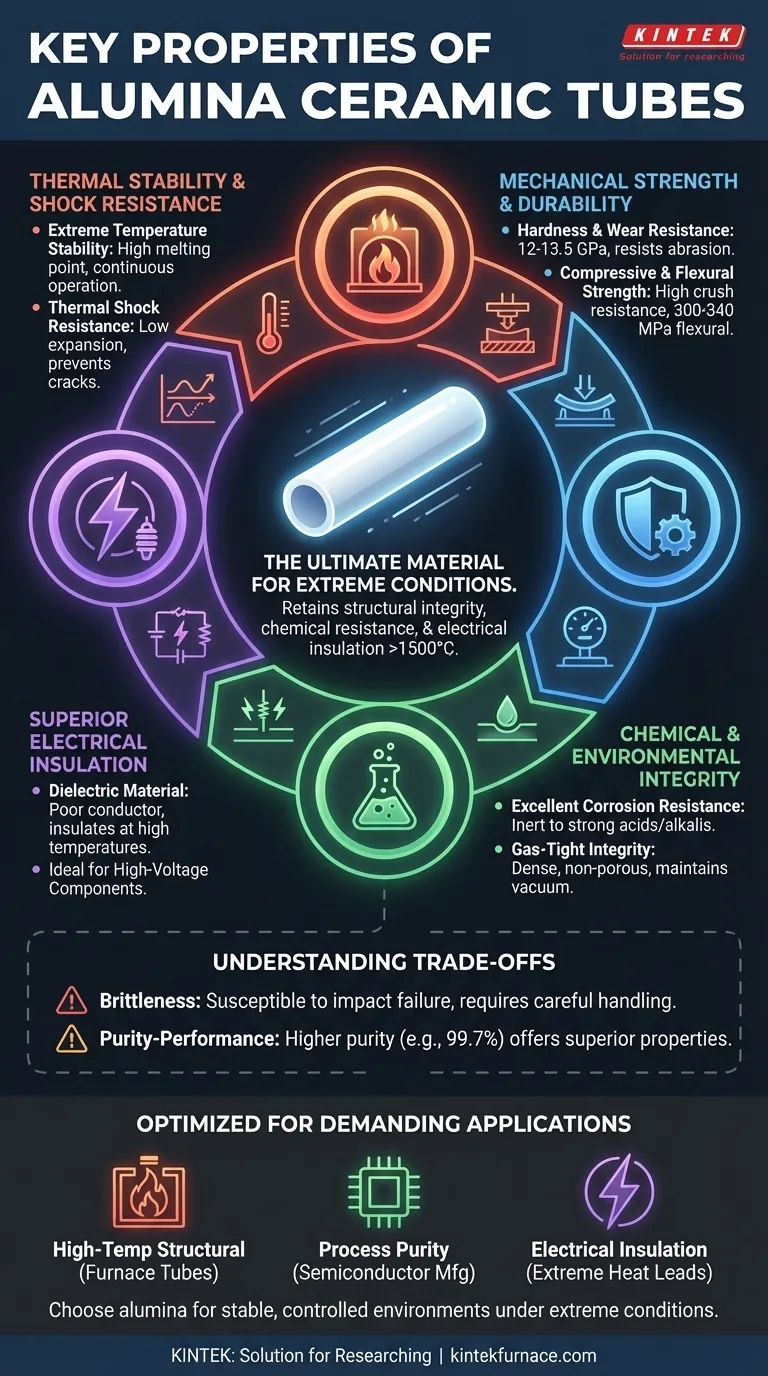
At their core, alumina ceramic tubes are defined by a unique combination of extreme thermal stability, high mechanical strength, chemical inertness, and excellent electrical insulation. These properties are retained even under severe operating conditions, making alumina a critical material for applications where plastics and metals would fail.
Alumina's true value lies not in a single property, but in its ability to simultaneously provide structural integrity, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation at temperatures exceeding 1500°C. This makes it an engineered solution for the most demanding industrial environments, though its primary trade-off is its inherent brittleness.

Unpacking the Thermal Properties
The most common reason for selecting alumina ceramic is its exceptional performance in high-temperature environments.
Extreme Temperature Stability
Alumina exhibits a very high melting point and maintains its structural integrity at continuous operating temperatures that would destroy most other materials. This makes it the standard choice for furnace tubes and kiln components.
Thermal Shock Resistance
The material has relatively low thermal expansion, meaning it does not expand or contract significantly with temperature changes. Combined with its good thermal conductivity for a ceramic, this grants it a high resistance to thermal shock, preventing cracks during rapid heating or cooling cycles.
The Mechanical Strength Profile
Beyond heat, alumina provides a robust mechanical profile, ensuring durability in harsh physical conditions.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
With a hardness rating between 12 and 13.5 GPa, alumina is an exceptionally hard material. This directly translates to superior resistance against abrasion, erosion, and wear, ensuring a long service life in abrasive environments.
Compressive and Flexural Strength
Alumina tubes possess very high compressive strength, meaning they are extremely difficult to crush. Their flexural strength (resistance to bending) is also high for a ceramic, typically ranging from 300-340 MPa, allowing them to serve as reliable structural components.
Chemical and Environmental Integrity
Alumina remains stable when exposed to a wide range of corrosive substances, making it ideal for containing or protecting sensitive processes.
Excellent Corrosion Resistance
Due to its chemical inertness, alumina is highly resistant to attack from most strong acids, alkalis, and other corrosive agents, especially at high temperatures. This is critical in chemical processing and metallurgical applications.
Gas-Tight Integrity
During manufacturing, alumina is sintered into a dense, non-porous material. This makes the tubes gas-tight, a crucial property for maintaining a vacuum or a controlled protective atmosphere inside a furnace or processing chamber.
Electrical and Dielectric Characteristics
A key distinguishing feature of alumina is its ability to insulate electricity, even when extremely hot.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Alumina is a dielectric material, meaning it is a very poor conductor of electricity. This makes it an ideal electrical insulator for high-voltage components, heating elements, and temperature measurement sensors (like thermocouples) used in high-temperature equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. Understanding alumina's limitations is key to successful implementation.
The Brittleness Factor
Like most ceramics, alumina is brittle. While it is very strong and hard, it is susceptible to catastrophic failure from sharp impacts or high tensile (pulling) stress. It requires careful handling and installation to avoid fractures.
Purity and Performance
The properties of alumina are directly linked to its purity, with common grades like 99.7% offering superior performance. Lower purity grades may have reduced temperature stability or chemical resistance, representing a cost-versus-performance trade-off.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal determines which of alumina's properties is most critical.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural support (e.g., furnace tubes): Rely on its combination of extreme temperature stability, high compressive strength, and thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is process purity and isolation (e.g., semiconductor manufacturing): Its chemical inertness and gas-tight nature are the most important factors for preventing contamination.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation in extreme heat: Its high dielectric strength, which it maintains at high temperatures, makes it the default choice for insulating electrical leads and components.
Ultimately, alumina ceramic is the material of choice for creating stable, controlled environments under conditions that are simply too extreme for anything else.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Thermal | Extreme temperature stability, high thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical | High hardness, wear resistance, compressive and flexural strength |
| Chemical | Excellent corrosion resistance, gas-tight integrity |
| Electrical | Superior electrical insulation, dielectric strength |
| Trade-offs | Brittleness, performance varies with purity |
Need reliable high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—ensuring optimal performance and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our alumina ceramic tube solutions can enhance your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control



















