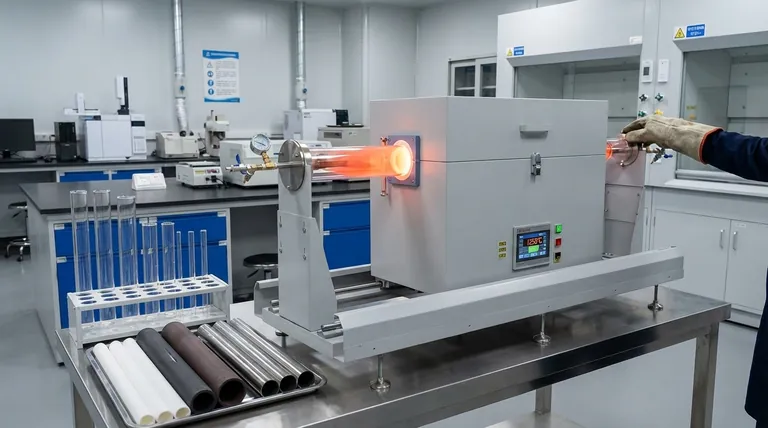
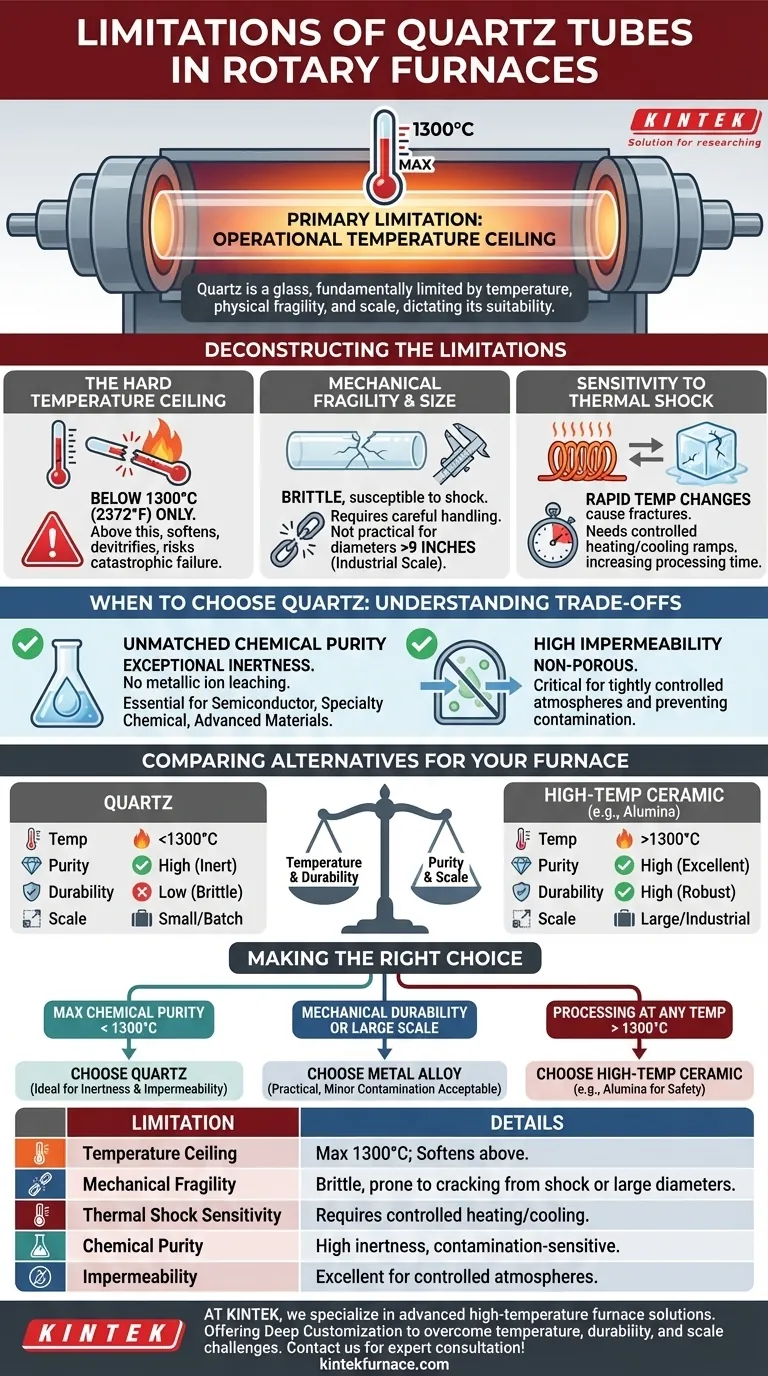
The primary limitation of a quartz tube in a rotary furnace is its operational temperature ceiling. While offering excellent chemical purity, quartz is fundamentally a glass and cannot be used for high-temperature processes, a constraint that dictates its suitability for specific applications. Its physical properties also introduce limitations regarding mechanical durability and scale.
Choosing a furnace tube is not just about temperature; it's a critical trade-off between chemical compatibility, mechanical resilience, and the physical scale of your operation. Quartz excels in purity but is constrained by temperature and fragility, making it a specialized tool, not a universal solution.

Deconstructing the Limitations of Quartz
To select the right material, you must first understand the specific boundaries of quartz as a furnace component. These limitations are not failures of the material, but inherent properties that define its use case.
The Hard Temperature Ceiling
The most significant constraint is that quartz tubes are only suitable for processing below 1300°C (2372°F). This is a non-negotiable physical limit.
Above this temperature, quartz begins to soften and devitrify, losing its structural integrity and potentially causing catastrophic furnace failure. This makes it entirely unsuitable for applications requiring higher thermal energy.
Mechanical Fragility and Size Constraints
As a form of glass, quartz is brittle and susceptible to mechanical shock. This requires careful handling during installation, maintenance, and operation to prevent cracking.
Furthermore, quartz is generally not practical for very large-diameter tubes. While excellent for lab-scale and high-purity batch processing, metal alloy tubes are often required for industrial-scale operations with tube diameters exceeding nine inches.
Sensitivity to Thermal Shock
Rapid temperature changes can induce thermal shock, leading to cracks or fractures. This necessitates controlled heating and cooling ramps, which can increase overall processing time compared to more robust materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Choose Quartz
Despite its limitations, quartz is often the superior choice for certain processes due to a unique combination of beneficial properties. Understanding these advantages is key to knowing when to specify it.
Unmatched Chemical Purity
The standout advantage of quartz is its exceptional chemical inertness. Unlike metal alloys, quartz will not leach metallic ions into the material being processed.
This makes it essential for applications involving high-purity products, such as in the semiconductor, specialty chemical, and advanced materials industries, where even trace contamination is unacceptable.
High Impermeability
Quartz tubes are non-porous and highly impermeable. This is critical for processes that require a tightly controlled atmosphere, preventing external contaminants from entering the reaction zone and ensuring process gasses do not escape.
Comparing Alternatives for Your Furnace
Your process requirements will point you toward quartz or one of its common alternatives. The decision hinges on the balance between temperature, purity, and scale.
Metal Alloy Tubes
Alloy tubes are more mechanically robust and can be manufactured in much larger diameters than quartz. However, they have their own strict limitations.
Most common alloys have a temperature ceiling below 1200°C, which is even lower than that of quartz. Critically, the metals in the alloy can react with the process material or off-gases, introducing contamination.
High-Temperature Ceramic Tubes (e.g., Alumina)
For processes that must run above 1300°C, advanced ceramics like Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) are necessary.
These materials can withstand much higher temperatures while also offering excellent chemical purity, combining the primary benefits of both quartz and metal alloys, though typically at a higher cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific process goal is the ultimate guide for material selection. Base your decision on your primary operational driver.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity below 1300°C: Quartz is the ideal choice due to its inertness and impermeability.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability or large-scale processing below 1200°C: A metal alloy tube is the more practical and robust solution, provided minor contamination is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is processing at any temperature above 1300°C: You must specify a high-temperature ceramic tube, such as alumina, to ensure operational safety and success.
Ultimately, selecting the correct tube material is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts process efficiency, product purity, and operational safety.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Ceiling | Maximum 1300°C; softens and devitrifies above this limit |
| Mechanical Fragility | Brittle, prone to cracking from shock or large diameters |
| Thermal Shock Sensitivity | Requires controlled heating/cooling to prevent fractures |
| Chemical Purity | High inertness, ideal for contamination-sensitive processes |
| Impermeability | Excellent for controlled atmospheres, prevents gas leaks |
Struggling with quartz tube limitations in your rotary furnace? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to overcome temperature, durability, and scale challenges. Enhance your lab's efficiency and safety—contact us today for expert consultation and tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the work process of a quartz tube furnace typically proceed? Master Precision Heating for Advanced Materials
- What is a Quartz Tube Furnace and what is its primary function? Essential for Real-Time Material Observation
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What happens to convective and radiative heat transfer effects at high furnace gas temperatures? Radiation Dominates for Superior Heating
- What is the necessity of using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes? Ensuring Integrity in Ti-Cu Alloy Heat Treatment



















