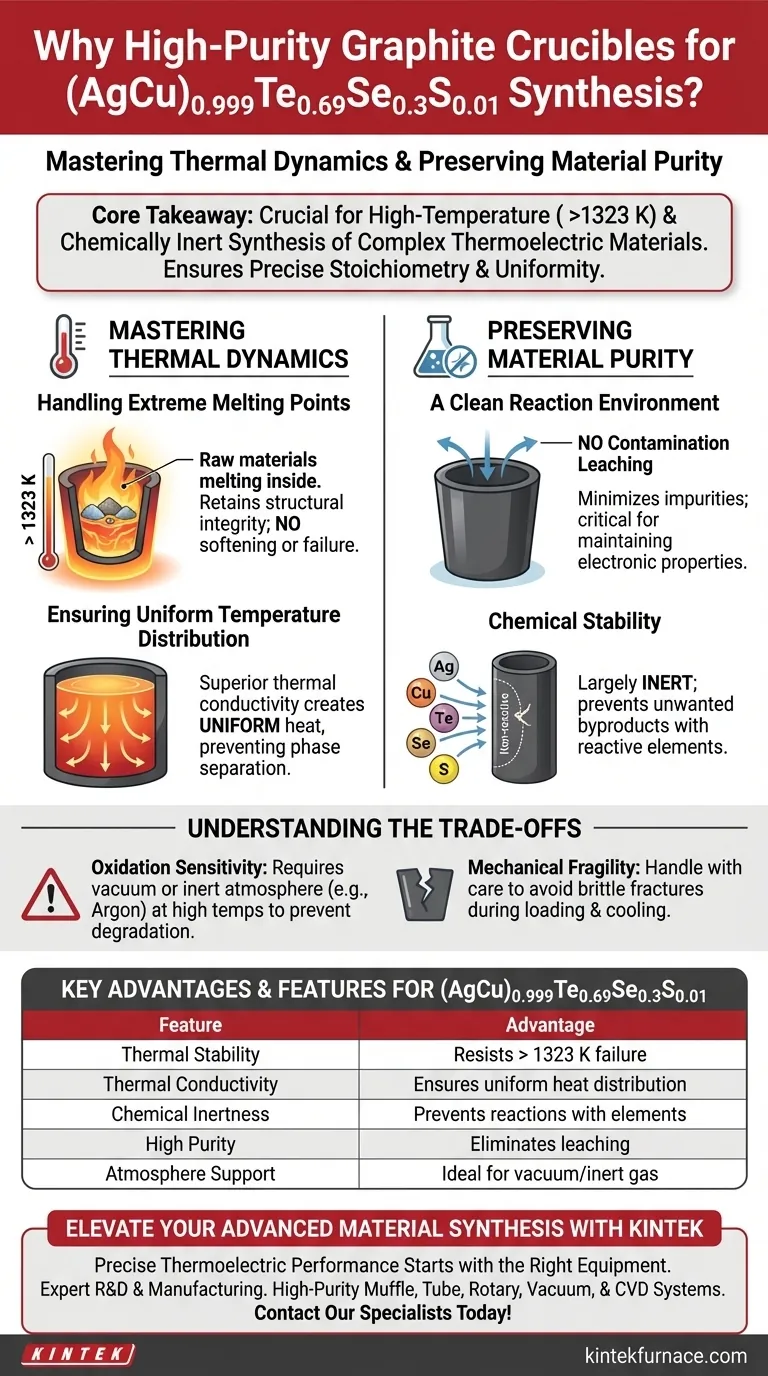
High-purity graphite crucibles are preferred for preparing (AgCu)0.999Te0.69Se0.3S0.01 because they provide a chemically inert environment capable of withstanding extreme processing temperatures. These crucibles ensure the synthesis occurs without contamination while maintaining the precise thermal control necessary for complex pseudo-ternary solid solutions.
Core Takeaway The success of synthesizing this specific thermoelectric material relies on the crucible’s ability to resist temperatures above 1323 K while maintaining chemical neutrality. High-purity graphite is essential for creating a clean reaction environment and ensuring the uniform heat distribution required for gradient-based preparation methods.

Mastering Thermal Dynamics
Handling Extreme Melting Points
The synthesis of (AgCu)0.999Te0.69Se0.3S0.01 requires subjecting raw materials to melting temperatures exceeding 1323 K.
Standard laboratory glassware or lower-grade ceramics often fail or soften at these extremes. High-purity graphite retains its structural integrity and stays solid well beyond these temperatures, ensuring the containment vessel does not fail during the melt.
Ensuring Uniform Temperature Distribution
In gradient-based preparation methods, uneven heating can lead to phase separation or inconsistent material properties.
Graphite possesses superior thermal conductivity. This property allows heat to spread evenly throughout the crucible walls, ensuring a uniform temperature distribution across the raw materials rather than creating localized hot spots.
Preserving Material Purity
A Clean Reaction Environment
Thermoelectric performance is highly sensitive to impurities. Even trace amounts of foreign elements from a crucible can degrade the electronic properties of the final material.
High-purity graphite provides a clean reaction environment. Because it is manufactured to minimize contaminants, it prevents the leaching of impurities into the melt, which is critical for maintaining the precise stoichiometry of the complex pseudo-ternary solid solution.
Chemical Stability
The elements involved in this specific formula (Silver, Copper, Tellurium, Selenium, Sulfur) can be reactive at high temperatures.
Graphite offers excellent chemical stability. It is largely inert in this context, meaning it will not chemically react with the molten mixture. This ensures that the final product is exactly what was calculated, without the formation of unwanted byproducts at the crucible interface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Oxidation Sensitivity
While graphite is thermally robust, it is susceptible to oxidation when exposed to air at high temperatures.
To use these crucibles effectively at 1323 K, the synthesis must typically occur in a vacuum or an inert atmosphere (such as argon). Using high-purity graphite in an oxygen-rich environment will result in the degradation of the crucible itself.
Mechanical Fragility
Despite their thermal resilience, graphite crucibles can be mechanically brittle.
They do not possess the ductility of metal crucibles. Researchers must exercise care during the loading of raw materials and the cooling process to prevent physical cracking or fracturing of the vessel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When setting up your synthesis for (AgCu)0.999Te0.69Se0.3S0.01, consider your primary objectives:
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Rely on high-purity graphite to eliminate the risk of chemical contamination or leaching from the vessel walls.
- If your primary focus is Homogeneity: Choose graphite to utilize its high thermal conductivity, ensuring the melt temperature is consistent throughout the sample.
Ultimately, the choice of high-purity graphite is a strategic decision to prioritize the structural and chemical integrity of the final thermoelectric material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage for (AgCu)0.999Te0.69Se0.3S0.01 Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Resists structural failure at temperatures exceeding 1323 K |
| Thermal Conductivity | Ensures uniform heat distribution to prevent phase separation |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reactions with Ag, Cu, Te, Se, and S elements |
| High Purity | Eliminates leaching of contaminants into the sensitive melt |
| Atmosphere Support | Ideal for vacuum or inert gas synthesis environments |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise thermoelectric performance starts with the right equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-purity Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique research needs.
Whether you are developing complex solid solutions or next-generation energy materials, our solutions ensure the thermal uniformity and chemical integrity your project demands.
Contact our specialists today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Mingyuan Hu, Jiaqing He. Helical dislocation-driven plasticity and flexible high-performance thermoelectric generator in α-Mg3Bi2 single crystals. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55689-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of using ceramic or quartz sample boats for solid fuels? Ensure Precise Thermal Analysis
- Why is a Pt5%Au crucible required for S53P4 bioactive glass? Ensure Purity at 1400°C
- What is the function of a water-cooled jacket on a sampling probe? Optimize Atomization and Protect Hardware
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in SnO2 film pre-treatment? Ensure Crack-Free Film Stabilization
- Why use graphite crucibles for sludge ash reduction? Unlock Superior Reduction & Heat Resistance
- What considerations lead to the selection of a corundum crucible for CVD sulfurization? Ensure Peak Sample Purity
- Why is it necessary to use high-purity alumina crucibles for sintering hydroxyapatite? Ensure Chemical Phase Purity
- Why are coating samples placed in specialized crucibles? Ensure Accurate Molten Salt Corrosion Testing Results



