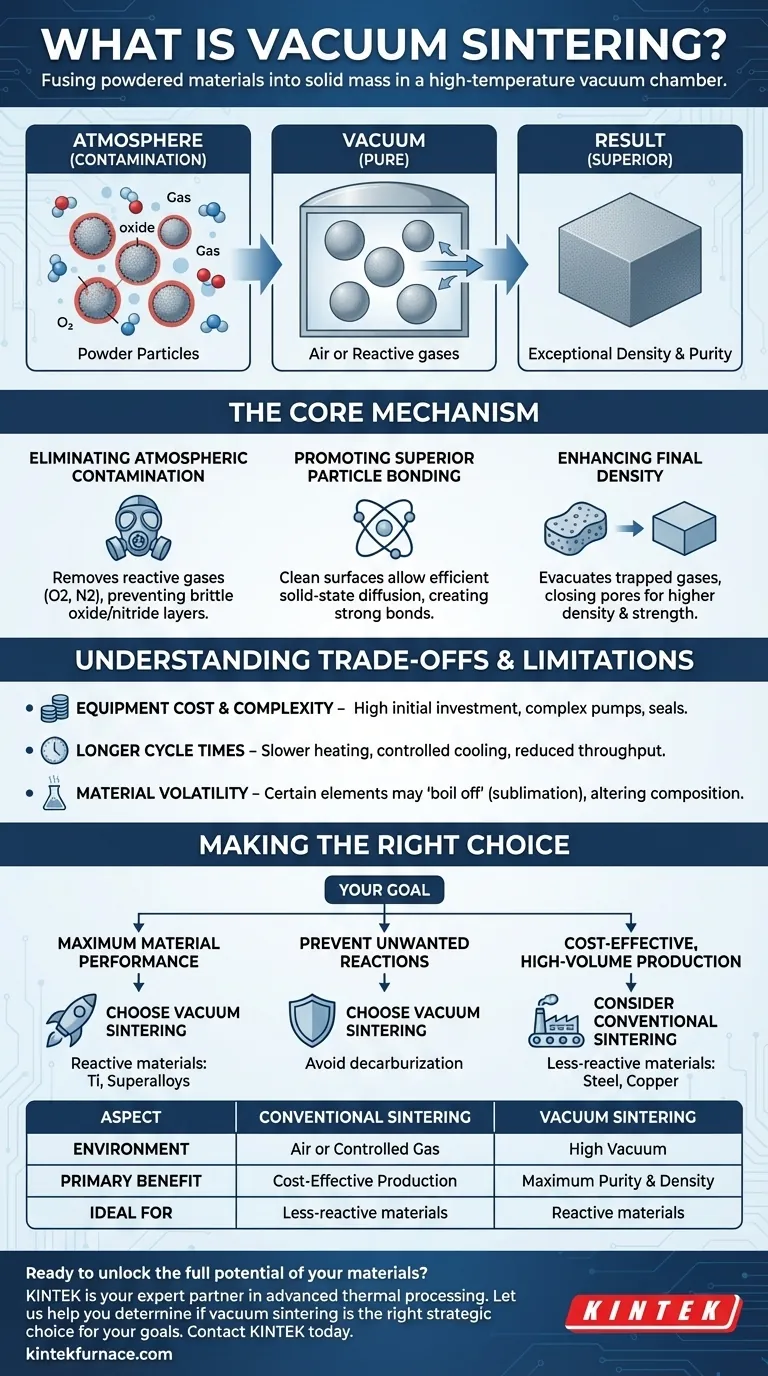
In simple terms, vacuum sintering is a high-temperature process used to fuse powdered materials into a solid mass inside a vacuum chamber. Unlike conventional methods that occur in air or a controlled gas, this technique removes the atmosphere to prevent contamination and promote superior bonding, resulting in components with exceptional density and purity without ever melting the base material.
The core purpose of using a vacuum is to create a chemically pure environment. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, vacuum sintering prevents contamination, purges trapped gases from within the material, and allows particles to bond more effectively, yielding a denser and stronger final product.

The Core Mechanism: How Vacuum Transforms the Process
Sintering works by heating a compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point, causing the particles' atoms to diffuse across their boundaries and fuse together. Introducing a vacuum fundamentally enhances this process.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
The primary role of the vacuum is to remove the air—and specifically, the reactive gases like oxygen and nitrogen—from the heating chamber. This prevents the formation of brittle oxide or nitride layers on the surface of the powder particles.
These unwanted layers act as a barrier, physically inhibiting the direct, atom-to-atom contact required for strong metallurgical bonds to form between particles.
Promoting Superior Particle Bonding
By removing the potential for oxide films to form, the powder particles remain chemically pure and "active" as they are heated. This pristine surface condition drastically improves the ability of atoms to diffuse between particles.
This process, known as solid-state diffusion, is the very foundation of sintering. A clean environment ensures this diffusion is as efficient as possible, creating a strong, homogenous final part.
Enhancing Final Density
Powdered materials naturally have microscopic voids, or pores, between particles, which are filled with air. During heating in a vacuum, this trapped air is pulled out of the part.
This evacuation of internal gases allows the material to consolidate more completely as it shrinks, closing these pores and leading to a final component with significantly higher density. Higher density is directly correlated with improved mechanical properties like strength and fatigue resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum sintering is not the universal solution. Its benefits must be weighed against practical and economic considerations.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces. They require complex vacuum pumps, control systems, and robust seals, representing a major capital investment.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of achieving a deep vacuum before heating, and the often slower, more controlled cooling cycles, results in longer overall processing times compared to conventional sintering. This can reduce throughput and increase the cost per part.
Material Volatility
Certain elements within an alloy can have a high vapor pressure. Under high heat and a deep vacuum, these elements can "boil off" or outgas from the material's surface. This phenomenon, known as sublimation, can alter the final chemical composition of the alloy and potentially contaminate the furnace interior.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding on vacuum sintering depends entirely on your material requirements, performance targets, and production constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum material performance: Choose vacuum sintering for reactive materials like titanium, tool steels, and superalloys where purity and density are non-negotiable for the application.
- If your primary focus is preventing unwanted reactions: Use vacuum sintering for alloys susceptible to decarburization (loss of carbon) or carburization (gain of carbon), as the vacuum environment is chemically neutral.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: Consider atmospheric or inert gas sintering for less-reactive materials like common steels or copper, where the lower cost and faster cycle times are more important than achieving ultimate density.
Ultimately, employing vacuum sintering is a strategic decision to trade higher process cost and complexity for uncompromising material quality.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Conventional Sintering | Vacuum Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Air or Controlled Gas | High Vacuum |
| Primary Benefit | Cost-Effective Production | Maximum Purity & Density |
| Ideal For | Less-reactive materials (e.g., common steels) | Reactive materials (e.g., titanium, superalloys) |
Ready to unlock the full potential of your materials?
Vacuum sintering is the key to achieving the ultimate material purity, density, and performance required for cutting-edge applications in aerospace, medical, and advanced manufacturing.
KINTEK is your expert partner in advanced thermal processing. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precisely engineered high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Let us help you determine if vacuum sintering is the right strategic choice for your goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments



















