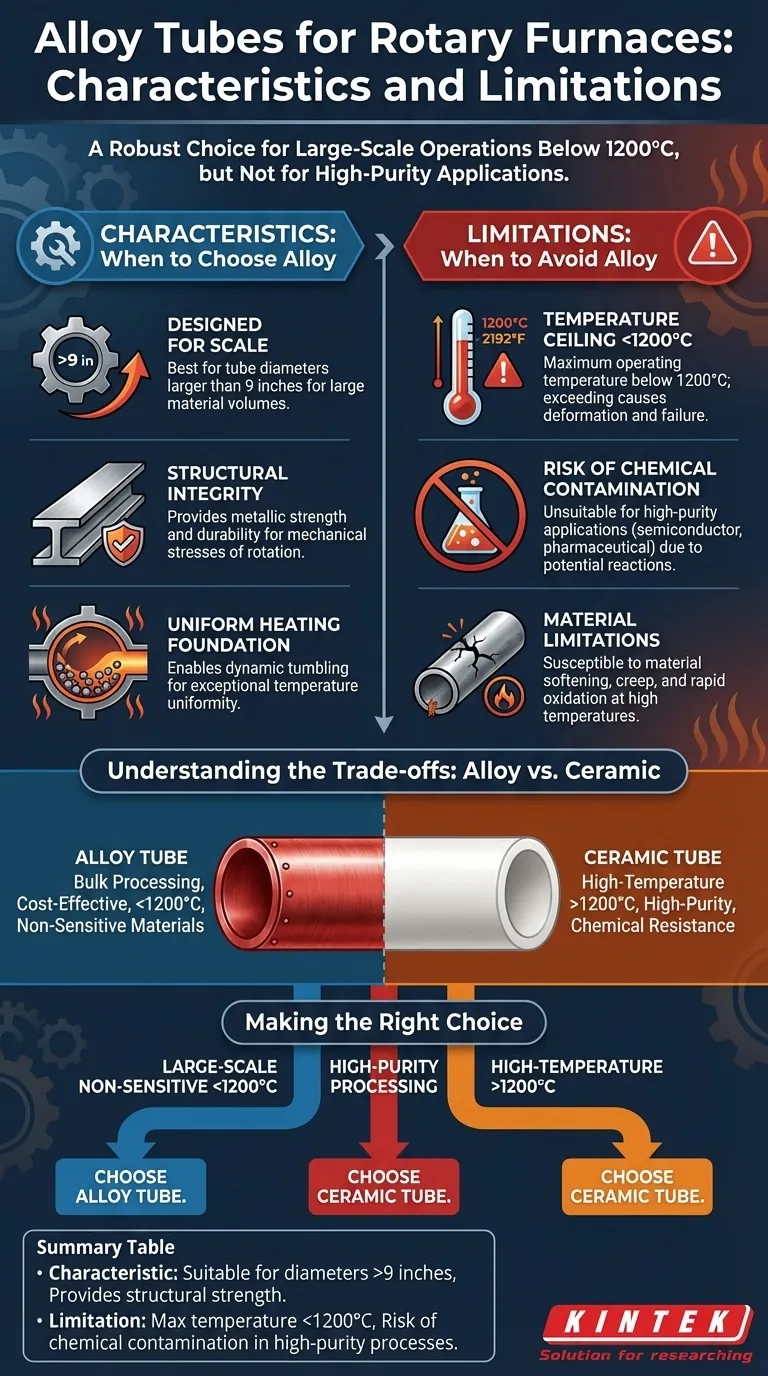
For rotary furnaces, alloy tubes are a robust choice for large-scale operations, but they come with two significant limitations. They are best suited for diameters larger than nine inches but cannot be used for processes requiring temperatures above 1200°C, and their metallic composition makes them inappropriate for high-purity applications where chemical reactions could contaminate the product.
The decision to use an alloy tube over a ceramic one is not about which is "better," but which is correct for the job. Alloy tubes provide structural integrity for large-diameter applications, but this comes at the cost of a lower temperature ceiling and the inherent risk of product contamination.

The Role of the Alloy Tube
A rotary tube furnace provides uniform heat treatment by continuously rotating the material inside a cylindrical tube. The choice of tube material is fundamental to the furnace's performance and the quality of the final product.
Designed for Scale
Alloy tubes are typically specified for applications requiring a tube diameter larger than nine inches. Their metallic nature provides the structural strength and durability needed to handle larger material volumes and the mechanical stresses of rotation at scale.
The Foundation of Uniform Heating
The primary advantage of a rotary furnace is its ability to tumble the material, ensuring every particle is exposed to the heat source and process atmosphere. This dynamic environment, managed by automated control systems, delivers exceptional temperature uniformity that is difficult to achieve in a static furnace.
Critical Limitations of Alloy Tubes
While strong and suitable for large diameters, alloy tubes have distinct operational boundaries that you must respect to ensure process integrity and safety.
The 1200°C Temperature Ceiling
The most significant limitation of common furnace alloys is their maximum operating temperature, which is typically below 1200°C (approx. 2192°F). Exceeding this thermal limit can lead to material softening, deformation (creep), and rapid oxidation, compromising the structural integrity of the tube and creating a significant safety hazard.
The Risk of Chemical Contamination
Alloy tubes are, by definition, composed of multiple metals. These metals can react with the material being processed or the off-gases produced during heating. This makes alloy tubes unsuitable for high-purity applications, such as those in the semiconductor, advanced materials, or pharmaceutical industries, where even trace amounts of metallic contamination can ruin the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Alloy vs. Ceramic
Choosing the right tube material involves a clear understanding of the trade-offs between alloy and ceramic options based on your specific process requirements.
When to Choose an Alloy Tube
An alloy tube is the correct choice when your process involves large material volumes, does not require temperatures above 1200°C, and is not sensitive to potential metallic contamination. They offer a cost-effective and mechanically robust solution for many industrial bulk processing applications.
When to Choose a Ceramic Tube
Ceramic tubes (such as Alumina) are the necessary alternative under two conditions. First, for high-temperature processing above the 1200°C limit of alloys. Second, for any high-purity application where the risk of chemical reaction and product contamination from an alloy tube is unacceptable.
Considering Other Key Parameters
Beyond material type, factors like tube thickness, rotational speed, and overall length must be optimized. Thicker walls offer greater durability, while rotational speed directly impacts heat transfer efficiency and material mixing. These parameters work in concert with the material choice to define the furnace's overall capability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your process goals directly dictate the appropriate tube material. Use these guidelines to make a definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is large-scale throughput with non-sensitive materials: Alloy tubes offer the best combination of size and cost-effectiveness for processes operating below 1200°C.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing: Ceramic tubes are the mandatory choice to avoid chemical reactions and ensure product integrity, regardless of temperature.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature treatment (above 1200°C): Ceramic tubes are your only viable option to safely withstand the required thermal load.
Ultimately, selecting the correct tube material is the foundation for a reliable, safe, and effective heat treatment process.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Limitation |
|---|---|
| Suitable for diameters >9 inches | Max temperature <1200°C |
| Provides structural strength | Risk of chemical contamination in high-purity processes |
Struggling with high-temperature or high-purity furnace needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced solutions for laboratories requiring precise thermal processing. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve reliable results with our tailored furnace solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















